The article was prepared with the participation of specialists from the Association of Expanded Polystyrene Manufacturers and Suppliers
The market for thermal insulation materials is represented by various categories, which greatly simplifies the selection of suitable insulation for specific tasks. One of the most popular insulators in the private sector is polystyrene foam; its popularity is explained by both its high technical characteristics and availability. Nevertheless, battles between supporters and opponents do not subside around it; it is quite difficult for a person far from construction to figure out which of the properties of insulation are real and which are from the category of “horror stories”. We will try to make the task easier for beginners, and it will be useful for more experienced craftsmen of our portal to refresh the information. And specialists from the Association of Expanded Polystyrene Manufacturers and Suppliers will help you separate the “wheat from the chaff.”
Consider:
- What is polystyrene foam?
- Main characteristics of expanded polystyrene.
- Scope of application of expanded polystyrene.
Types of material
Expanded polystyrene is classified depending on the manufacturing technology used. There are currently four subtypes of material available:
- Pressless foam plastic (labeled EPS - foreign production, or PSB - domestic). The most common insulation material for construction. It has large granules and a soft structure. There are modified versions with increased fire protection.
- Extruded (labeled XPS and EPS, respectively) is characterized by high compressive strength characteristics, due to which it is used for insulating foundations and concrete floors. It has small grains and a dense structure.
- Pressed polystyrene foam (for example, PS-1) and autoclave foam are not particularly widespread now due to the unprofitability of the production process.
Video description
Floor insulation with extruded polystyrene foam.
Blocky
The essence of the method is to mix vinylbenzene with a benzene medium until the particles are evenly distributed relative to each other. Mixing at the initial stage occurs at a temperature of 90C, the second stage involves increasing the temperature to 220C. Block formation is completed at a residual value of 15% styrene that has not converted to polystyrene. Further vacuuming removes the mixture from unpolymerized vinylbenzene.
Today, the block method is considered the most popular in the production of polystyrene due to the production of high-quality material. The polymer has high purity and strength. The advantages of this method are the maximum wastelessness and profitability of the production process.
Main brands of foam plastic
After foaming the polystyrene, the raw materials for the finished products are loaded into a container. Steam is injected into it under pressure. The granules foam and become saturated with air. At the next stage, the finished granules are dried from moisture; hot air is used for this.
When drying, the granules are shaken periodically. The finished granules are placed in bins that are calibrated according to foam grades. Molding occurs under pressure. When molding, the following types of foam are obtained, which differ in density:
- PSB-S-15;
- PSB-S-25;
- PSB-S-35;
- PSB-S-50.
The last number in the marking determines the density of the foam for insulation. Many developers do not know what the specific gravity of foam is. Density (specific gravity) is the mass of a product in its volume. The density of polystyrene grade PSB-S-15 is 15 kg/m³. Accordingly, one cubic meter of PSB-S-15 polystyrene boards weighs 15 kg.
The question arises of how to independently determine the density of foam plastic without special equipment. This is easy to do: you need to calculate the cubic capacity of the finished product and weigh it on the scales. To make a claim, the store must have in hand a state verification certificate of the scales. Weighing can be carried out directly in the store or at the construction warehouse of the materials supplier. This technical calculation of foam density will be the most optimal.
A product with low density has lower compressive strength . It is not able to withstand shock and static loads. The facade can be damaged when removing snow or leaves. Subsequent restoration of the coating and painting work will require additional costs. However, the low density of foam guarantees lower cost with the same thermal insulation properties. The choice of density is based on the scope of application of each brand of product.
PSB-S -15
This grade has the lowest compressive strength at a linear deformation of 10% (not less than 0.04 MPa). The tensile strength of PSB-S-15 foam when bending should not be lower than 0.07 MPa.
PSB-S-15 slabs provide good thermal insulation. Foam plastic, the density of which is not more than 15 kg/m³, has a thermal conductivity of 0.036 W/(m.k). This type of insulation is used to insulate unloaded structures and planes , such as building facades, roofs, ceilings, and gables.
PSB-25
Foam grades with a volumetric weight of 25 kg/m³ are the most popular among private developers. Medium-density slabs combine reasonable prices and good thermal insulation characteristics. This type is versatile and has proven itself well in insulating various structures.
The volumetric weight of foam is in the range of 15-25 kg/m³. The thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam with a volumetric weight of 25 kg/m³ should be less than 0.033 W/(m.k). The linear deformation indicator should not be lower than 0.15 MPa. Ultimate bending strength – 0.32 MPa.
PSB-S-35
PSB-S-35 slabs have a fairly wide range of applications. The density of polystyrene foam PSB-S-35 should be in the range of 25-35 kg/m³. This insulation will last up to 40 years. It is less fragile than PSB-S-15 and PSB-S-25. Strength and durability are achieved through closer bonding of styrene molecules.
The thermal conductivity of polystyrene with a volumetric weight of 35 kg/m³ should be less than 0.033 W/(m.k). Ultimate bending strength – 0.38 MPa, linear deformation index – 0.26 MPa. This is a hard and durable material.
PSB-S-50
PSB-S-50 is a dense foam that can withstand mechanical and impact loads. It is used for thermal insulation:
- foundations;
- pile foundations;
- floors of industrial enterprises;
- heated roads, parking lots and lots;
- plating of ships and floating craft.
Expanded polystyrene with a density of 45-50 kg/m³ is supplied to order due to low demand and high cost.
The thermal conductivity of such a material should be less than 0.033 W/(mk). The linear deformation indicator approaches 0.38 MPa. Ultimate bending strength – 0.42 MPa. This is the densest material.
Scheme of application of various brands
The following key types of expanded polystyrene are produced, differing in density and other characteristics:
- PSB-S-15, the density of this brand of foam is up to 15 kg/cu.m.
- PSB-S-25, from 15 kg/cu.m. up to 25 kg/cu.m.
- PSB-S-35, from 25 kg/cu.m. up to 35 kg/cu.m.
- PSB-S-50, from 35 kg/cu.m. up to 50 kg/cu.m.
The thermal conductivity component of foam plastic, expressed in digital values, refers to the range 0.037 W/mK - 0.043 W/mK. The indicated value can be correlated with the thermal conductivity of air, which is equal to 0.027 W/mK.
Use of polystyrene foam PSB-S-15
Polystyrene foam PSB-S-15 can be used for insulation of house facades. This type of insulation is practically not used in construction. It is used in structures that are attached to structures. These can be open balconies or verandas that serve a decorative function. Using PSB-S-15 foam plastic, shapes for facades are formed, and this allows :
- frame the corners of the house, windows;
- separate floors by creating cornices.
What is PSB-S-25 suitable for?
The density of the foam is calculated by analogy with determining the density of brick. For example, if 1 cube of foam has a density of 25, then its weight will be 25 kg. The flexural and compressive strength of foam depends on its density. The density of polystyrene foam and its brand are completely different characteristics. For example, if we take into consideration SPB-C25 or SPB-C50, the density parameter will fluctuate between 35−50 or 15−25.
Plates with a density of 25 are used to insulate the facades of a house. The standard is foam plastic, the thickness of which is 5 cm. This type of insulation is used for many purposes. Its thickness can be changed - this will depend on consumer preferences.
Polystyrene foam of maximum thickness can be used to insulate walls that are exposed to atmospheric agents. They can also be used to insulate walls, since such material perfectly prevents the appearance of fungus.
Based on the designation of the material, it is used in various construction structures, and this does not impair its quality characteristics.
Application of polystyrene foam PSB-S-35
In order to perfectly align the walls, you can change the thickness of the polystyrene foam tiles. It is not recommended to abuse the size of the thickness of the material, since this will provoke certain problems with fixing the drainage system at the corners of the building.
Before choosing insulation of the required thickness, it is recommended to find out in advance what the amount of gas pipe stock is , because it should never be covered, as this may disrupt the aesthetics of the appearance of the building. In this case, it is advisable to prefer PSB-S-35 material with a thickness of 5 cm over material with a density of 25 and a thickness of 10 cm, especially since their prices are practically the same.
Insulation with a density of 35 can be used to insulate the slopes of windows and doors, and the facades of buildings. As a rule, it costs twice as much as the same polystyrene material with a density of 25. With a thickness of 5 cm, it can be used to insulate non-residential structures and garages. With a thickness of similar insulation of 7 centimeters, it can be used for thermal insulation of residential premises.
Due to the normal level of density, it is possible to use a heat insulator with a minimum thickness , which does not imply a deterioration in the quality of insulation. If the polystyrene foam heat insulator turns out to be harder, then it can be used to provide ideal insulation of basement walls and foundations.
Overview of extruded polystyrene foam
Density is the main characteristic of polystyrene. Classification is made precisely on this basis. Depending on its performance, the directions in which it is used will also change. This material is actively used for insulating apartments and private houses.
Extrusion method (extrusion)
The concept itself carries a description of the manufacturing process. This term literally means punching using specially designed holes.
This technology imparts many qualities to the final product, for example:
- Reliable performance in water resistance.
- Giving minimum values in the thermal conductivity index.
- Decrease in heat capacity.
Types of foam depending on density, manufacturing technology, sheet shape and size
Low density and light weight, excellent thermal characteristics and good sound insulation make polystyrene foam one of the most popular thermal insulation materials. Modern technologies make it possible to produce various types of foam, which differ in characteristics, cost and purpose. Knowing the differences will help you choose the optimal material for various jobs.
Density of mineral wool thermal insulation
In this regard, denser materials should be used in loaded areas. This is the only way to avoid deformation of the insulation. Finally, the method of its installation depends on the specific gravity of the insulation. Thus, lightweight, low-density heat insulators can be used between the joists and sheathing elements. If this same option is mounted on walls, it will simply slide off, so the choice is made in favor of more durable mats and sheets.
In addition, dense insulation does not require additional mechanical protection; they are strong enough to withstand mechanical loads. And more friable materials - polystyrene foam, polystyrene foam, mineral wool - always need additional protection. As a rule, consumers often pay attention to the performance characteristics of insulation rather than to physical properties such as density.
Wall insulation
As we learned from the material above, it is necessary to use different materials for different parts of the walls. If you do not want, for example, rotting and destruction processes to begin in your wooden bathhouse constructed with XPS, the installation of extruded polystyrene foam is excluded. Correctly, it is very simple and it is not difficult to stick to it.
The density of traditional polystyrene foam for wall insulation is 25, extruded polystyrene is 15. When working with traditional polystyrene foam, it is best to use slabs with a thickness of 50 mm; extruded polystyrene foam requires the same indicators. You can get by with a thickness of 30-40 mm.
Classification
Marking 31C
Marking 31C has established itself as a high-quality element of insulation of unloaded sections of structures. An excellent example in this direction is work with foundation walls. This marking can be found in the underfloor heating product.
31C has also found wide application in work on insulation of sewer systems. Operation is intended exclusively in structures that are protected from fire, since its fire resistance level corresponds to category G4.
Marking 35
Marking 35 has significant differences from 31C. They consist in the difference in specific gravity indicators and the general level of fire resistance. In the creation of expanded polystyrene with the marking 35, a fire retardant is used, with the help of which it is possible to increase fire resistance.
Due to its fire resistance qualities (low flammability), the product has also proven popular for roofing. The most popular work in which grade 35 polystyrene foam is used is the insulation of all kinds of structures that perform enclosing functions.
Marking 45
Expanded polystyrene with the marking 45 is superior to the first two options due to the fact that its compressive strength has a huge margin. It can be successfully used not only in insulation; it opens up all its possibilities in such large-scale work as road construction. Expanded polystyrene grade 45 is also actively used in work on runways.
- The specific gravity of polystyrene foam has little effect on heat retention performance.
- The specific gravity indicator has an impact on the strength characteristics.
- The effectiveness of insulation (thermal insulation) is affected by the thickness of the sheet.
Markings of polystyrene foam 31 and 31C have basically similar qualities. The most striking difference between these two brands lies in the categories that are responsible for fire resistance. 31 has category G1, and 31C G4.
An opposite example is marked polystyrene foam 45 and 45C. Unlike expanded polystyrene 31 and 31C, these are different on literally every point. One of the few indicators that these brands of expanded polystyrene have in common is fire resistance at the G4 level.
Scope of application of extruded polystyrene foam
Let us consider in more detail the possible areas of use of polystyrene foam boards. Operational and mechanical characteristics allow the active use of polystyrene foam for:
- Thermal insulation of private households and ASG facilities;
- Protection against freezing of the cushions of highways, main pipelines, runways;
- Thermal insulation of foundations, retaining structures and roofs;
- Production of household and industrial refrigeration units, refrigerators;
- Installation of various types of hydraulic barriers;
- Production of packaging and disposable tableware;
- Making household items.
Despite the fact that the scope of use of extruded panels is quite extensive, there are some limitations.
Characteristics of expanded polystyrene
The main characteristics by which the quality of a material is assessed are density and thermal conductivity. Many people think that the density of the foam somehow affects its thermal conductivity, but in fact this is not the case. The densest type of polystyrene foam (having the largest cubic meter weight) has a thermal conductivity coefficient approximately equal to the lightest type of material. Consequently, density only affects strength (well, and cost - a dense sheet is always more expensive). The density of modern types of expanded polystyrene varies from 15 to 50 kg/m³. The characteristics of the material are usually indicated in the marking, for example, the presence of the letter C (in this form PSB-S) indicates the “self-extinguishing” property.
The undoubted advantages of expanded polystyrene include its low cost, excellent thermal insulation qualities and low water absorption capacity. The main disadvantage is the danger of fires. The material emits extremely toxic smoke when burned, so it is not recommended for use in areas with increased fire hazard, for example, in kitchens.
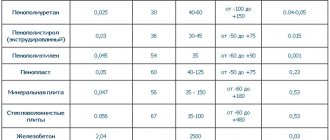
Comparison of the characteristics of polystyrene foam and extruded polystyrene foam
| No. | Characteristics | EPPS | Styrofoam |
| 1. | Water absorption, % by volume for 30 days | 0,4 | 4 |
| 2. | Water absorption, % by volume for 24 hours | 0,2 | 2 |
| 3. | Vapor permeability, mg/m.h.Pa | 0,018 | X |
| 4. | Thermal conductivity, W/(mxC) | 0,028-0,034 | 0,036-0,050 |
| 5. | Ultimate strength during static bending, (kg/cm2) MPa | 0,4-1 | 0,07-0,20 |
| 6. | Compressive strength at 10% linear deformation, MPa, N/mm2 | 0,25-0,5 | 0,05-0,2 |
| 7. | Density, kg/m3 | 28-45 | 15-35 |
| 8. | Operating temperature range, C | from -50 to +75 | from 50 to +75 |
Thermal conductivity and density of penoplex, comparison with polystyrene foam PSB
A comparative table of the values of the thermal conductivity coefficient, density of penoplex and polystyrene polystyrene PSB of various brands in a dry state at a temperature of 20...30°C is presented. Their operating temperature range is also indicated.
Penoplex thermal insulation, in contrast to non-pressed polystyrene foam PSB, is produced at elevated temperatures and pressures with the addition of a foaming agent and extruded through an extruder. This production technology provides penoplex with a closed microporous structure.
Penoplex, compared to polystyrene foam PSB, has a lower thermal conductivity coefficient λ , which is 0.03...0.036 W/(m deg) . The thermal conductivity of penoplex is approximately 30% lower than that of such traditional insulation as mineral wool. It should be noted that the thermal conductivity coefficient of polystyrene foam PSB, depending on the brand, is in the range of 0.037...0.043 W/(m deg).
The density of penoplex ρ according to the manufacturer is in the range from 22 to 47 kg/m 3 depending on the brand. The density of PSB expanded polystyrene is lower - the density of the lightest brands PSB-15 and PSB-25 can range from 6 to 25 kg/m 3, respectively.
The maximum temperature for using Penoplex expanded polystyrene is 75°C. For PSB foam it is slightly higher and can reach 80°C. When heated above 75°C, penoplex does not melt, but its strength characteristics deteriorate. The manufacturer does not report how much the thermal conductivity coefficient of this thermal insulation material increases under such conditions.
Thermal conductivity and density of penoplex and expanded polystyrene PSB
| Brand of expanded polystyrene | λ, W/(m K) | ρ, kg/m 3 | trab, °С |
| Penoplex | |||
| Penoplex comfort slabs | 0,03 | 25…35 | -100…+75 |
| Penoplex Foundation | 0,03 | 29…33 | -100…+75 |
| Penoplex Roofing | 0,03 | 26…34 | -100…+75 |
| Penoplex segments grade 35 | 0,03 | 33…38 | -60…+75 |
| Penoplex segments grade 45 | 0,03 | 38…45 | -60…+75 |
| Penoplex Block | 0,036 | from 25 | -100…+75 |
| Penoplex 45 | 0,03 | 40…47 | -100…+75 |
| Penoplex Slope | 0,03 | from 22 | -100…+75 |
| Penoplex Facade | 0,03 | 25…33 | -100…+75 |
| Penoplex Wall | 0,03 | 25…32 | -70…+75 |
| Penoplex Geo | 0,03 | 28…36 | -100…+75 |
| Penoplex Base | 0,03 | from 22 | -100…+75 |
| Expanded polystyrene PSB (foam plastic) | |||
| PSB-15 | 0,042…0,043 | up to 15 | up to 80 |
| PSB-25 | 0,039…0,041 | 15…25 | up to 80 |
| PSB-35 | 0,037…0,038 | 25…35 | up to 80 |
| PSB-50 | 0,04…0,041 | 35…50 | up to 80 |
Definition and properties
Polystyrene foam is an insulating material that has excellent heat and sound insulation properties.
The cost expression of polystyrene foam boards is much lower than for other insulation materials. The use of expanded polystyrene slabs in construction work helps reduce operating costs for heating or cooling residential or commercial buildings by tens of times.
There are several points of view that are associated with the concept of density. The unit of measurement for this parameter is kilogram per cubic meter. This value is calculated from the ratio of weight to volume. It is impossible to measure with one hundred percent accuracy the qualitative properties of polystyrene foam, which are associated with its impermeability and density. Even the weight of this insulation does not affect its thermal insulation capabilities.
Structure and composition of the finished material
Polystyrene foam is made from polystyrene foam balls that are filled with air.
Each thermal insulation material necessarily contains air located in the pores. The improved thermal conductivity index directly depends on the size of the atmospheric air masses contained in the material. The more there are, the smaller the thermal conductivity component will be. The foam manufacturing process comes from polystyrene foam beads that retain air.
In connection with the above, we can conclude that the concentration of polystyrene foam affects its thermal conductivity. If this value changes, then changes in thermal conductivity indicators occur within the boundaries of percentages. One hundred percent retention of air in the insulation is associated with its exceptional heat-saving ability, since air has the lowest thermal conductivity coefficient.
Due to the low thermal conductivity of the insulation, a high percentage of energy saving is ensured. If we compare brick with polystyrene foam, their ability to save energy will be noticeably different, because 12 cm of thermal insulation thickness is equivalent to 210 cm of thickness of a brick or 45 cm of log wall.
Technical characteristics: table
| Index | EPS, Extruded polystyrene foam | Foam plastic PSB-S-15t – PSB-S-50 | ||
| Type 30 | Type 35 | Type 45 | ||
| Vapor permeability mg/(m*h*Pa) | 0,008 | 0,007 | 0,007 | 0,05 |
| Density kg/m³ | 25 – 30 | 28 – 38 | 38 – 45 | 8 – 35 |
| Water absorption per day, no more than % by volume | 0,4 | 0,4 | 0,2 | 1,8 – 4 |
| Compressive strength (10% linear deformation) not less than mPa (kgf/cm²; t/m²) | 0,20 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 0,4 – 0,20 |
| Thermal conductivity at 25±5 °C W / (m*K) | 0,027 | 0,028 | 0,030 | Dry 0.038 – 0.043 |
| Fire resistance, category | G1* | G1* | G4* | G3* |
| Specific heat capacity kJ/(kg*°K) | 1,45 | 1,45 | 1,40 | 1,26 |
| Static bending strength, mPa | 0,25 | 0,4 | 0,4-0,7 | 0,6 – 0,35 |
| Sound insulation improvement index, dB | 23 | 23 | 23 | |
| Self-burning time, sec. | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
- *G1 – Low flammability;
- *G3 – Normal flammability;
- *G4 – Highly flammable.
The choice of insulation is made not only based on thermal conductivity, heat capacity and other technical characteristics. It is also necessary to take into account the fact that rodents can damage the casing. Read carefully which insulation is not chewed by rats and mice.
The main criteria for choosing a humidifier for the home are discussed in this topic.
How to choose
To facilitate the selection of a suitable brand of expanded polystyrene, it is recommended to pay attention to the following criteria.
Manufacturers
To create reliable thermal protection, it is recommended to give preference to well-known brands that produce insulation that meets the requirements and declared characteristics. It is possible to produce high-quality material only if you have modern equipment and adherence to the technological process. Among the companies that deserve trust are:
- Technoplex;
- KNAUF;
- URSA;
- PENOPLEX;
- TechnoNIKOL;
- Elite-Plast.
The main argument in favor of the products of a particular manufacturer is the availability of a certificate of quality and environmental friendliness of the raw materials used for the production of expanded polystyrene.
Length, width, thickness
Manufacturers produce standard and non-standard slab sizes. The sheets have different lengths, thicknesses and widths. The predetermining parameter when choosing insulation is thickness. It varies from 20 to 100 mm. A clear understanding of the purpose for which insulation is being purchased - external or internal work, for the floor or roof - will help you decide on a purchase.
Standard sheets have a length and width of 1000, 2000 mm. Upon special order, the manufacturer cuts the slabs according to individual parameters. Sheets available for sale:
- 1200x600 mm;
- 500x500 mm;
- 900x500 mm;
- 1000x1000 mm;
- 1000x500 mm.
If the length of the product exceeds 2000 mm and the width is 1000 mm, GOST standards allow cutting slabs 10 mm smaller. With a sheet thickness of up to 50 mm, there may be a difference of 2 mm (in either direction).
Interior or exterior work
Expanded polystyrene is not produced separately for interior and exterior use. The insulation is selected taking into account the brand, thickness and density of the sheet.
| Place of application | Plate thickness, mm |
| First floor (for floor) | from 50 |
| Second floor (for floor) | 20-30 |
| Additional sound insulation on the floor | 40 |
| For interior wall cladding | 20-30 |
| For external wall cladding | 50-150 |
Sheet sizes
Extruded polystyrene foam is produced in slabs with the following parameters:
- width range – 500-600 mm;
- length range – 1200-2400 mm;
- thickness range – 20-150 mm.
At the request of the client, sheets can be cut into different sizes.
Types of expanded polystyrene foam - EPS
The classification of expanded polystyrene foam is based on:
- density;
- manufacturing technology;
- plate shape.
Brands and types of expanded polystyrene foam by density
Depending on the maximum density value, foamed polystyrene foam is divided into grades.
The following types of this foam are produced by density:
| Foam brand | Minimum density value, kg/cub.m. | Thermal conductivity of the material in a dry state, at a temperature of (25 ± 5) 0 C, W/ (m*K) |
| PPS10 | 10 | 0,044 |
| PPS12 | 12 | 0,042 |
| PPS13 | 13 | 0,041 |
| PPS14 | 14 | 0,040 |
| PPS16F | 16 | 0,038 |
| PPS17 | 17 | 0,039 |
| PPS20 | 20 | 0,038 |
| PPS23 | 23 | 0,037 |
| PPP25 | 25 | 0,036 |
| PPS30 | 30 | 0,037 |
| PPS35 | 35 | 0,038 |
Expanded polystyrene foam boards depending on manufacturing technology
Depending on the manufacturing technology, the following types of polystyrene foam are produced:
- P – produced by cutting from large blocks;
- RG – cut graphite-containing from large blocks;
- T – thermoformed.
Foamed polystyrene foam boards depending on the plate shape
Depending on the shape of the foam plates, they are produced in two types:
A – cut slabs with a continuous, smooth side edge.
B - cut or formed slabs with a quarter-size side edge for easier and more efficient installation.
Dimensions of expanded polystyrene foam boards
Modern technologies make it possible to produce polystyrene foam boards of various sizes. According to GOST, the length of the slabs varies from 500 to 6000 mm in increments of 50 mm, and the width - from 500 to 2000 mm in increments of 50 mm. Foam thickness from 10 to 500 mm in 5 mm increments.
Example and explanation of the symbol for expanded polystyrene foam boards
The markings, which indicate not only the overall dimensions, but also the type of material and type of edge, allow you to understand the specifics of expanded polystyrene foam boards.
The symbol may indicate special characteristics, for example, the color of the foam or brand. Also, the marking must indicate GOST, in accordance with which the material is produced.
Example of decoding symbols: PPS16F-R-A-2000x1000x150 GOST 15588-2014
- expanded polystyrene for facade systems (PPS16F);
- density – 16 kg/cub.m. (PPS16F);
- produced by cutting from large blocks (P);
- has a continuous, smooth side edge (A);
- length – 2000 mm;
- width – 1000 mm;
- thickness – 150 mm;
- manufactured in accordance with GOST 15588-2014.
Deciphering the markings allows you to ensure that the material is suitable for the planned work.
Polystyrene foam - how much does a cubic meter weigh?
A popular misconception is that the specific gravity of polystyrene foam should correspond to the brand. That is, if we buy grade 35 polystyrene foam, then the specific gravity of one cubic meter of polystyrene foam should correspond to 35 kg. In fact, according to GOST, the number in the stamp indicates the maximum possible weight per cubic meter, within the limits specified in the same GOST. Thus, the 15th density includes all polystyrene foam boards weighing up to 15 kg/m3 (in reality 11–12 kg/m3), the popular 25th grade includes polystyrene foam, whose specific weight ranges from 15.1 kg/m3 to 25 kg/m3 (most often in practice - 17–18 kg/m3), grade 30 includes polystyrene foam weighing from 25.1 to 35 kg/m3. In the latter case, most often manufacturers offer foam with a real density of 26–27 kg/m3. Deception? Rather, savings - given the high competition in the manufacturer market, everyone is trying to offer the material cheaper than others. And this can only be done by reducing the amount of raw materials and deteriorating the quality of the products.
Determining the quality and brand of polystyrene foam by density (weight-to-volume ratio, kg/m3) is the biggest misconception. Density is only one characteristic that plays a role in determining the grade of material produced. According to GOST 15588-86, foam plastic is characterized by compressive strength, bending strength, thermal conductivity, water resistance, slab burning time and structural stability. Of all these characteristics, density is far from the most important. For example, for 25th density polystyrene foam, GOST defines a compressive strength of at least 0.08 MPa. For grade 15, this characteristic is 0.04 MPa. GOST has one very important point - if expanded polystyrene does not correspond to its brand in any characteristic, it must be assigned to a brand of a lower class . That is, if you buy expanded polystyrene, the specific gravity of which is from 15.1 to 25 kg/m3, but the compressive strength of the material is less than 0.08 MPa, it should be classified as grade 15.
What density of foam is best to use for sound insulation?
Polystyrene foam by itself is not an effective soundproofing material. But it can only be included in noise-absorbing or reflective structures. For sound insulation of interior and apartment partitions and ceilings, as well as as a filler for doors and various lightweight panels, foam with a density of 20-25 kg/m3 is used. Insulation made from polystyrene foam panels with a rigid cardboard outer lining can reduce noise levels by 2-5 decibels. In addition, foam plastic on a rigid base copes more effectively with shock sound vibrations, intercepting up to 95% of sound.
In addition to the thickness, the shape of the surface of the soundproofing panel is also extremely important. The classic and most effective profile is an equilateral pyramid with its vertices directed towards the sound source.
In part, such specialized ceiling coverings can replace facing panels made of expanded polystyrene with a relief pattern. Their efficiency is much lower, but when using them there is no need for an additional suspended or suspended ceiling.
Return to list of questions
What's better - is polystyrene foam safe?
In Russia and the CIS countries, there is a certain prejudice towards polystyrene foam facing material. But you can check how safe this material is based on approved documents. Thus, environmental and fire safety are confirmed by many studies and results:
- Research Institute named after Erisman under No. 03/PM8;
- Republican level Scientific Research Center of Hygiene, Republic of Belarus;
- Research Center for Fire Safety of the Russian Federation;
According to the material safety scale approved by BREEM, the material is assigned the highest class A+. All these indicators taken together allow us to speak about its high quality and practicality of use in many construction areas and areas.
You can find out about the percentage of harmful substances in the composition of the building material itself from the available certificates - every conscientious manufacturer attaches them to their product. And even if the material is in doubt, it will still be located outside the house, but not inside. Therefore, cladding with foam plastic and decorative coating is the right choice. The main thing is to correctly calculate the number of slabs, the density of the insulation layer itself and select the adhesive composition - you should not be afraid of poisoning with harmful compounds released into the air from this insulation.
Classification of façade foam plastic by production method
Conventional foam for wet plaster for facades Foam or expanded polystyrene (EPS) is a rigid insulating material produced in the form of slabs of various densities and thicknesses. The raw materials for its production are polystyrene granules, and the foaming agents are low-boiling hydrocarbons and gas-forming agents. When heated, the granules increase in volume by 10-30 times. Carbon dioxide, isopentane or other reagents foam polystyrene. As a result, in the finished product the polymer occupies only 2% of the volume, and the rest is occupied by gas.
According to the production method, PPP is divided into two types:
- Produced by the sintering method, when, when heated, the granules are sintered together with the simultaneous formation of the product.
- Obtained by foaming from a granular mass to which a gas-forming agent is added.
Various production methods make it possible to obtain a material similar in composition, but differing in structure (open or closed) and cell density.
At what temperature can foam plastic be glued?
The temperature at which facade insulation is carried out with foam plastic depends not on the insulation, but on the glue that is used to attach it. For example, the manufacturer recommends using Ceresit CT 83 glue to perform work in the temperature range from 0 to 30. There are some nuances to using the adhesive mixture at high temperatures. It is necessary to mix small quantities and keep it in a constantly closed container. Too much water will evaporate from the finished mixture and it will lose its elasticity; re-adding water is not recommended. A new portion of the solution should be mixed.
Read more: https://srbu.ru/qa/article/3277-tolshchina-penopolistirola-stepen-utepleniya.html
0