The high thermal conductivity of windows is the main reason for a noticeable increase in the cost of heating rooms and problems with maintaining a comfortable temperature in severe frosts. This characteristic depends on several factors. The energy efficiency of windows is influenced to varying degrees by double-glazed windows, profiles, fittings and even the quality of installation. To reduce energy losses, the Russian authorities have introduced special standards. Since 2015, the minimum heat transfer resistance of windows, according to a special government decree, has increased by 50%. The purpose of this decision is to stimulate builders and the population to more actively implement energy-efficient technologies. More stringent requirements for profile structures have entailed an increase in costs for the manufacture of heat-saving models. However, in the future, owners of energy-efficient windows have the opportunity to save big on space heating and quickly return the money spent. In order for the purchase to be as profitable as possible, it is necessary to correctly determine the reduced heat transfer resistance of windows at the order stage. This article will tell you what you need to pay attention to when choosing components and how to correctly calculate possible heat loss.
What determines heat loss in a house?
A decrease in indoor temperature is caused by various reasons. Heat leaks, to a greater or lesser extent, occur through walls, ceilings, and floors. This is a continuous and inevitable process. However, most heat is lost through window openings. If you put your hand on a regular thin glass pane on a cold day, you can feel the cold. The lower the glass temperature, the higher the thermal conductivity of plastic windows and the more intense the process of energy exchange between the street and the interior. On average, up to 44% of generated heat is lost through openings.
That is why the types of components for assembling window and door units are of great importance. The heat transfer resistance class of windows, which directly affects energy losses, depends on them. Maintaining the temperature in rooms in the range of 20-24°C will be much easier and cheaper if you choose the right profiles, fittings and double-glazed windows. Construction regulations make the task easier. Since 2003, in the process of drawing up projects and during the construction of residential buildings, it is required to adhere to the provisions of SNiP 23-02-2003 “Thermal protection of buildings”. These provisions are supplemented by Law No. 261-FZ, which tightened the requirements for energy saving of blocks from profile systems.
Climatic conditions
The choice of profiles and double-glazed windows is also directly influenced by weather conditions.
The heat transfer resistance of PVC windows, which in the south allows you to maintain a room temperature of 20-24°C, is not suitable for the northern regions. For operation in these climate zones, other designs will be required. If you install “southern windows” in the central or western regions, at a frost of -20-25 °C, the temperature in the interior can drop to 15-16 °C. This means that these zones require models with improved thermal characteristics. The average annual wind speed in the regions is also important. This factor is not always taken into account, which predictably leads to problems. Indeed, in areas with the same average temperature in winter, heat loss will be higher where the wind speed is higher. Air flows from the street quickly reduce the temperature of double-glazed windows. As a result, heat loss in the premises increases.
According to SP 50.13330.2012, each region of Russia has its own thermal conductivity coefficient for windows. These requirements are based on the results of tests carried out in real and laboratory conditions. Moreover, the coefficients in different areas of Russian regions may differ. This explains the large area of the regions and republics of the Russian Federation. The table shows the average values of the heat transfer coefficients of windows, which are recommended to be used when choosing profile systems and models of double-glazed windows.
| Region of the Russian Federation | Allowable window energy efficiency (m²×°C/W) |
| Altai | 0,64 |
| Adygea | 0,35 |
| Astrakhan region | 0,48 |
| Bashkortostan | 0,6 |
| Buryatia | 0,67 |
| Dagestan | 0,35 |
| Kaliningrad region | 0,42 |
| Komi | 0,69 |
| Krasnodar region | 0,35 |
| Leningrad region | 0,54 |
| Moscow region | 0,52 |
| Magadan Region | 0,77 |
| Omsk region | 0,64 |
| Oryol Region | 0,5 |
| Rostov region | 0,42 |
| Tatarstan | 0,58 |
| Sakha (Yakutia) | 0,8 |
The table selectively includes regions with mild, moderate and severe winters. This information will help you perform calculations correctly and minimize possible heat loss.
General definition of the term
The concept of heat transfer resistance (HTR) is formulated in GOST R 54851-2011. Windows, along with walls, doors, roofing, etc., are structural elements that enclose the internal space to create a comfortable human living environment. STP fencing is the R coefficient, the value of which demonstrates the thermal insulation properties of the structure. The greater the absolute value of R, the less heat loss from the room there will be.
The unit of measurement R in the SI system is [m2* 0С/W]. The value of R is equal to the temperature difference on the outer (Tn) and inner (Tvn) surfaces of the fence for a heat flow Q of 1 W power passing through 1 m2 of thermal protection.
The formula for calculating R is as follows:
R = (Tvn - Tn) / Q
The higher the R value, the less heat loss will be. This formula resembles the expression for Ohm's law, so R is sometimes called thermal resistance, by analogy with the electrical term.
What is the thermal conductivity of a window and what does it depend on?
To simplify it as much as possible, the thermal conductivity of PVC windows is the ability of a profile structure with closed sashes to retain a certain amount of energy indoors. However, such a definition is not enough to understand the essence of the process. After all, through the same double-glazed windows, heat leakage occurs in different ways:
- 30% of energy losses occur due to convection inside double-glazed windows and air chambers and heat transfer through solid components of window or door units;
- 70% of the heat goes outside the room along with infrared waves.
This simple analysis allows you to understand how you can significantly reduce energy leakage.
Since infrared waves pass through glass, it is these areas of window and door units that require double attention. After all, double-glazed windows occupy the largest area in window openings and the maximum amount of heat escapes through them. Statistics show that the energy efficiency of profile structures can be significantly increased if it is possible to block infrared waves. At the same time, PVC systems cannot be ignored, since the coefficient of resistance to heat transfer of double-glazed windows to a certain extent depends on their characteristics. For example, the cross-sectional shape of the profiles affects the planting depth and the maximum thickness of the double-glazed windows. The total energy efficiency of windows depends on the dimensions mentioned. In addition, good profiles slow down the process of heat exchange around the perimeter of light openings and the spread of cold from cooled walls. These processes are interconnected and cause a decrease in temperature in the interior.
The last factor that influences the level of thermal conductivity of windows is tightness. However, this parameter is quite difficult to calculate mathematically. Therefore, it is enough for the window customer to know that to ensure tightness, high-quality fittings and profile reinforcement are required. You also need to pay attention to the quality of the installation. If the installation is not carried out according to the rules, the structure may depressurize around the perimeter of the frames. Read more about installation requirements on OknaTrade.
How to calculate the total thermal conductivity of a window
Determining the exact heat transfer resistance of windows is quite simple. To do this, you will need to use thermal information about profiles and double-glazed windows. Moreover, you cannot focus on only one of the coefficients. To obtain reliable data, it is necessary to take into account the thermal conductivity of sashes, frames and double-glazed windows. When making calculations you will need to use:
- R sp – glass unit coefficient.
- R p – window frame coefficient.
- β is the ratio of the area of the translucent part of the structure to the total area of the window.
The thermal conductivity of the window, taking into account these data, is calculated by the formula:
R= R sp×R p/((1- β)×Rsp + β×R p)
The coefficients differ for different profiles and double-glazed windows. There is no average. Indeed, in this case, all windows would have the same ability to retain heat. The exact values of the coefficients are given in this article in the sections on PVC systems and double-glazed windows. To calculate the binding area, you need to multiply the length of the constituent elements of the sashes and frames by the width of the profiles, and then sum the resulting values. The glazing area is equal to the area of the light openings.
Warm designs, methods, materials
In order to increase the heat transfer resistance of the entire structure of a private house, as a rule, building materials with a low thermal conductivity coefficient are used. Thanks to the introduction of new technologies in construction, such materials are becoming more and more available. Among them are the most popular:
- Tree.
- Sandwich panels.
- Ceramic block.
- Expanded clay concrete block.
- Aerated concrete block.
- Foam block.
- Polystyrene concrete block, etc.
Wood is a very warm, environmentally friendly material. Therefore, when building a private house, many people choose it. It can be either a log house, a rounded log or a rectangular beam. The material used is mainly pine, spruce or cedar. However, this is a rather capricious material and requires additional measures of protection from weather conditions and insects.
Sandwich panels are a fairly new product on the domestic building materials market. Nevertheless, its popularity in private construction has increased greatly recently. After all, its main advantages are its relatively low cost and good resistance to heat transfer. This is achieved due to its structure. On the outside there is rigid sheet material (OSB boards, plywood, metal profile), and on the inside there is foam insulation or mineral wool.
Heat transfer of PVC profile
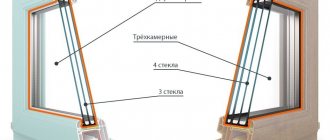
Requirements for energy efficiency of plastic systems are regulated by provisions from GOST 30673-99. Since frames and sashes occupy approximately 30% of the opening area, the heat transfer resistance coefficient of a window depends by a third on the properties of PVC profiles. The characteristics of plastic systems are influenced by the number of chambers, the thickness of the external and internal walls, the presence of a reinforcing liner and the installation depth. You also need to take into account the location of the internal cameras relative to each other.
Comparative table of characteristics of popular PVC profiles
About 10 years ago, buyers most often chose 3-camera systems. Today, window and door blocks assembled from such profiles are used mainly for use in the southern regions and glazing of unheated premises. This is due to the fact that significantly more 5-chamber profiles of different brands began to be sold on the Russian market and consumers give preference to energy-efficient technologies. The best way to demonstrate how different systems affect the overall heat transfer resistance of windows is a comparison table of several brands of 3- and 5-chamber profiles.
| Profile system brand | Heat transfer resistance of 3-chamber profiles | Heat transfer resistance of 5-chamber profiles | ||
| Installation depth 58 mm | Installation depth 70 mm | Installation depth 70 mm | Installation depth 80 mm | |
| REHAU | 0,63 | — | 0,83 | — |
| VEKA | 0,64 | — | 0,77 | — |
| KVE | 0,7 | 0,8 | 0,83 | 0,93 |
| NOVOTEX | 0,64 | 0,8 | 0,86 | — |
| Salamander | — | — | 0,91 | 1,25 |
| KRAUSS | 0,62 | 0,73 | 0,75 | — |
| Gealan | 0,63 | — | 0,82 | 0,85 |
| Aluplast | 0,62 | 0,71 | 0,83 | — |
When studying the factors that influence the thermal conductivity coefficient of PVC windows, the table shows that this value even depends on the brand. If you compare systems with the same parameters, profiles from reputable brands will be more energy efficient. This feature is explained by the composition of the PVC mixture, the favorable location of the chambers and the thickness of the walls, as well as the number of additional internal jumpers. At the same time, it is not recommended to prematurely label all 3-chamber profiles as cold systems. From the same table it can be seen that some designs are practically not inferior in terms of heat saving to 5-chamber windows.
Some manufacturers use a trick and indicate the thermal conductivity coefficient of plastic windows, which are assembled from profiles without reinforcement. This is incorrect information, since steel liners reduce the energy efficiency of sashes and frames by approximately 10%. After all, metal is an excellent heat conductor. Since windows without reinforcement are subject to temperature and wind deformations, the option of ordering such models cannot be considered. Therefore, you always need to study only the characteristics of profiles with internal metal liners.
Building blocks
The high heat transfer resistance of all building blocks is achieved due to the presence of air chambers or a foam structure in their structure. For example, some ceramic and other types of blocks have special holes that run parallel to the wall when laying. In this way, closed chambers with air are created, which is a fairly effective measure of preventing heat transfer.
In other building blocks, the high heat transfer resistance lies in the porous structure. This can be achieved by various methods. In foam concrete aerated concrete blocks, the porous structure is formed due to a chemical reaction. Another method is to add porous material to the cement mixture. It is used in the production of polystyrene concrete and expanded clay concrete blocks.
Heat transfer of double glazing
Since light openings occupy up to 70% of the total area of the profile structure, they have the greatest impact on energy efficiency.
The heat transfer resistance of double-glazed windows can be considered a key parameter when searching for suitable windows. This indicator helps to assess possible heat loss. If the sashes and frames are assembled from 6-chamber energy-efficient profiles of the new generation, and basic single-chamber double-glazed windows with a thickness of 16-20 mm are installed in the light openings, the windows will let in cold and will be unsuitable for use in the central, western and northern regions. To reduce the heat transfer coefficient of a double-glazed window, it is impossible to endlessly increase its thickness. The number of cameras is also limited. Therefore, to reduce heat loss, technologies have been developed that have significantly improved the energy efficiency of double-glazed windows:
- Injecting inert gas into the internal chambers - this method helps reduce convection.
- Applying a special metallized layer to the inside of one of the glasses, which transmits light and reflects infrared windows.
- Equipping double-glazed windows with invisible heating elements that act as a thermal curtain.
Currently, manufacturers most actively use option 2. Selective energy-saving double-glazed windows literally retain heat indoors and reduce heating costs. A single-chamber model of this class can replace a heavy 2-chamber double-glazed window with a thickness of 40 mm. You can learn more about them from the feature article on OknaTrade. The combined use of an inert gas and a selective layer is also effective.
Heat transfer resistance coefficient of double-glazed windows
The higher the given heat transfer resistance of a double-glazed window, the warmer the window.
This physical quantity is calculated using the formula: Ro=1/k, where k is the thermal conductivity coefficient used in countries with DIN standards.
In Russia, they chose the inverse value because it is intuitively understandable to our citizens. Indeed, as Ro increases, the energy efficiency of the window increases - the value of the coefficient determines how much heat will pass through 1 m² of double-glazed window at a certain temperature difference. When manufacturing products, manufacturers must focus on the heat transfer resistance of the glass unit; GOST allows a range of Ro from 0.3 to 0.8 m²×°C/W.
Calculation of thermal conductivity coefficient
For consumers, the most simplified information is used, since the buyer is interested in the final result. In reality, calculating the thermal conductivity coefficient is a rather complex process. After all, a double-glazed window consists of several components:
- spacer frame;
- air or inert gas;
- selective layer;
- glass.
All of the listed materials have different thermal conductivities, and this factor is taken into account in laboratory tests and calculations.
However, to understand the processes taking place, in most cases a simplified formula is used: Ro=S×T/W, where
T – temperature difference in the room and outside; S – glass unit area; W is the amount of thermal energy passing through the light opening.
For customers, this formula comprehensively characterizes the heat-protective properties of a double-glazed window. In addition, it is quite enough to independently determine heating costs in winter. Using this formula, you can calculate how much energy will leave the interior through the light opening.
Heat transfer resistance of double-glazed window (table)
When ordering windows, the buyer does not need to carry out calculations independently or seek help from managers. Manufacturers have provided all the necessary thermal characteristics of the double-glazed windows models in demand in our country. In the vast majority of cases, this information corresponds to real data and can be safely used. When studying the heat transfer resistance of double-glazed windows, the table helps to quickly find a suitable model. After all, it organizes information as simply and clearly as possible.
| Type of glass unit | Model thickness (mm) / Number of chambers | Inner chamber width (mm) | Heat transfer resistance coefficient Ro (m²×°C/W) | Sound. (dB) |
| 4 – 8 – 4 | 16 / 1 | 8 | 0,32 | 30 |
| 4 – 12 – 4 | 20 / 1 | 12 | 0,34 | 30 |
| 4 – 20 – 4 | 28 / 1 | 20 | 0,35 | 32 |
| 4 – 10 – 4 – 10 – 4 | 32 / 2 | 10/10 | 0,46 | 36 |
| 4 – 14 – 4 – 14 — 4 | 40 / 2 | 14/14 | 0,5 | 37 |
| 4 – 18 – 4 – 18 – 4 | 48 / 2 | 18/18 | 0,53 | 38 |
| 4 – 12 – 4k | 20 / 1 | 12 | 0,5 | 32 |
| 4 – 12a – 4k | 20 / 1 | 12 | 0,55 | 32 |
| 4k – 12 – 4k | 20 / 1 | 12 | 0,53 | 32 |
| 4k – 12a – 4k | 20 / 1 | 12 | 0,59 | 32 |
| 4 – 10 – 4 – 10 – 4k | 32 / 2 | 10/10 | 0,64 | 36 |
| 4 – 10a – 4 – 10a – 4k | 32 / 2 | 10/10 | 0,77 | 38 |
| 4 – 10 – 4k – 10 – 4k | 32 / 2 | 10/10 | 0,8 | 36 |
| 4 – 10a – 4k – 10a – 4k | 32 / 2 | 10/10 | 0,95 | 38 |
The formula for a double-glazed window must be deciphered in the following sequence: glass - inner chamber - glass. The Latin letter “a” means that the inert gas argon is pumped into the chamber, and “k” means that a metallized coating with an energy-saving effect is applied to the glass. The table shows that the warmest are double-glazed windows with a selective layer and gas in 2 chambers. For comparison, models with the same dimensions and parameters were specifically taken to demonstrate the advantages of using low-emissivity coating and argon.
In the selection process, it is not recommended to focus only on the heat transfer coefficient of double-glazed windows - the table contains information about sound insulation, which also needs to be taken into account. This is especially true when ordering plastic windows for use in noisy areas.
If, when ordering, you ignore the reduced heat transfer resistance of a window and focus only on the cost, you can lose a lot of money. Moreover, the expected losses, taking into account the constant increase in the cost of energy resources during the operation of the windows, can be many times greater than the amount saved during the purchase. To prevent this from happening, for assembling structures it is recommended to give preference to:
- 5 or 6-chamber profiles of class “A” with a system depth of 70 mm (an increase in the number of internal chambers and the number of sealing contours is welcome);
- selective double-glazed windows with a thickness of 32 mm or more.
The overpayment for such models is usually fully refunded within 2-3 years, and throughout the subsequent period of operation, energy-efficient windows will bring profit in the form of reduced heating costs. However, such models are needed not only for the sake of economy. They will allow you to maintain a comfortable temperature even during periods of extremely low temperatures and strong winds.
When choosing a double-glazed window, it is important to consider the area of light openings. Indeed, with an increase in this parameter, heat loss increases. This means that in this case, the most efficient double-glazed windows will be required. For small windows, on the contrary, the area of the profile structure is comparable to the area of the glazing, so you can choose a model with less energy efficiency.
The nuances of using insulation
If the heat transfer resistance of the wall is insufficient for a given region, then insulation can be used as an additional measure. Insulation of walls is usually done from the outside, but if necessary, it can also be used on the inside of load-bearing walls.
Today there are many different insulation materials, among which the most popular are:
- Mineral wool.
- Polyurethane foam.
- Expanded polystyrene.
- Extruded polystyrene foam.
- Foam glass, etc.
All of them have a very low thermal conductivity coefficient, so for insulating most walls, a thickness of 5-10 mm is usually sufficient. But at the same time, one should take into account such a factor as the vapor permeability of the insulation and wall material. According to the rules, this indicator should increase outward. Therefore, insulation of walls made of aerated concrete or foam concrete is possible only with the help of mineral wool. Other insulation materials can be used for such walls if a special ventilation gap is made between the wall and the insulation.
Plastic windows - which ones are warmer?
The thermal insulation of a plastic profile is determined by the width of the profile and the number of air chambers inside - the more of them, the warmer the profile. For warm windows in an apartment, you need to choose a profile with a width of 70mm with a number of cameras of at least 5. For windows in a private house, it is better to give preference to a profile with a width of 76-80 mm with 6 air chambers.
Photo: profile systems of various widths, © rehau
Wooden windows - which ones are warmer?
Thermal insulation of wooden windows depends on the width of the profile and the density of the wood. The denser the wood, the less porosity it has and the lower its thermal insulation. For example, the porosity of pine is 53-70%, and that of oak is 32-61% - windows made of pine beams will be slightly warmer than oak.
Photo: modern warm wooden windows are made from laminated veneer lumber, © depositphotos Wood is traditionally considered the most suitable material for warm windows. But this statement is already outdated. As laboratory test data show, high-quality plastic and warm aluminum windows are not inferior to wooden ones made from eurobeams in terms of heat transfer resistance, and sometimes even surpass them (see table below). The choice of material from the point of view of heat conservation is more of a personal preference of the property owner.
Normative references:
- SNiP 2.01.07-85 Loads and impacts.
- .
- SNiP 23-03-03 Noise protection.
- SNiP 3.04.01-87 Insulating and finishing coatings
- GOST 30971-2012 Assembly seams of junctions of window blocks to wall openings.
- GOST 7076-99 Construction materials and products. Method for determining thermal conductivity and thermal resistance under stationary thermal conditions
- GOST 7502-98 Metal measuring tapes. Specifications
- GOST 10174-90 Polyurethane foam sealing gaskets for windows and doors. Specifications
- GOST 17177-94 Heat-insulating construction materials and products. Test methods
- GOST 25898-83 Construction materials and products. Methods for determining vapor permeation resistance
- GOST 26433.0-85 System for ensuring the accuracy of geometric parameters in construction. Rules for performing measurements. General provisions
- GOST 26433.1-89 System for ensuring the accuracy of geometric parameters in construction. Rules for performing measurements. Factory-made elements
- GOST 26433.2-94 System for ensuring the accuracy of geometric parameters in construction.
- Rules for performing measurements of parameters of buildings and structures
- GOST 26589-94 Roofing and waterproofing materials. Test methods
- GOST 26602.2-99 Window and door blocks. Methods for determining air and water permeability
- GOST 26602.3-99 Window and door blocks. Method for determining sound insulation.
Breathability
Enormous air flows pass through the wall of an ordinary house. To see this clearly, hold a lit candle to an electrical outlet on an outside wall in windy weather. The flame will flicker and may even go out
The filter media for most climate control heating units is stranded fiberglass, the same type used for insulation. Fiberglass is used in air filters because it creates less resistance to air flow and is cheaper. In other words, so that the air flow passes through it without difficulty. This is an excellent property for a climate control filter, but can such a material effectively insulate a structure? Enormous air flows pass through the wall of an ordinary house. To see this clearly, hold a lit candle to an electrical outlet on an outside wall in windy weather. The flame will flicker and may even go out.
The average house with all doors and windows closed allows in the same amount of air as if the doors were wide open. Even if we carry out the installation of fiber thermal insulation perfectly and reduce the infiltration of air from one side of the wall to the other to almost nothing, we still will not be able to stop the movement of air in the ceiling and walls in the vertical direction through the thermal insulation itself.
Advantages of s/p with energy-saving I-glass
Firstly , I-glass reflects long-wave thermal rays towards their emitter (that is, in winter towards the apartment where heating devices are working, and in summer towards the street where there are sun-heated stones, asphalt, etc.), which is significant reduces heating costs in winter (up to 60%) and air conditioning costs in summer (up to 30%). In other words, the coating leaves heat where there is more of it (thermos effect). The thermal insulation capacity of s/p with I-glass is significantly higher compared to conventional two-chamber s/p.
Secondly , s/p with I-glass has a significant gain in terms of indoor comfort. For example, at an outside temperature of -26 °C and a room temperature of +25 °C, for a regular single-chamber bathroom the glass temperature on the inner surface of the room will be +5 °C, for a regular 2-chamber bathroom +11 °C , and for a single-chamber s/p with I-glass +14° C. And if you install a 2-chamber s/p with a maximum thickness of 42 mm (possible when using a PVC profile with an installation depth of 70 mm) with I-glass, then the temperature at the window will be more than +17 °C! This means that the room heating mode can be changed, because... the heating system does not need to compensate for the significant “cold” zone near the window.
The area near a window made of conventional glazing leads to the so-called “draft” effect associated with noticeable convection of cold air near the window (the same “draft” can easily be felt by the hand in which you are holding a popsicle - even being in an apartment where there is no wind, the hand feels “ cold breeze"). Consequently, the use of s/p with I-glass increases the usable living area of the room due to the comfortable window space (in a small apartment you can move a table or bed closer to the window), and also prevents moisture from settling on the glass, thereby eliminating the appearance of condensation.
Thirdly , the weight of such a single-chamber s/p is 10 kg per 1 sq.m. s/p is lower compared to 2-chamber, which allows you to design large areas of window and door sashes, significantly reduces the load on the sash fittings of your window and increases its service life.
Fourthly , this I-glass prevents wallpaper, upholstery and interior items from fading due to the lack of solar overheating in the summer without the use of curtains or tinted glass. At the same time, the transparency of I-glass is comparable to the transparency of ordinary glass. A similar set of properties is not available to any other type of glazing today.
To make sure that you are the happy owner of windows with such glass, you can hold the flame of a lighter to the window at dusk and see among the reflections one reflection with a tint of a different color, as in the picture.
To summarize all of the above, let’s say that by installing plastic windows and doors produced by our company Eurostyle with energy-saving double-glazed windows in your home, you save money and create comfortable indoor conditions, which means a good mood and health for you and your loved ones!
.