Foamed materials, e.g. expanded polystyrene (popular polystyrene foam) and extruded polystyrene have good thermal insulation properties (0.032-0.045 W / (mK)). Both of them are formed as a result of foaming polystyrene granules, as a result of which the process of producing extruded polystyrene is accompanied by extrusion of the molten mass and rolling it to the required thickness.
These materials are versatile; low weight (closed in pores, air makes up more than 90% of their volume) and high rigidity and resistance to compression. These features mean that foam materials can carry significant loads.
Another advantage is their low absorption - they can be used without any problems in areas where they are most susceptible to moisture. When in contact with water, they retain their dimensions (do not deform) and physical properties.
Where the influence of moisture is continuous – extruded polystyrene is perfect. Its surface is covered with a kind of rolled epidermis, which significantly reduces water absorption.
Foam thickness for external wall insulation
The article outlines what thickness of polystyrene foam is best to choose for external insulation of the walls of a house.
A comparative diagram of the thermal conductivity of various building materials is presented. Tip : In addition to this article, be sure to read about choosing foam density. Also, do not forget that polystyrene foam can be hazardous to human health. It is possible that, having learned about the harmfulness of this material, you will adjust your plans for construction work.
Now let's move on to the main topic.
Are you planning to make your home warmer? Have you decided to use foam plastic for this? Then you will be interested to know what thickness of polystyrene foam is the most optimal for insulating walls outside.
Indeed, there are materials on the market with a wide variety of sizes. So which one should you choose to solve this problem?
So, first of all.
One of the thinnest insulation materials
The benefits of insulation using expanded polystyrene are difficult to overestimate. However, one of the most significant of them is its thickness. This means that the product has practically the lowest thermal conductivity coefficient.
The only material that foam plastic is inferior to is penoizol, which is a multicomponent liquid material. However, it can only be used for insulating non-residential structures.
The reason for this is the high toxicity of the material. In addition, only professional builders can work with foam insulation, but with the help of polystyrene foam, anyone can complete the finishing independently.
What do you need to know about sizes? What are they?
Foam sheets can be standard or custom sizes.
The length and width of the standard sheet are 1000, 2000 mm. The manufacturer can cut products into other non-standard sizes.
You can often find sheets of 1200x600 that meet the needs of the buyer and are in good demand. This can be a sheet with dimensions of 500x500, 1000x1000, 1000x500 mm.
On order, you can receive a batch of expanded polystyrene with sides of 900x500 or 1200x600 and other sizes, which does not contradict the standards.
GOST allows cutting products 10 mm smaller if its length is over 2000 and its width is 1000 mm. In thickness for slabs up to 50 mm, a difference of ±2 mm is allowed, and over 50, a difference of ±3 is allowed.
If the length is not suitable for the buyer, then companies selling such products offer individual cutting.
Length and width are important only for transporting building materials from the manufacturer to the customer. The main role is given to the thickness of the material.
The length of extruded polystyrene foam (EPS) sheets is 1200-2400 mm, width - 500-600 mm, and thickness 20-150.
To select a specific value, it is recommended to start from the scope of application, for example, for thickness, the following tips:
- for the floor on the first floor - from 50 mm;
- for the second floor and above – 20-30 mm;
- for additional sound insulation on the floor - 40 mm;
- for internal wall cladding – 20-30 mm;
- for external wall cladding – 50-150 mm.
Physical properties of foam plastic
The main characteristics of porous polystyrene include:
- strength – polystyrene foam does not have outstanding strength characteristics and is capable of crumbling and breaking even under weak mechanical stress. It can be easily damaged using sharp objects or simply hitting the surface. To reduce the likelihood of destruction, the foam is covered with layers of harder material that evenly distributes external loads;
- flexibility - expanded polystyrene is weakly susceptible to bending influences and can break under them at any time. For the same reason, foam plastic boards are installed only permanently, avoiding any torsional loads;
- thermal conductivity - the presence of gases (natural heat insulators) in hollow capsules provides the material with a low heat transfer coefficient. This is also facilitated by the lack of convection inside the pores due to their small diameter. It will take a long time to completely heat a piece of polystyrene foam to a given temperature;
- tendency to shrinkage - free-standing polystyrene foam slabs are susceptible to slight shrinkage caused by gravity. The shrinkage amount is 1.5-3 mm over six months. At the end of this period, the natural compaction of the material stops;
- thermal expansion - with increasing temperature, the linear dimensions of the slab increase (the process is reversible). Numerical expansion indicators correspond to approximately 1 mm per 1 m of foam board when the temperature changes by 15-20 ° C;
- vapor absorption - polystyrene foam is less resistant to diffusion penetration of moisture than to the effects of liquid water, therefore in particularly humid rooms its surface is additionally covered with a layer of metal foil. In its absence, some water vapor can penetrate through the layer of material and condense when the temperature drops, which negatively affects the entire thermal insulation system.
Slab size
Foam boards are produced mainly in three sizes: 0.5 * 1, 1 * 1 and 2 * 1 m. It is immediately worth noting that this insulation is easy to cut, so no problems should arise during the installation process. So, it is better to choose the material that is most suitable for the area of the insulated surface. As a rule, for insulating balconies, loggias and apartments in apartment buildings, the choice is made on slabs measuring 0.5 * 1 m : they are most convenient to work with, they are more economical, and it will be easier to insulate all kinds of complex facade details with such material. But if you need to insulate a private house, the walls of which have a regular flat surface, then it makes sense to use slabs measuring 1 * 1 m. The largest material, slabs measuring 2 * 1 m are used least often for particularly large buildings.
Where is it used depending on the size?
This durable, moisture-resistant insulation is used for outdoor work. To insulate a wall with polystyrene foam, you first need to determine what density, size, and type of polystyrene foam you will need for the job.
The choice depends on the expected loads that this material will bear during operation.
When insulating a vertical wall, the loads will be minimal; sheets of any brand will do.
Even PSB-S 15 will give the same result as PSB-S 25 when it comes to wall insulation in areas with mild winters.
This is due to the fact that the principle of operation of the foam is based on gluing polystyrene balls, between which and inside there are multiple air chambers.
It is known that the less mass and more air, the better the thermal insulation effect.
It is inconvenient to work with low-density sheets, which are more fragile and break. PSB-S 25 has a higher density, making finishing easier.
Expanded polystyrene 25 is often used for external insulation of walls of non-residential premises. They are used to decorate balconies, loggias, garages, shopping centers, and various institutions.
For northern regions with cold winters, it is believed that a sheet thickness of 5 cm is enough to keep the room warm on the coldest nights.
Polystyrene foam grade 100 is used for thermal insulation of industrial freezers , as well as for insulation of houses in the harsh climate of the Far North.
A sheet size of 10 cm will ensure maximum thermal protection. When choosing a brand of expanded polystyrene, you can choose a sheet that has various parameters.
A non-standard sheet 500x500 is sometimes much more convenient to work with than a standard long one with dimensions of 2000x1000 mm.
For insulating the walls of a house, sheets measuring 1000x1000 and 1000x500 mm are suitable. They are convenient to work with and result in fewer joints that will have to be sealed hermetically.
To fill smaller areas, existing sheets are cut into suitable pieces. In all non-standard situations in finishing, it is better to use a sheet of large sizes to make it easier to cut configurations.
During the installation process, such sheets are adjusted to the required parameters by cutting polystyrene foam into pieces. This material is easy to cut.
Expanded polystyrene, having dimensions of 2000x1000 mm, is more difficult to install. When working alone, it is easier to lay two sheets of 1000x1000 each than one sheet measuring 2000x1000 mm.
How to determine the optimal foam thickness?
It is necessary to select the appropriate foam thickness for home insulation based on the following factors:
- type of wall material used;
- climatic features of a particular region.
In order to calculate the thickness of the foam, you must use the following formula:
R=P/K, where R is thermal resistance; P – insulation thickness; K – thermal conductivity coefficient.
Dependence on region of residence
The value of thermal resistance depends on the region of residence and is a tabular value that must be looked for in specialized reference books. It also depends on the type of structure and can differ significantly for the floor, ceiling and walls. For an average residential area, the thermal resistance value for walls is 3.5 m2 ∙K/W, for floors - 4.6 m2 ∙K/W, for ceilings - 6 m2 ∙K/W.
Sealing cracks and preparing sheathing
Installing polystyrene foam on the sheathing is the most labor-intensive process among the insulation options. Most often, sheathing is done in the case of finishing siding.
Sealing cracks
If you plan to install siding on the wall of a house made of beams, you must first seal the seams properly, clean the surface of dust and debris, and seal the cracks with sealants, polyurethane foam, or a mixture of sawdust and PVA.
If the wall is concrete, brick or foam blocks, then the cracks in such houses are cleaned of sand, treated with a primer, then sealed as follows :
- if there is a small gap . Using a prepared mixture of cement and sand with the addition of PVA, seal the gap with a spatula;
- if the gap is medium in size . Make holes for dowels at a distance of 20 cm. Using screws and washers, pull the metal mesh over the gap and seal it, pressing it into the mesh with plaster. Next apply the finishing layer;
- for a large crack . Seal the gap with polyurethane foam, cut off any irregularities and seal it with two layers of plaster.
Large cracks can be repaired using anchors:
- knock down the plaster, seal the cracks with polyurethane foam;
- install a channel in the opening and attach a reinforcing mesh to it;
- you can use staples made of reinforcing mesh;
- apply plaster;
- putty.
Sealing cracks
When the wall is prepared for laying insulation, you can install the sheathing.
Preparing the sheathing
The sheathing for siding can be made from metal profiles and wooden beams . In humid climates, it is advisable to install metal slats.
Before you begin installing the sheathing, you should determine the location of the siding:
- with horizontal siding . The beam or metal profile is installed perpendicularly;
- with vertical siding . Frame boards or metal profiles are installed in a horizontal position.
The pitch of the sheathing is determined by the width of the polystyrene foam sheet: in width it should fit tightly between the sheathing slats and not form gaps.
The order of work is determined in steps:
- treat the wall with special mastic;
- frame boards are secured around the entire perimeter of the walls using galvanized screws and plastic dowels;
- if holes form between the timber and the wall, these gaps are sealed with pieces of polystyrene foam by gluing them to the wall.
When the sheathing is installed, then proceed to the installation of polystyrene foam panels.
CAREFULLY!
If the sheathing is made of wood, the boards must be pre-treated with antiseptic agents.
Lathing does not require special skills, but it should be noted that the choice of materials should be made based on climate conditions.
Lathing for siding
Wooden sheathing
Calculation of the required insulation thickness
The thickness of the insulation layer depends on the following factors:
- thickness, design, thermal conductivity of the wall material;
- climatic zone of the building;
- the presence of additional layers in the structure (for example, a layer of internal plaster).
For simplicity, we will calculate the thickness of the insulation for the wall of a house made of foam concrete blocks 30 cm thick with internal plaster 20 mm thick, built in the Moscow region.
The normalized heat transfer resistance of walls for different regions of the Russian Federation is determined from the table:
The heat transfer resistance of the wall should be 3.16 m2 °C/W.
Using the table, we find data for the wall - 0.703 m2 °C/W and the plaster layer - 0.035 m2 °C/W.
We subtract individual data from the standard value:
3.16–0.703–0.035= 2.422 m2 °C/W
The thickness of polystyrene foam for wall insulation should provide such resistance to heat transfer.
We determine the thickness using the formula
- δ – insulation thickness, m;
- λ – thermal conductivity of the material, W/m2 °C.
Calculation example
Let's assume that for thermal insulation we purchased PPS20 F RG material. The density of the foam is 20 kg/m3, thermal conductivity under the worst operating conditions is 0.033 W/m2 °C.
δ = 2.422x0.033=0.079, or rounded 80 mm
Since slabs up to 50 mm thick can most often be found on sale, it makes sense to use two 50+30 mm or 2x40 mm slabs for insulation.
Wall pie when using insulation - polystyrene foam on the outside
A wall pie refers to layers of materials that are laid in a certain order, each of which performs its own functions to ensure a normal microclimate in the room.
When thermally insulating brick walls with polystyrene laid outside, the wall pie looks like this:
- interior plaster;
- outer wall;
- adhesive solution for gluing polystyrene foam;
- insulation (expanded polystyrene);
- adhesive solution for gluing the next layer;
- fiberglass mesh;
- adhesive composition;
- primer;
- finishing plaster.
NOTE!
When arranging a wall using polystyrene foam, it is necessary to lay the layers in strict sequence.
Internal and finishing plaster can be replaced with other finishing materials that are provided for in design solutions.
Wall cake "wet"
Types of polystyrene foam for home insulation
To understand what kind of polystyrene foam is needed for specific types of work, it is worth carefully studying the types of material. Classification of heat insulators for walls and floors of a house is carried out according to the following criteria:
- raw materials for manufacturing;
- density;
- sizes.
Depending on the raw materials used, there are such types of foam as polyurethane, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polyethylene. The first has high elasticity and is a foam rubber that is actively used in the furniture industry. In construction, polyurethane foam is made from such foam.
Polyethylene foam is produced in the form of sheets and is used for packaging fragile items. The usual construction foam is PVC. Expanded polystyrene of this type is suitable as insulation for a house inside and out.
The density of the foam is an important indicator. The area of use of the material depends on it (whether it can be used in the construction of walls, floors, foundations, etc.). Before buying foam insulation for your home, it is better to familiarize yourself with what it is, depending on the feature in question:
- PSB 50 is a high-density material. It is rarely found in construction due to the desire of customers to reduce financial costs. This material is suitable as insulation from the outside and from the inside. Such material can be laid as part of the floor of premises with constant occupancy of people, furniture and equipment.
- PSB 35 is suitable for insulating the walls of a house from the outside and inside. This type of insulation can also be laid in the attic floor pie, provided there is a strong concrete screed. The density of expanded polystyrene 35 is the most common.
- PSB 25. The density of the material allows it to be used as wall insulation on the room side. When laying, it is necessary to ensure a gap between the heat insulator and the finishing material. It is strongly not recommended to use it for floors and external insulation.
- PSB 15 is the minimum density used in construction. This type is best suited for thermal insulation of temporary structures (for example, cabins), containers and wagons.
What is extruded polystyrene. Differences between EPP and conventional polystyrene and foam
EPP, polystyrene foam and expanded polystyrene are classified as synthetic polymers. Their production technology ensures high quality characteristics. Polystyrene foam is made from a polymer composition. The resulting granules reach 3-5 mm in diameter. After this, they are pressed using an adhesive composition.
When considering what expanded polystyrene is, it should be taken into account that it is a material that has a uniform structure, including granular cells of no more than 0.1-0.2 mm. To obtain the material, polystyrene granules are mixed with special foaming agents (they can be carbon dioxide or a mixture of freons). After this, sheets are formed under pressure. After drying, they can be used in construction.
Polystyrene foam and polystyrene have much in common with extruded polystyrene foam, but the latter has a more complex production technology. When manufacturing the material, the granules are first melted to a homogeneous mass. After this, special additives and additional components are introduced into the composition, due to which the substance acquires a viscous-fluid state. Thanks to this, a material is obtained that has unbreakable intermolecular bonds.
There are no pores in the finished slabs, and the cells present in this material are filled with gas. Thanks to this structure, the vapor permeability of the material is extremely low. The density of extruded polystyrene foam is much greater than that of polystyrene foam and polystyrene, so it has better performance characteristics.
Advantages and disadvantages
EPS boards have a lot of advantages, but this material also has some disadvantages. The advantages include:
- low thermal conductivity;
- waterproof;
- ability to withstand deformation loads;
- increased rigidity;
- resistance to temperature changes;
- long period of use;
- light weight;
- environmental friendliness.
This insulation is quite rigid, so rodents rarely damage it. At the same time, mice can make moves in the slabs. The water resistance of EPP boards can be a big disadvantage in some cases. When using material to insulate the walls of a wooden house, mold may occur under the formed cake.
Vapor retention near walls can contribute to the appearance of dampness and musty odors. In addition, when heated to temperatures above 75°C, stoves can release substances that can negatively affect human health.
What are the advantages of high-density polystyrene foam?
When insulating a facade, it is advisable to combine the functionality of the coating with preserving the architectural features of the house. Thick cladding can significantly worsen the aesthetic perception of the facade. The problem is solved by using high-density foam.
The suitability of the dense material for finishing door and window slopes, insulating walls and ceilings operated in unfavorable conditions has been proven. Insulation of the PSB-S-35 brand has proven itself to be an excellent insulation material for foundation foundations and the installation of protective cladding for external foundation waterproofing.
- The increased cost of dense foam is offset by the use of the characteristics of the entire range. Depending on the complexity of the work, you can use less expensive insulation with a density of 25 or even 15 kg/m3.
- Choosing the optimal option will help to implement all project requirements at lower costs. In a facade thermal insulation system, medium-density insulation can be used; it is advisable to use a more advanced material for finishing the foundation.
Advantages and disadvantages of expanded polystyrene
The polystyrene foam material is a porous, air-containing raw material , used in most cases as a heat-insulating material.
In industry, the material can also be used as electrical insulating and packaging material.
The material has become widely used due to its quality indicators:
- low level of water absorption;
- low thermal conductivity;
- ease;
- biological stability;
- durability;
- compressive strength;
- not affected by temperatures;
- ease of installation;
- low price of material.
Comparison of insulation materials
Despite the impressive list of positive indicators, polystyrene foam has disadvantages that must be taken into account during installation:
- low sound insulation;
- instability to solvents and many chemicals;
- afraid of fire. When burned, it releases harmful toxic substances;
- poor resistance to ultraviolet radiation;
- easily susceptible to the influence of rodents and insects, which, by making holes in the material, provoke its destruction;
- low vapor permeability;
- fragility.
IMPORTANT!
Expanded polystyrene is sometimes compared in terms of characteristics and external indicators with another similar material - polystyrene foam.
However, the production technology of these materials is different : polystyrene foam is produced by extrusion, when the granules melt when combined into a single structure, polystyrene foam is produced by gluing granules with dry steam.
Specifications
Features of foam insulation
Material selection
The photo shows expanded polystyrene slabs, which are successfully used for insulation.
Polystyrene foam, which is used for construction purposes, is most often expanded polystyrene. There are other types of foam, but I'll talk about the white cellular material.
Construction foam plastic has a cellular structure and is white in color.
The material is called expanded polystyrene (PPS, EPS, PSB, PSB-S) and is made from molten polystyrene by adding foaming agents. The resulting foam is then sintered and polymerized, resulting in a relatively strong and lightweight substance.
Polystyrene foam exhibits unexpectedly high strength.
Depending on the formulation and production method, PPS may have different properties. For example, if the material was made by extrusion, then it will have increased strength and lower thermal conductivity. And if PPS is treated with fire retardants, it will not support combustion.
Extruded polystyrene foam or EPS.
Obviously, foam plastic can be different, and our goal is to choose from this variety the type that will most fully satisfy the tasks assigned to it. Our task is to insulate housing.
The insulation layer should be on the outside. This is a requirement of SNiP 3.03.01-87 (PZ 2000). The easiest way is to buy polystyrene foam for outdoor use without delving into the nuances and characteristics. But this approach can play a cruel joke, and an unscrupulous seller will sell you an unsuitable cheap product at the price of expensive façade polystyrene foam.
According to building regulations, the walls are insulated from the outside.
How to choose facade foam? It is important to consider several characteristics here:
- Density _ The density of foam plastic for facade insulation must be at least 25 kg/m³. But practice shows that it is better to overpay and take material with a density of 35 kg/m³;
- Flammability group . The legislation of the Russian Federation prohibits the use in construction of materials not treated with fire retardants. This is especially true for ventilated facades. I would advise using polystyrene foam of the G1-G2 group for “wet” facades and strictly G1 for ventilated structures;
- Thickness _ This indicator depends on the climatic characteristics of your region, as well as on the thickness and material of the external walls of the house.
What density is needed?
To insulate a house, foam plastic of different densities is used, depending on what goals are being pursued and what specifically needs to be insulated. So, to insulate the walls from the outside, it is better to opt for polystyrene foam with a density of 25 kg/m³ ; if you need to insulate the floor, then use denser slabs - 35 kg/m³ ; the same material is also used for roofing. But to insulate walls from the inside, it is better to choose polystyrene foam with a density of 15 kg/m³ .
It is better not to use foam plastic with a density of 15 kg/m³ for insulating external walls. Of course, this is not prohibited, but its durability, strength and reliability will be in question, which is easy to check yourself, because you just need to compress the material. As a result, you can get less durable insulation, and in terms of thermal insulation, such foam is inferior to its denser counterpart. But it is worth noting that such material can be used to insulate non-permanent structures: stalls, small shops, warehouses. Also, foam plastic with a density of 15 kg/m³ can be used to insulate some parts of the facade that are adjacent to the house, but do not require serious insulation: veranda, technical buildings, open balconies.
Foam plastic with a density of 35 kg/m³ is used extremely rarely for wall insulation: it copes with its tasks perfectly, but has a high price. In some cases, by the way, when thermal insulation properties are especially important, it is more profitable to use a thinner sheet of denser foam than medium-density foam of double thickness. But in most cases, it is the material with a density of 25 kg/m³ that is in highest demand.
How long will it last
Foam plastic is resistant to moisture and aggressive substances of organic origin, so the service life before replacement is, according to manufacturers, 700 freeze-defrost cycles.
This is significantly longer than the service life of the plaster layer, in which, in addition to the composition itself, the polymer mesh is destroyed. Based on the recommended operating parameters, you can expect the service life of external foam insulation to be from 20 to 40 years. It all depends on the quality of the building materials and the careful work carried out.
Insulating the walls of a house with polystyrene foam is one of the available ways to save heat in winter and coolness in summer. A simple installation process that anyone can master makes insulation with foamed polystyrene a popular method that allows significant savings on the purchase of materials and wages for builders.
Technical characteristics overview
There are different brands of polystyrene foam, each of which has its own set of properties and parameters. Based on this information, a choice should be made.
Thermal conductivity index
Closed cells represent the structure of the foam plastic, due to which this type of insulation acquires the ability to retain heat in the room. The thermal conductivity coefficient is: from 0.033 to 0.037 W/(m*K).
Due to the low thermal conductivity of the insulation, a high degree of energy saving is ensured.
Insulation is considered effective if the value of this parameter is no more than 0.05 W/(m*K). There are more effective materials, however, the average characteristics of polystyrene foam allow it to be successfully used to this day.
Soundproofing qualities, wind protection
The best material for protection against extraneous noise is a material that has the following technical characteristics: low thermal conductivity and at the same time the ability to allow air to pass through. Porous foam fits these criteria. This means that this type of insulation does an excellent job of protecting the object from noise.
Moreover, the greater the thickness of the sheet, the better the soundproofing qualities of the material. If you need to protect an object from the wind, then foam plastic will successfully solve this problem, since it consists of many closed cells.
Moisture absorption
The ability of this type of insulation to absorb water is quite low, which allows it to be considered non-hygroscopic. The moisture absorption rate with constant contact with water throughout the day corresponds to 1%.
The material is indifferent to moisture and practically does not absorb it.
This is slightly more than that of penoplex (0.4%), but also less than that of most of some other analogues, for example, mineral wool. Due to its low hygroscopicity, the service life of the foam is significantly extended, as the risk of mold or mildew formation is reduced.
Temperature
The insulation in question does not change its properties with a significant increase in temperature (up to 90 degrees). Low values also do not have a detrimental effect on this type of material, so it is used, in particular, for thermal insulation of external walls. But during installation using adhesive, it is recommended to observe the temperature regime: not lower than +5 and not more than +30 degrees.
Influence of external factors
These include: temperature changes, wind load, rain, snow and any mechanical source of pressure. The strength of the foam sheet is low under the influence of the last of the factors considered.
Due to its thermal insulation characteristics, polystyrene foam is widely used for insulating walls, roofs, ceilings, and balconies.
This is due to its low weight and large-cell structure. Moreover, the thickness of the material practically does not change the situation. If we compare it with penoplex, this option has high strength characteristics.
Degree of resistance to chemicals and microorganisms
When in contact with a number of substances, the properties of the foam do not change, these include: salt solutions, alkali, acid, gypsum, lime, bitumen, cement mortar, some types of paints and varnishes (silicon-based and water-soluble compositions). It is necessary to avoid contact of polystyrene-based insulation with the following substances: solvents, acetone, turpentine, gasoline, kerosene, fuel oil.
Fire safety
The insulation belongs to highly flammable materials (flammability categories G3 and G4), however, its burning time, provided that the ignition source is eliminated, does not exceed 3 seconds.
If you choose polystyrene foam insulation, be aware that it does not resist fire well.
It would be a misconception to consider such a material completely safe, but it is still often used, due to the release of less energy during combustion, as well as spontaneous attenuation.
Answers from experts
Engineer:
Both brick and foam are different.
Formally, the thermal conductivity of red brick is 10 times greater than that of highly porous foam. (0.56 and 0.05 W/m*deg - respectively)
That is, feel free to multiply the thickness of the foam by 11 and get the thickness of the brick wall.
Kirill Gribkov:
none
Bolt-gnawer:
Extruded polystyrene foam "Extraplex" with a thickness of 20 mm is equivalent in its heat and sound insulating properties to a brick wall with a thickness of 370 mm
Samson Altunyan:
Hello, the best!
You forgot to mention the conditions (parameters) of the assessment...
1) If you mean thermal conductivity? . The engineer answered you.
2) If we are talking about mechanical strength? . Polystyrene foam is NOT a replacement for brick. Especially in earthquake-prone regions.
3) Durability? The brick will last longer.
4) Resistance to environmental influences (temperature changes, humidity, etc.)? Foam plastic, in this case, is not even a building material...
5) Safety (physiological, chemical, environmental)?..Again, the comparison will be in favor of fired clay (brick)...
And generally speaking.. . That's not what they teach you... ;-( Foam plastic is NOT a good choice of material for construction or interior decoration. And in this ODIN is absolutely right...
Good luck to you!
Nurgaliev Marat:
5 cm of penoplex is half a meter of brick!!! And don't listen to the reindeer herders!
kukuzya:
I read the answers and I'm confused. What kind of tusk do you need to be in order to answer the question about the equivalence of brick and foam plastic and compare their load-bearing abilities... Of course, they compare thermal conductivity...
ST:
10cm of foam replaces 50cm of brick
Lulechka:
thickness is the same. in terms of strength, thermal insulation and other qualities - this is for builders!!!
Igor Chekalin:
Considering the beginning of winter, I suspect that we are talking about thermal conductivity?
Is the brick hollow or solid, silicate, ceramic, silica or even slag? The difference between different types is almost two times, and with silica it is 5 times.
For the worst case - solid sand-lime brick - the thickness ratio is approximately 20 times. That is, in terms of thermal conductivity, a 250mm wall (ordinary one-brick masonry) corresponds to only 13mm of polystyrene foam. For hollow bricks the ratio is ~10 times. That is, in our case - ~25mm foam. However, brickwork is almost airtight, and when insulated with foam plastic, there are gaps at the joints, loose edges, etc., so it’s not entirely correct to take such a formal and mathematical approach.
Well, more accurate numbers - google for “thermal conductivity table of building materials”
Alexander Kulikov:
The thickness of your knowledge of the Russian language...
Albert Belkov:
In fact: 1 cm of foam plastic in terms of thermal conductivity can be estimated as half a brick inside the masonry or backfill.
ST:
10cm of foam replaces 50cm of brick
Insulate from inside or outside?
All methods of insulating a building are divided into internal and external. Experts prefer the second method, because in this case, the insulated structures remain under the heat-protective layer. This prevents them from being exposed to negative environmental factors.
Often it is not possible to carry out work on the outside, for example, if the building is of historical value and changing the appearance of its facades is unacceptable. In this case, the method of thermal insulation from the inside is used.
Benefits of internal thermal protection
Compared to external insulation, internal insulation of a house can be done at any time of the year and in any weather conditions.
The facade of the building will not be changed, which is very important if the house was built relatively recently. And finishing the internal surfaces of the walls will cost much less. But despite the obvious advantages of this method, the disadvantages are quite noticeable.
Disadvantages of insulating walls from the inside
The obvious disadvantage of this type of wall decoration is the noticeable reduction in the internal area of the premises.
Such insulation leads to a shift of the “dew point” (the area where steam turns into water) deeper into the insulation layer closer to the inner surface of the walls. Thus, in the cold season, the insulation may become wet and lose its thermal insulation capabilities.
Penoplex Roofing properties and characteristics
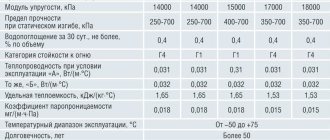
Penoplex insulation of the “Roofing” series is a renamed material “Penoplex 35”, which is recommended for use in insulating pitched and flat roofs of any design. The use of the “Roof” series makes the further operation of the roof as simplified as possible, since the reliability and long service life of the insulation minimize the possibility of repairing the roof surface. The popularity of this innovative insulating material is also due to the fact that greenhouses and summer gardens can be built on such a surface - such trends are now in fashion. Penoplex can withstand such high loads that it doesn’t care about soil loads of up to several tons. Characteristics of the foam insulation brand “Roof” are in the table below:
What to choose
If we compare these two insulation materials, then Technoplex is more technologically advanced and has better qualities, but the difference between it and Penoplex is so insignificant that it is impossible to say for sure which one should be chosen.
By choosing polystyrene foam insulation, regardless of whether it is Technoplex or Penoplex, you can get not only thermal insulation, but also sound and vapor barrier.
Please note: the service life of extruded polystyrene foam boards is more than 50 years, which is a long time. . However, it is worth remembering that polystyrene foam is still a chemical insulation, not a natural one.
Therefore, when burned, it releases very corrosive substances
However, it is worth remembering that polystyrene foam is still a chemical insulation, not a natural one. Therefore, when burned, it releases very caustic substances.
How many bricks does Penoplex replace?
Tightening requirements for heat and energy conservation of building structures requires at least a twofold increase in the thickness of walls and ceilings. For brick and concrete walls this figure is 90 and 110 mm, respectively. The problem is solved by using perfect facade and foundation thermal insulation. So how much brick does Penoplex replace, and why is this material considered optimal for insulating almost any building structure?
The material is difficult to counterfeit, so the risk of purchasing a low-quality counterfeit is reduced to zero.
What properties of Penoplex determine the high level of consumer demand?
When choosing a material, its unique low thermal conductivity, light weight, simple installation and long service life are taken into account.
- New generation extruded polystyrene foam thermal insulation differs from polystyrene foam in its perfectly homogeneous structure, resistance to compression loads and other adverse external influences.
- For all its advantages, mineral wool has strict weight restrictions. Therefore, to insulate devices that do not have a sufficient safety margin, lightweight materials based on polystyrene foam are used.
The disadvantages of Penoplex Facade, which you can buy from our company at any time of the year - zero vapor permeability and fairly low heat resistance, are partially or fully compensated by the use of façade systems with slot ventilation and the installation of heat-resistant protective and decorative coatings.
As for the insulation of underground structures, including foundation ones, in this case moisture- and frost-resistant polystyrene foam does not have a worthy alternative.
The strength of the foundation lining is sufficient to protect the waterproofing from damage by seasonal movements of heaving soils. The range of polystyrene foam insulation includes panels of different sizes: from 30 to 100 mm thick. In most central regions, panels with a thickness of 50-60 mm are in high demand. You can buy Penoplex 50 mm in Moscow with significant discounts at promotional and seasonal sales of building materials.
How much brickwork does Penoplex take?
For those who plan to order Penoplex, the ratio of thermal insulation material to brick plays an important role. We will tell you about the most popular thickness of thermal insulation boards and their correspondence to the thickness of the brickwork.
- Penoplex 20 mm replaces a brick wall with a thickness of 370 mm - this is almost 40 cm, that is, 2 times the thickness of the insulation itself. If you wanted to purchase reliable thermal insulation, but you were only stopped by ignorance of how much brick a 2 cm thickness of Penoplex replaces, today you learned an additional plus in the piggy bank of this material!
- How much does Penoplex 30 mm replace brickwork? Based on the data on the correspondence of 2 cm of insulation to a brick wall, it turns out that Penoplex 30 mm replaces as much as 555 mm of brickwork in terms of energy efficiency. Here is your answer to how many bricks 30 mm thick Penoplex replaces!
- What brick thickness does Penoplex 50 mm replace? A pleasant surprise awaits you! The technical characteristics of Penoplex 50 mm in comparison with brick will conquer not only the homeowner, but also the experienced developer. Brickwork 925 mm thick can be compared with 50 mm Penoplex - that’s how many bricks this insulation replaces!
Now that you have found out what wall thickness Penoplex replaces, there is no reason to put off the purchase of thermal insulation material - call us and order insulation at a favorable price today!
Expanded polystyrene insulation in country and cottage-type houses
Many developers use the material for external insulation of facades and ceiling structures of country houses, which are being converted for year-round living. The main range of applications for polystyrene foam insulation is finishing foundations, blind areas, and insulating cement screeds under floor tiles.
Unlike mineral wool, expanded polystyrene does not require film or mastic waterproofing, so it can be mounted directly on a flat ground surface.
The more than moderate cost of polystyrene foam materials is complemented by the possibility of do-it-yourself installation, which allows you to reduce the cost of thermal insulation work by 35-40%.
Buy high-quality Penoplex insulation from our company right now at a competitive price!
Which is better - polystyrene foam or polystyrene foam?
Foam plastic is foamed polystyrene. The name expanded polystyrene is commonly understood as extruded polystyrene, produced under the brands PENOPLEX, TECHNOPLEX, URSA.
It has a higher density, the material is durable, and has grooves at the edges for a tight fit of the sheets. There is no crumbling when cutting, which reduces the amount of debris.
The price of extruded polystyrene is significantly higher than polystyrene foam, but the main characteristic of the materials - thermal conductivity - is comparable in terms of performance to PSB-25.
Among the advantages is that the material is better resistant to moisture, which is important when insulating basements and ground floors. Installing penoplex on walls has no benefits compared to polystyrene foam.