Foam density is an indicator that determines the strength characteristics of thermal insulating polystyrene foam. This thermal insulation material consists of 98% air bubbles and 2% pure polystyrene. Polystyrene is the basis of expanded polystyrene.
It is obtained by the polymerization of styrene. Expanded polystyrene has become widespread due to a number of advantages:
- No toxic compounds.
- High thermal insulation properties, thermal conductivity in a dry state – 0.029-0.036 W/(m.k).
- Light weight.
- Polystyrene foam does not enter into chemical reactions with building materials (cement, bitumen, acrylic, gypsum putty).
- Resistance to microorganisms, algae, mold, fungus.
- Durability.
The physical and mechanical properties of polystyrene foam may vary. They depend on the quality of the raw materials and the method of polymerization of styrene.
Main brands of foam plastic
After foaming the polystyrene, the raw materials for the finished products are loaded into a container. Steam is injected into it under pressure. The granules foam and become saturated with air. At the next stage, the finished granules are dried from moisture; hot air is used for this.
When drying, the granules are shaken periodically. The finished granules are placed in bins that are calibrated according to foam grades. Molding occurs under pressure. When molding, the following types of foam are obtained, which differ in density:
- PSB-S-15;
- PSB-S-25;
- PSB-S-35;
- PSB-S-50.
The last number in the marking determines the density of the foam for insulation. Many developers do not know what the specific gravity of foam is. Density (specific gravity) is the mass of a product in its volume. The density of polystyrene grade PSB-S-15 is 15 kg/m³. Accordingly, one cubic meter of PSB-S-15 polystyrene boards weighs 15 kg.
The question arises of how to independently determine the density of foam plastic without special equipment. This is easy to do: you need to calculate the cubic capacity of the finished product and weigh it on the scales. To make a claim, the store must have in hand a state verification certificate of the scales. Weighing can be carried out directly in the store or at the construction warehouse of the materials supplier. This technical calculation of foam density will be the most optimal.
How not to make a mistake when choosing sizes?
Professional builders use special computer programs. It is necessary to enter data about the room: ceiling height, wall width, doorways, window sizes. Markings will be made automatically and the optimal length and width of the foam will be selected.
If there is no such software, you can create an estimate yourself, armed with a tape measure, a pencil and a piece of paper. Having constructed a drawing on paper, you can make a cutting sketch and determine the number of sheets taking into account their area.
What density foam is best for different types of insulation?
High-density PSB is best used for insulating industrial facilities, utilities, parking lots, roads and sidewalks. It is used in industry and the highway sector. It is able to withstand high static and dynamic loads on the plane.
This begs the question, what is the best characteristic of polystyrene foam for insulating a house? Density 35 kg/m³ is the volumetric weight of polystyrene foam for insulating walls outside. Polystyrene PSB-S-35 and PSB-S-25 correspond to this density and are suitable for thermal insulation of facades of residential buildings . Its structure will not be destroyed by mechanical impact on the plane of the slabs.
The slabs are easy to install and process, allowing you to obtain a thermal insulation effect at low material costs. This is the most popular type of slab.
PSB-S-15 foam plastic slabs can also be used to insulate house facades. It is important to exclude static and shock loads on the surface of the insulation during operation of the building. It can also be used to fill voids in structures, insulate attics, insulate underground spaces and voids in ceilings.
Properties and characteristics of the material
Foam plastic can withstand temperature fluctuations from -50 to +75°C without changing technical characteristics. A detailed description of its properties will help you get acquainted with the technical characteristics of polystyrene foam:
- Thermal conductivity. A special production technology provides foam boards with high thermal insulation properties. Cells in the form of closed polyhedra, the size of which does not exceed 0.5 mm, prevent the penetration of cold air and significantly reduce heat transfer. As the density of the material increases, this indicator changes.
- Sound insulation and wind protection. The walls of the room, in the decoration of which foam boards are used, are reliably protected from the wind. Among the technical characteristics, noteworthy is the high degree of sound insulation, which is also ensured due to the cellular structure of the material. Comment! To reduce the level of noise penetration, it is enough to use foam plastic boards with a thickness of 2-3 cm. The thicker the boards, the better sound insulation can be achieved.
- Moisture resistance. Expanded polystyrene is valued by builders for its low hygroscopicity relative to other materials. Water is not able to penetrate the walls of the cells, but only seeps through the channels.
- Durability and strength. Foam plastic retains its original technical characteristics for a long time. The plates are able to withstand significant pressure without deformation or destruction. A clear example is the use of polystyrene foam in the construction of runways. The thickness of the polystyrene foam board directly affects the strength of the material, and the correct installation is also important.
The resistance of foam plastic to aggressive environments deserves careful study. The stability indicators of polystyrene foam boards directly depend on the composition of the active substance. Polystyrene foam slabs are resistant to solutions:
- cement;
- gypsum;
- bitumen;
- acids, alkalis and salt solutions;
- sea water;
- not susceptible to water-soluble and acrylic paints.
Prolonged contact with substances that contain oils of plant and animal origin, diesel fuel and gasoline can negatively affect the technical characteristics of the foam.
When expanded polystyrene boards are used in the construction of objects, contact with compounds that aggressively affect the structure of the material should be avoided. Among them:
- turpentine;
- acetone;
- organic paint solvents;
- ether with acetic-ethyl base;
- all kinds of saturated hydrocarbons and substances obtained by petroleum refining.
This includes fuel oil, diesel fuel, kerosene and gasoline. Contact with the above components leads to disruption of the structure and loss of qualities specified in the technical characteristics, and can also provoke complete dissolution.
Attention! The artificial origin of polystyrene foam acts as an unfavorable environment for the appearance and development of microorganisms. But with significant contamination of the surface of polystyrene foam boards, the proliferation of microorganisms becomes possible.
Among the positive qualities of foam boards, which are not reflected in the technical characteristics, are ease of use and simple installation. Light weight ensures ease of work; the structure does not create difficulties when cutting and subsequent installation is necessary.
Expanded polystyrene is included in the category of environmentally friendly building materials; during operation it does not emit toxic substances. When working with it, the use of personal protective equipment is not required. Numerous summary tables of technical characteristics do not reflect the many positive qualities of the building material. It does not generate dust when cutting, is valued for its lack of odor, does not irritate mucous membranes and skin, and is not toxic.
Fire safety is an important quality characteristic of foam plastic. When choosing a building material, special attention is paid to this indicator. High-quality products must be resistant to open fire. Expanded polystyrene boards belong to flammability class 3-4. This material does not support the combustion process. The temperature at which it can ignite is 2 times higher than that of wood (+491°C compared to +230°C).
If a fire retardant is present in the composition of expanded polystyrene, the flammability class of such material is reduced to G2-G1. In the marking, this feature is expressed by the letter C. Ignition of a foam board can occur as a result of prolonged contact with an open fire. Termination of exposure to fire leads to its attenuation on the surface of the polystyrene foam plate within 4 seconds.
Individual technical characteristics of polystyrene foam boards are presented in the summary table:
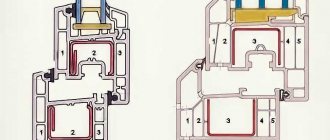
External insulation wall pie
The structure of a wall pie with external insulation method is quite simple.
Since the most efficient removal of steam from the wall material requires the tightest possible fit of the insulation, no film materials are installed between the wall and the foam.
On the outside, too, no waterproofing is done if the “wet” method is used as cladding - applying plaster or decorative tiles or similar materials using cement mixtures.
If a ventilated facade is used, then the gap between the foam plastic and the facade according to the technology should be at least 40 mm , therefore, to protect the insulation from moist air, it is possible (but not necessary) to install a layer of a waterproof, vapor-permeable membrane with an exit to the outside.
Wall cake composition:
- The outer surface of the wall.
- Insulation (foam plastic).
- A layer of plaster or tiles glued to a suitable mixture.
For ventilated facades:
- External surface of the wall.
- Foam layer.
- Layer of vapor-hydroprotective membrane.
- Counter grille creating a ventilation gap.
- Ventilated facade.
wall pie
Equivalent to polystyrene foam PSB-35S 50mm relative to brickwork?
The ratio of the thermal insulating properties of various materials can be determined by the value of the thermal conductivity coefficient. The higher the thermal conductivity, the faster the room will cool.
For expanded polystyrene PBS35S it is 0.038 W/m*K. And for ordinary clay bricks, thermal conductivity varies between 0.384 - 0.814 W/m*K. We get a 10-fold difference in the thermal conductivity of materials. Consequently, a 20mm thick PBS35S polystyrene board will provide the same thermal insulation as 200mm brickwork, and a 50mm PBS35S board corresponds to a half-meter wall thickness.
Accordingly, the wall ratio can be calculated from:
- wood - pine along the grain 0.18 W/m*K;
- foam concrete depending on density - 0.1-0.38 W/m*K;
- autoclaved aerated concrete in a dry state 0.09-0.12 W/m*K. Read more: https://srbu.ru/qa/article/2935-ekvivalent-penopolistirola-psb-35s-50mm-otnositelno-kirpichnoj-kladki.html
Read more: https://srbu.ru/qa/article/143-plotnost-penoplasta-kakaya-ona-byvaet-i-na-chto-ona-vliyaet.html
Return to list of questions
Preparing the wall surface
The wall surface must meet the following requirements:
- No loose plaster.
- No old paint.
- The surface of the wall should be stable and not crumble when you run your hand over it.
- The plane of the wall must be flat, the maximum difference is 1-2 cm. Deeper depressions must be plastered or sealed.
If necessary, the wall is plastered or coated with a deep penetration primer (if it is very crumbling).
Surface preparation
How does the degree of insulation depend on the thickness of polystyrene foam?
The degree of insulation of a room is directly dependent on the thickness of the insulation. And it is calculated by the formula R=p/k, where
- R – thermal resistance standard for the region;
- p – material thickness;
- k is the thermal conductivity coefficient, which depends on the density of the material.
For expanded polystyrene it is:
| Density kg/m3 | Thermal conductivity coefficient W/ (m*K) |
| 40 | 0,038 |
| 100 | 0,041 |
| 150 | 0,05 |
| 33 (extruded) | 0,031 |
The thermal resistance standard for the region is taken from SNiP 23-01-99 “Climatology”.
Return to list of questions