Expanded polystyrene boards, colloquially referred to as polystyrene foam, are an insulating material, usually white. It is made from thermally expanded polystyrene. In appearance, the foam is presented in the form of small moisture-resistant granules; during the melting process at high temperatures, it is smelted into one whole, a slab. The sizes of the granule parts are considered to be from 5 to 15 mm. The outstanding thermal conductivity of 150 mm thick foam is achieved due to a unique structure - granules.
Each granule has a huge number of thin-walled micro-cells, which in turn increase the area of contact with air many times over. We can say with confidence that almost all polystyrene foam consists of atmospheric air, approximately 98%, in turn, this fact is their purpose - thermal insulation of buildings both outside and inside.
Everyone knows, even from physics courses, that atmospheric air is the main insulator of heat in all thermal insulation materials; it is in a normal and rarefied state, in the thickness of the material. Heat-saving, the main quality of polystyrene foam.
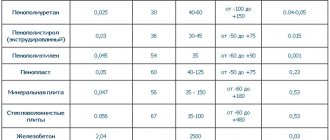
As mentioned earlier, polystyrene foam is almost 100% air, and this in turn determines the high ability of polystyrene foam to retain heat. This is due to the fact that air has the lowest thermal conductivity. If we look at the numbers, we will see that the thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam is expressed in the range of values from 0.037 W/mK to 0.043 W/mK. This can be compared with the thermal conductivity of air - 0.027 W/mK.
While the thermal conductivity of popular materials such as wood (0.12 W/mK), red brick (0.7 W/mK), expanded clay (0.12 W/mK) and others used for construction is much higher.
Polystyrene foam provides a high level of energy saving due to its low thermal conductivity. For example, if you build a wall of brick with a thickness of 201 cm or use a wood material with a thickness of 45 cm, then for foam plastic the thickness will be only 12 cm for a certain amount of energy savings.
Therefore, polystyrene foam is considered to be the most effective material among the few for thermal insulation of external and internal walls of a building. Residential heating and cooling costs are significantly reduced through the use of polystyrene foam in construction.
The excellent qualities of polystyrene foam boards have found their application in other types of protection, for example: polystyrene foam, which also serves to protect underground and external communications from freezing, due to which their service life increases significantly. Polystyrene foam is also used in industrial equipment (refrigerators, refrigerators) and in warehouses.
What should you buy?
The building materials market offers a huge selection of polystyrene foam boards. The high thermal conductivity of insulation boards depends on their type. For example: a sheet of polystyrene foam PSB-S 15 has a density of up to 15 kg/m3 and is 2 cm thick. For a sheet from 2 to 50 cm, the density is no more than 35 kg/m3. When comparing polystyrene foam with other similar materials, you can easily trace the dependence of the thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam boards on its thickness.
So, for example: the thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam is 50 mm, twice that of mineral wool of the same volume; in this case, the thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam with a thickness of 150 mm will generally be 6 times higher than these indicators. Basalt wool is also very inferior to polystyrene foam.
In order to apply one of the insulation methods, it is necessary to select the correct dimensions of the material. The following algorithm can be used to calculate:
- It is necessary to clarify the overall thermal resistance. This value depends on the region in which the calculation needs to be performed, namely on its climate.
- To calculate the thermal resistance of a wall, you can use the formula R=p/k, where its thickness is equal to the p value, and k is the thermal conductivity coefficient of the foam.
- From constant indicators we can conclude what resistance the insulation should have.
- The required value can be calculated using the formula p=R*k; the value of R can be found based on the previous step and the thermal conductivity coefficient.
general description
Polystyrene foam is a slab of varying thickness, consisting of foam material - polymer. The thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam is ensured by air, of which it consists of 95-98%, i.e. gas that does not allow heat to pass through.
Since polystyrene foam is basically air, it has an extremely low density and, accordingly, a low specific gravity. Also, foam plastic has very good sound insulation (thin cell partitions filled with air are a very poor conductor of sounds).
Depending on the source raw material (polymer) and manufacturing processes, it is possible to produce foam of different densities, resistance to mechanical factors, and resistance to other types of influence. In connection with the above, the choice of a certain type of foam and its use is determined.
Foam brands
If you are interested in the question of what is the best brand to buy polystyrene foam, and what is its thermal conductivity, then we will answer it for you. Below are the most popular product brands, as well as the density values and thermal conductivity of the foam.
- PSB-C15. With a thermal conductivity of 0.042 W/mK and a density of 11-15 kg/m3
- PSB-S25. With a thermal conductivity of 0.039 W/mK and a density of 15-25 kg/m3
- PSB-S35. With a thermal conductivity of 0.037 W/mK, and a density of 25-35 kg/m3
Our list is completed by polystyrene foam PSB-S5, whose thermal conductivity is 0.04 W/mK and density is 35-50 kg/m3. Having analyzed the density and thermal conductivity, we can say with confidence that density does not significantly affect the main quality of the foam, heat saving.
More on this topic on our website:
- Extruded or extruded polystyrene foam - technical characteristics of insulation Extruded polystyrene foam, being a high-tech material, can rightfully be called unique. That is why it has become so widespread in construction, plumbing production and a number of other areas...
- The well-known foam plastic, which once competed exclusively with glass wool, today itself has a lot of derivative materials, which, by the way, often give way to other modern types of insulation. By the way,…
- The first question that arises for those who decide to build their own house is what material to use for this. The choice of foundation depends on this, in turn...
- We live far from the hottest country on Earth, which means we have to heat our homes for at least most of the year. This explains...
The concept of thermal conductivity
In general terms, the process of thermal conduction is characterized by the transfer of thermal energy from more heated particles of a solid to less heated ones. The process will continue until thermal equilibrium occurs. In other words, until the temperatures become equal.
In relation to the building envelope (walls, floor, ceiling, roof), the heat transfer process will be determined by the time during which the temperature inside the room becomes equal to the ambient temperature.
The longer this process takes, the more comfortable the room will feel and more economical in operating costs.
Numerically, the heat transfer process is characterized by the thermal conductivity coefficient.
The physical meaning of the coefficient shows how much heat passes through a unit of surface per unit time. Those. the higher the value of this indicator, the better the heat is conducted, which means the faster the heat exchange process will occur.
Accordingly, at the design stage it is necessary to design structures whose thermal conductivity should be as low as possible.
Which sheets to choose?
To achieve the most effective thermal insulation of a wall, it is necessary to correctly calculate the thickness of the insulation used. For example, let’s calculate how thick the insulation is needed for a wall one brick thick.
First you need to find out the total thermal resistance. This is a constant value depending on the climatic conditions in a certain area of the country. In the south of Russia it is 2.8 kW/m2, for a temperate climate - 4.2 kW/m2. Then we find the thermal resistance of the brickwork: R = p/k, where p is the thickness of the wall, and k is a coefficient indicating how strongly the wall conducts heat.
Having the initial data, we can find out what thermal resistance of the insulation needs to be used by applying the formula p=R*k. where R is the total thermal resistance, and k is the thermal conductivity value of the insulation.
Let’s take, for example, foam plastic grade PSB-S 35, which has a density of 35 kg/m3 for a wall, one brick thick (0.25 m) in the region of central Russia. The total thermal resistance is 4.2 kW/m2.
First you need to find out the thermal resistance of our wall (R1). The coefficient for sand-lime hollow brick is 0.76 W/m•C (k1), thickness - 0.25 m (p1). Finding the thermal resistance:
R1 = p1 / k1 = 0.25 / 0.76 = 0.32 (kW/m2).
Now we find the thermal resistance for the insulation (R2):
R2 = R – R1 = 4.2 – 0.32 = 3.88 (kW/m2)
The thermal resistance value of PSB-S 35 foam (k2) is 0.038 W/m•C. Find the required foam thickness (p2):
p2 = R2*k2 = 3.88*0.038 = 0.15 m.
Conclusion: under the given conditions we need polystyrene foam PSB-S 35 15 cm.
In a similar way, calculations can be made for any material used as insulation. Thermal conductivity coefficients of various building materials can be found in specialized literature or on the Internet.
Why is thermal insulation needed?
The relevance of thermal insulation is as follows:
Keeps you warm in winter and cool in summer.
Heat loss through the walls of a typical multi-storey residential building is 30-40%. To reduce heat loss, special thermal insulation materials are needed. The use of electric heaters in winter contributes to additional energy costs. It is more profitable to compensate for these costs by using high-quality thermal insulation material, which ensures heat retention in winter and coolness in the summer heat. At the same time, the cost of cooling the room with air conditioning will also be minimized.
Increasing the durability of building structures.
In the case of industrial buildings using a metal frame, insulation helps protect the metal surface from corrosion, which is the most detrimental defect for this type of structure. And the service life of a brick building is determined by the number of freeze/thaw cycles. The impact of these cycles is perceived by the insulation, because the dew point is located in the thermal insulation material, and not in the wall material. Such insulation allows you to increase the service life of the building many times.
Protection against increasing noise levels is achieved by using such noise-absorbing materials (thick mattresses, sound-reflecting wall panels).
Increasing the usable area of buildings.
The use of a thermal insulation system makes it possible to reduce the thickness of external walls, while increasing the internal area of the building.
Rating of the best sofa manufacturers
| Nomination | place | factory | rating |
| The best factories of inexpensive sofas | 1 | 4.8 | |
| 2 | 4.7 | ||
| 3 | 4.6 | ||
| 4 | 4.5 | ||
| The best sofa factories in the middle and premium price segments | 1 | 4.9 | |
| 2 | 4.9 | ||
| 3 | 4.8 | ||
| 4 | 4.7 | ||
| 5 | 4.7 | ||
| 6 | 4.6 |
Comparison of styrene with penoplex
Polystyrene foam and penoplex are relatively identical materials, made using the same granules. The only difference is the gluing technology, which gives unexpected results when comparing indicators.
The fact is that during the production of penoplex, styrene beads are processed under pressure at high temperatures. The result is a plastic mass that, when frozen, is homogeneous and durable. The air bubbles that remain inside are evenly distributed throughout the entire part of the stove.
When forming foam, the material pre-loaded into the mold is simply doused with steam. As a result, it gets a “popcorn” structure, and, as a result, the bonds between loose granules are much weaker.
Based on this, it can be noted that the thermal conductivity of extruded polystyrene foam is better and corresponds to 0.028-0.034 W/mS. Thus, only 30 mm of this material will be needed to replace 40 mm of conventional foam.
The structure of penoplex differs from polystyrene foam Source pgsstore.ru
Important! In cases where there is no need for high strength of the insulated wall, then you can safely give preference to budget polystyrene foam. True, you should first determine its optimal thickness, depending on climatic factors and operating conditions.
Features of application and numbers in markings
Foam insulation can be used for indoor and outdoor conditions. This can be determined by the thermal conductivity coefficient. For example, if the product name contains the number “15”, then such sheets are suitable for gluing to vertical structures indoors. The thickness of this raw material is insignificant, and therefore will not use up useful space.
Low thermal conductivity foam for outdoor conditions Source 27del.ru
There is also a coefficient with the number “25”; this is a higher quality insulation, used only for thermal insulation of walls on the outside of the house. It is also often used in attics or basements where an enhanced level of thermal insulation is required. Expanded polystyrene with this coefficient can be used to insulate interfloor ceilings and roof slopes in multi-storey apartment buildings and the private sector.
Foam plastics, which are labeled with the number “35,” have the lowest thermal conductivity value. They try to insulate buried foundations, runways, highways and other capital industrial structures with such materials. It is irrational to use such insulation boards for a home.
Classification of expanded polystyrene
According to the production method, this material is figuratively divided into 2 large classes, which have very different properties. The first is done at high temperature by sintering granules. The second involves mixing the pellets at very high temperatures with the future addition of a special blowing agent and removal from the extruder.
The first class is called pressless; it can be easily installed by eye. The material looks like balls interlocked together, somewhat similar to a beehive. We need to remember the polystyrene foam in which any household appliances (microwave, refrigerator) were supplied. The second class is called press, because the granules are connected to each other much more tightly. It is much harder to break or crumble. Accordingly, different brands are distinguished.
Other properties of the described insulation materials
Mineral wool insulation is not flammable. The fire resistance of these materials is determined not only by the properties of the material, but also by the conditions under which they are used.
The degree of fire resistance is greatly influenced by what materials the insulation is combined with. The method of arrangement of protective and covering layers also plays a role.
As for expanded polystyrene, it is a self-extinguishing material. Therefore, walls decorated with it do not ignite so quickly. And if this does happen, the flame also spreads over their surface more slowly than in the case of other insulation materials.
Mineral wool is a non-flammable substance. Therefore, the flammability of surfaces lined with it, as well as the spread of flame along them, is minimal. Since the basis of this insulation – basalt – is a natural stone, mineral wool can withstand temperatures up to 1000 °C, and can resist the spread of fire for up to three hours.