Comfort in any room is largely determined by its lighting. The best source is sunlight, which can be obtained from windows. With proper glazing, the room will not only be light, but also warm and cozy.
According to SNiP, in order to ensure a minimum amount of light penetrating into the room, the glazing area is about 10–12.5% of the total. In addition to the linear dimensions of the window, their ratio is also important. For better visual perception, it is recommended to bring the width to height ratio as close as possible to the parameters of a harmonic rectangle, say, 80 to 130.
Why is it important to know the window area?
Windows are very specific designs.
On the one hand, they provide sufficient illumination of the room, on the other hand, they are the largest “black hole” through which heat escapes to the street. The size of windows also plays an important role in the subjective perception of comfort: too small or poorly located ones make the room uncomfortable and dark, too large ones can make a person feel insecure.
Both extremes are usually the result of errors in construction calculations or lack thereof.
According to construction rules, the minimum amount of light penetrates into a room in which the total area of all windows is 10–12.5% of the total area of the room.
If we take into account physiological indicators, then optimal lighting is achieved with a window width that is equal to 55% of the width of the room.
In this case, not only the width and height of the window is important, but their ratio. The closer the proportion is to a harmonious rectangle, the better it is perceived visually and the more convenient it is to use.
A window that is close to ideal is a rectangle with the correct proportions (for example: 80 cm wide and 130 cm high).
In order to make it convenient to look outside, the upper edge of the wall under the window should be no higher than 90–100 cm. In turn, the upper edge of a convenient window is at a height of about 200–220 cm from the floor and leaves enough space for attaching curtains, blinds or roller box.
According to SP 402.1325800.2018:
5.4 For space heating, heating gas boilers with a closed or open combustion chamber, including single-circuit and double-circuit, or heating devices designed to operate on gas fuel, boilers with a coaxial chimney, gas convectors and other gas-using equipment that have permits for use should be provided , issued in the manner established by the current legislation of the Russian Federation. For hot water supply, flow-through, capacitive gas heaters or double-circuit boilers should be used. Gas-using equipment must be factory-made and equipped with automatic regulation and safety. Gas boilers must comply with GOST R 51733, GOST R 54826, GOST R 54438, GOST R 54439, gas tank water heaters - GOST R 54821, gas convectors - GOST R 51377.
Installation of gas convectors should be carried out in accordance with Appendix E.
5.5 When installing a gas stove and instantaneous water heater or heating boiler with a closed combustion chamber in the kitchen, the volume of the kitchen should be taken in accordance with 5.1.
When installing a gas stove and a cylinder water heater, a gas stove and a heating boiler with an open combustion chamber (single-circuit or double-circuit) in the kitchen, the volume of the kitchen must be 6 m larger than the volume provided for in 5.1.
When installing gas equipment intended for heating and hot water supply in a separate room (heat generator room), the area of this room (heat generator room) must be determined from the conditions of ease of installation and maintenance of the equipment, but be at least 15 m3 with a height of at least 2.5 m (for heating boiler with an open combustion chamber).
5.6 Gas-using equipment powered by natural gas may be placed in the basement and basement floors of single-apartment and semi-detached residential buildings. It is not permitted to install technical devices and gas-using equipment in bathrooms and sanitary facilities.
Requirements for emergency exits from premises where gas-using equipment is installed must comply with current fire safety standards.
5.7 It is not allowed to provide for the installation of more than two heating boilers or two storage tank water heaters in one room.
5.8 Gas generators should be installed in accordance with the requirements of the manufacturers’ instructions: in a heated ventilated room, in an unheated ventilated room, and also outdoors under a canopy.
At existing facilities, gas generators should be installed after performing a hydraulic calculation of existing gas networks and checking the capacity of the metering station.
5.9 Ventilation of rooms intended for installation of gas-using equipment must be natural. The exhaust is provided at the rate of three air exchanges per hour, and the influx is based on the volume of the exhaust and an additional amount of air for gas combustion. The dimensions of exhaust and supply devices are determined by calculation.
Requirements for ventilation and smoke ducts must be provided in accordance with Appendix G SP 402.1325800.2018.
In kitchen-dining rooms, the hood is provided at the rate of one air exchange per hour and an additional air volume of 100 m3/h for operating a gas stove (SP 60.13330).
5.10 As easily removable enclosing structures, it is necessary to use glazing of window openings with a glass area at the rate of 0.03 m2 per 1 m3 of room volume or use window structures with double-glazed windows in accordance with GOST R 56288. Reinforced glass, other double-glazed windows, triplex, stalinite and polycarbonate for easily removable structures do not apply.
5.11 The door from the room where gas-using equipment is installed must open outward.
5.12 The distance from the building structures of the room to the heating gas-using equipment should be taken in accordance with the requirements of the manufacturer’s instructions. If there are no requirements in the instructions, gas-using equipment should be installed based on ease of installation, operation and repair. In this case, the following requirements must be met:
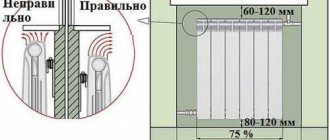
- wall-mounted gas-using equipment for heating and hot water supply must be installed on walls made of fireproof materials at a distance of at least 2 cm from the wall, including the side wall;
- walls made of fire-resistant and non-combustible materials must be insulated with fireproof materials or factory-made screens made of tempered laminated glass in accordance with GOST 30698, which do not support combustion and the spread of flame over an insulated surface, at a distance of at least 3 cm from the wall, including the side wall. The insulation should protrude beyond the dimensions of the equipment body by 10 cm and 70 cm from above;
- the installation height of wall-mounted equipment should be convenient for operation and repair;
- the horizontal clear distance from the protruding parts of the heating equipment to the household gas stove must be at least 10 cm;
- When installing equipment on a wooden floor, the latter must be insulated with fireproof materials with a fire resistance rating of at least 45 minutes. The floor insulation must protrude beyond the dimensions of the equipment body by at least 10 cm.
We recommend: Knife for cutting insulation: tools, characteristics and properties of insulation
5.13 In existing single-apartment residential buildings, the installation of gas stoves is allowed in rooms that meet the requirements of 5.1, but have a minimum height of up to 2.0 m inclusive, if these rooms have a volume of at least 1.25 times more than the standard specified in 5.1. Moreover, in houses that do not have a dedicated kitchen, the volume of the room in which the gas stove is installed must be twice as large as specified in 5.1.
In kitchens and rooms with sloping ceilings, having a height in the middle part of at least 2.0 m, the installation of gas-using equipment should be provided in that part of the kitchen where the height is at least 2.2 m.
Conversion to gas fuel of existing factory-made heating boilers intended for solid or liquid fuel is possible when the boilers are equipped with gas burners with automatic safety devices in accordance with GOST 17356.
5.14 Each facility where gas-using equipment is installed must be equipped with a gas metering unit in accordance with the current legislation of the Russian Federation. Installation of gas metering units should be carried out in accordance with Appendix B.
5.15 When the gas pressure in internal gas pipelines is above 0.0025 MPa, regulators-stabilizers in accordance with GOST R 54824 must be installed in front of the gas-using equipment, ensuring optimal gas combustion mode.
According to SP 42-101-2003 it is recommended:
pp. 6.17 ....In the room where gas-fired heating equipment is installed, it is allowed to use window openings as easily removable enclosing structures, the glazing of which must be carried out according to the condition: the area of individual glass must be at least 0.8 m2 with a glass thickness of 3 mm, 1.0 m2 - at 4 mm and 1.5 m2 - at 5 mm .
pp. 6.18 It is recommended that the following conditions be observed for rooms intended for the installation of gas-fired heating equipment:
- height of at least 2.5 m ( 2 m - with equipment power less than 60 kW);
— natural ventilation at the rate of: exhaust — in the amount of 3 air changes per hour
- window openings with a glazing area at the rate of 0.03 m2 per 1 m3 of room volume and structures enclosing from adjacent rooms with a fire resistance limit of at least REI 45 - when installing equipment with a capacity of over 60 kW or placing the equipment in the basement of the building, regardless of its power;
- exit directly to the outside - for premises on the ground and basement floors of single-apartment and semi-detached residential buildings when installing equipment with a capacity of St. 150 kW in accordance with the requirements of MDS 41-2
pp. 6.19 In residential buildings, it is recommended to install household gas stoves in kitchens that meet the requirements of manufacturers’ instructions for installing gas stoves, including in kitchens with sloping ceilings, having a room height in the middle part of at least 2 m , while the installation of the stoves should be be provided in that part of the kitchen where the height is at least 2.2 m.
pp. 6.23 In the absence of requirements in the manufacturer’s passports or instructions, gas-using equipment is installed based on the conditions of ease of installation, operation and repair, and it is recommended to provide for the installation of:
gas stove:
- near a wall made of fireproof materials at a distance of at least 6 cm from the wall (including the side wall). It is allowed to install the slab against walls made of fire-resistant and combustible materials, insulated with non-combustible materials (roofing steel on an asbestos sheet with a thickness of at least 3 mm, plaster, etc.), at a distance of at least 7 cm from the walls. Wall insulation is provided from the floor and must extend beyond the dimensions of the slab by 10 cm on each side and at least 80 cm on top;
wall-mounted gas-using equipment for heating and hot water supply:
- on walls made of fireproof materials at a distance of at least 2 cm from the wall (including from the side wall);
- on walls made of fire-resistant and combustible materials, insulated with non-combustible materials ( roofing steel on an asbestos sheet with a thickness of at least 3 mm, plaster, etc. ), at a distance of at least 3 cm from the wall (including from the side wall).
The insulation should protrude beyond the dimensions of the equipment body by 10 cm and 70 cm from above. The horizontal clear distance from the protruding parts of this equipment to the household stove should be at least 10 cm.
When installing the above equipment on a wooden floor, the latter must be insulated with fireproof materials, providing a fire resistance limit of at least 0.75 hours. The floor insulation must protrude 10 cm beyond the dimensions of the equipment body.
6.24 The clear distance from protruding parts of gas-using equipment in passage areas must be at least 1.0 m.
According to MDS 41-2.2000 it is recommended:
clause 5.1 When placing a gas stove, instantaneous water heater for hot water supply and a heating unit for heating with a power of up to 60 kW in the kitchen, the kitchen room must meet the following requirements:
— room volume of at least 15 m3 plus 0.2 m3 per 1 kW of power of the thermal unit for heating;
pp. 5.2 When placing thermal units with a total power of up to 150 kW in a separate room located on any floor of a residential building, the room must meet the following requirements:
— the volume and area of the room are designed based on the conditions for convenient maintenance of thermal units and auxiliary equipment, but not less than 15 m3;
Let’s remember the formula for calculating the area of a room: a square meter is how much and how to measure
When carrying out repair work, the question arises: a square meter is how many materials are needed to cover it.
In order not to spend extra money, it is better to first calculate the square meters of the room and only then go to the store with specific requirements.
On packages with paints, plaster, and primer, it is necessary to indicate for what size room this amount of the mixture is designed.
The main question is how many packages or cans are needed to cover the wall or floor area.
Double-glazed windows: bulky or energy-saving
Of course, in a residential area, the double-glazed window must be sealed, and in our area it must also be double-glazed.
For houses whose owners are concerned about energy saving, double-glazed windows with improved thermophysical characteristics are offered - with argon filling and heat-reflecting coating (the so-called I-glass and K-glass). According to manufacturers, they can reduce heat loss by 30-40% compared to conventional ones, and in some cases, make do with a lightweight single-chamber design instead of a bulky and heavy two-chamber one. Heat-reflective coatings work, as they say, on two fronts - retaining heat in winter and preventing the room from turning into a greenhouse under direct sunlight.
One of the areas of application for improved single-chamber double-glazed windows is large glazing surfaces. But thin window glass is not an option in this case - in translucent structures, thick glass is used - from 8 mm. A square meter of such sheet glass weighs 20 kg, and the total weight of structures consisting of double-glazed windows of frame and frame profiles can be calculated in tons; their design requires precise calculations, and installation requires special equipment and highly qualified performers.
What is a square meter
First you need to decide what a square meter is. People who did not study mathematics well at school still sooner or later face the problem of counting the amount of building materials. Therefore, a square meter is the main reference point when determining the area of a room.
If you draw a square (this is a geometric figure with equal sides), and the side is equal to 100 cm, then when multiplied by 100 we get the number 10000 cm. This means that the size of this figure is 10000 cm2. It could be simpler. Calculate in meters: 100 cm is 1 m. We apply the formula for calculating the area - we multiply the two sides, that is, we multiply 1 by 1, we get 1 m. This means that the size of the square is 1 sq.m.
Formula for calculating square meters
To calculate the area, you need to apply the formula per square meter A XB, where number A is the length of one side, and number B is the length of the second side. They can be the same if the shape of the floor or wall is square.
Most often, it is not square, but rectangular, that is, number A will have one value, and number B will have another. They will need to be multiplied in your head, or using a multiplication table, or on a calculator. And the resulting number will be the area that will need to be covered with paint or something else.
It happens that the shape of the floor is not standard, but, for example, trapezoidal. Then it’s more difficult, especially for those people who don’t know what a triangle is (this also exists in nature). To calculate the size of a trapezoid, you must first calculate the area of the rectangle in the middle, then the size of each triangle on the sides, then add these three numbers. Isn't it easier to immediately call a team of workers? Let them think about how to calculate the square meters of the room.
Measuring tools
To correctly calculate the total quadrature you will need a tool such as:
- construction tape of at least 5 meters;
- pen or pencil;
- calculator;
- building level or similar device with a scale;
- stepladder or stool;
- a sheet of paper for notes.
Prepare everything you need to measure walls.
You can also use special services available on the Internet, however, their accuracy is not always correct, and for maximum accuracy it is better to do everything yourself.
Before calculating the area of the walls of the room, it is necessary to provide free access to them and move furniture away to allow unhindered movement
This is very important, because from the initial data obtained from the measurement, we obtain the total volume of the room, as well as the square footage of the ceiling and floor
For maximum accuracy, it is recommended that before taking measurements, mark a straight line slightly above the level of the baseboards using a building level or any other long and level strip. Next, the tape measure is applied horizontally to the surface above the baseboard and the data obtained is recorded on paper. The next step is to measure the distance from the floor to the ceiling, again leaning the tape measure against the wall.
Don't forget to write down all the data you receive.
If the room has the shape of a rectangle, then to obtain the total area of the room it is enough to multiply the resulting width by the length. For example, if a wall is 5 meters long and 3 meters wide, then multiply 5 by 3 to get 15 squares.
Similarly, we measure each wall and add the resulting values into one total. For example, in a rectangular room there are 2 walls of 15 square meters and 2 of 8, we add these values 15x2=30, 8x2=16, 30+16=46. In total, the total surface area of the walls of the room was 46 squares.
How to calculate square meters of a wall with a window
It will be more difficult to deal with the wall on which the window is located.
In this case, you need to separately calculate the size of the wall, and separately the size of the window. Then subtract the smaller from the larger area. The result will be the number of square meters that will need to be covered with paint or plaster.
- Using the scenario already completed, calculate the size of the wall. Let there be an already known number - 15.4 m2.
- Next, measure the height and length of the window. Multiply numbers. For example: length 1.5 m, height 1.2 m. If you multiply, you get 1.8. This means the window area is 1.8 square meters. m.
- We take the area of the wall and subtract the window size from it: 15.4 – 1.8 = 13.6. The area that will need to be tidied up is 13.6 square meters. m.
General requirements for the premises
Each room equipped with a gas boiler has its own requirements, some of which are general.
- A boiler room of any type must have water supplied to replenish the system and a sewerage system to drain the coolant.
- Mandatory ventilation and removal of the combustion product through the chimney. If the boiler is of low power up to 30 kW, then the exhaust can be removed through the wall.
- Natural lighting is a must. The glazing must have an area of at least 0.8 m2, and then it is normalized to 1 m3 - 0.03 m2 of glazing. The window must be hinged and open outward.
- The window should have a window or transom for ventilation in case of gas leaks.
We recommend: Heating system with forced circulation: single-pipe, two-pipe scheme for one-story and two-story houses
According to the latest version of SNiP, a room for gas equipment for hot water supply and heating with a power of over 60 kW must be equipped with an air pollution control system, which, if triggered, stops the gas supply automatically.
And when determining the size of the boiler room, for the boiler and the heating boiler, their power is summed up.
How to calculate the approximate size of a window in an apartment or house
Even at the design stage, all parameters of optimal glazing for each specific room are determined. The calculations are quite complex for a non-specialist, so let’s consider their results for one living room at an angle of incidence of daylight from 18 to 30 degrees.
For comfortable lighting, the ratio of the glass area to the floor area of this room should be from 1/8 to 1/5. This means that the window will occupy an area of 14–17% of the floor area.
The angle of incidence of sunlight depends on the number of storeys and the presence of neighboring buildings. The closer the neighboring houses are and the higher they are, the larger this angle, which means the less illumination in your room. This may have to be compensated for by larger window sizes.
As for the height of the window sill, it is determined by the purpose of the room:
- in living rooms - from 70 to 90 cm;
- in work areas - from 90 to 100 cm;
- in the kitchen - 125 cm;
- in bathrooms and utility rooms - from 130 to 150 cm;
- in dressing rooms - 175 cm.
Determining the size of windows for the room
Windows are necessary primarily to ensure that there is sufficient light in the room during the daytime.
Since there are a large number of house designs with different room sizes and different ceiling heights, the window sizes need to be known at the design stage. In order to provide comfortable lighting, the window area should be approximately 1/8 - 1/5 of the floor area. Building regulations require that in residential premises, windows make up at least 1/10 of the floor area of that room.
Let's give an example of how to calculate the required window size. A window with an area of 17% of the floor area will be enough to provide good illumination of the entire room. The required window size in a living room is determined depending on the floor area. For example, in a room with an area of 20 sq. m window area should be calculated as follows: 20 x = 2.8 sq. m, where 0.14 is 14% of the floor area in the room.
One nuance should be noted for yourself: the closer the neighboring houses are located and the higher they are, the greater the angle of incidence of the light will be and, accordingly, the less lighting will be. Such insufficient illumination will be compensated by large window sizes. For rooms similar to residential premises, the height of windows should be no less than 1.3 m.
How to determine the height of windows and window sills? The height of the window sills directly depends on the functional purpose of the room:
- in residential premises it is 70-90 cm (in order to provide an unobstructed opportunity to view the view from the window)
- in work areas it is 90-100 cm (in order to conveniently place tables in front of the window)
- in kitchens it is 125 cm (so that work tables can be placed in front of the windows)
- in bathrooms and utility rooms it is 130-150 cm
- in dressing rooms it is 175 cm.
How experts calculate glazing area
From the point of view of designers, windows are the most vulnerable points in the building envelope. Through them there is intense energy exchange between the room and the environment.
To save heat, it is desirable to have windows of a minimum area, but this desire conflicts with lighting standards. Therefore, there are regulatory documents that allow us to resolve this contradiction.
Calculation of window area is carried out according to the methods given in SNiP (“Building Norms and Rules”). They provide illumination standards for various types of premises, corresponding coefficients and formulas.
In a simplified way, the area of light openings can be calculated based on the recommended ratios between the areas of windows and floors. These data were not taken out of thin air, but were obtained on the basis of many years of data analysis in various regions of the world.
The relevant information was summarized and compiled into easy-to-use tables.
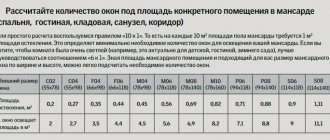
For example, for civil buildings in the climatic conditions of the middle zone at an altitude not higher than 800 m above sea level, with slight shading by nearby buildings, the ratio of glazing area to floor area will be as follows:
- living rooms - 1/8–1/6;
- kitchens and corridors - 1/10–1/8;
- staircases - 1/14–1/10;
- classes and audiences - 1/4–1/3;
- playing and dining rooms in kindergartens - 1/4–1/3;
- hotel rooms - 1/8–1/6;
- library reading rooms - 1/6–1/5;
- offices and laboratories of the research institute - 1/7–1/5;
- administrative premises - 1/10–1/6;
- sports gymnasiums - 1/6–1/5;
- gyms - 1/5–1/4;
- medical offices - 1/7–1/5;
- hospital wards - 1/7–1/6;
- restaurant halls - 1/8–1/6;
- trading floors of stores - 1/8–1/6.
Window calculator
Window calculator
How to calculate the cost of metal-plastic windows using a calculator?
— the metal-plastic window opens
- the window opens and tilts for ventilation
2. In the lower left corner of the plastic window calculator, you can select the type of double-glazed window. A single-chamber double-glazed window consists of two glasses and an air chamber between them. Double-glazed window - three glasses and two chambers between them. The price of a metal-plastic window equipped with an energy-saving single-chamber double-glazed window is similar to the price of a window with a single-chamber double-glazed window, since energy-saving coating comes as a gift. An energy-saving single-chamber double-glazed window is inferior to a double-chamber one in terms of sound insulation, but is identical in terms of thermal insulation.
3. You can set the size of PVC windows using the sliders of the window calculator by pulling them or enter them manually in the appropriate cells. Dimensions are given in millimeters. There is no need to specify a unit of measurement.
Window sizes are limited by maximum and minimum dimensions. If you want to calculate plastic windows of smaller or larger sizes, select the appropriate window configuration. For example, the maximum dimensions of a double-hung window are 1800 x 1700 mm. In order to calculate a window with large dimensions, it is necessary to select three-leaf windows.
The most common sizes of plastic windows in typical houses:
Khrushchev - two-leaf window: width - 1300 mm; height - 1340 mm, windows with three sashes: width - 2050; height - 1340 mm
Brezhnevka - two-part windows: 1500 x 1500 mm, three-part windows: 2100 x 1500 mm
Windows in the 137 series - double-leaf: 1150 x 1420 mm, three-leaf: 1700 x 1420 mm.
4. This section will help you find out the remaining sizes of plastic windows and doors in houses of standard construction, the Stalin era and the old building.
5. After you have chosen the configuration of the plastic window and the dimensions to calculate the cost of the window, its installation and finishing, you need to click on the Calculate button located in the upper right corner of the window calculator interface.
6. If you encounter any difficulties during the calculation process, we will be happy to calculate the cost of metal-plastic windows and doors by phone
(812) 677-32-65 or you can send a request for a cost calculation by email.
Results of price calculation using a window calculator
If you are interested in the cost of a plastic window without installation and finishing work, the price is shown in the right block, top line. The price of the window includes all the main elements: white PVC profile (German Rehau profile, Euro line or Korean LG Hausys profile, L-600 line), double-glazed window, set of fittings (German fittings Roto NT or Siegenia AUBI), handles, hinge plugs, stand profile. The price of the window does not include fastening elements - anchor plates and bolts, as well as additional accessories such as comb opening limiters, window care kits, handles with locks.
Installation 1 - right side of the window calculator (block with prices)
Clarifying calculation
However, these are not the only guidelines for calculating window sizes. There are other quite working methods for determining the area of light openings using special formulas, in which one of the most important parameters is also the floor area.
But the glazing area values found using tables or formulas are still approximate. An accurate calculation of the natural illumination of the premises must be made.
Today, different countries use several different methods for calculating the KEO (daylight coefficient):
- protractor method
- grid method
- ray method
- luminous flux utilization factor method
- analytical methods
They all give similar results.
How to calculate the main window dimensions
When designing a home, the minimum area of windows and their installation location are determined. Based on this, it is possible to calculate more accurate and specific parameters for each window of each room in order to find out the glazing area. When making calculations, it is customary to determine the maximum window height for a particular room in order to take advantage of optimal natural lighting conditions.
Taking into account the fact that the height of the window sill is 70-90 cm, and in houses with central heating 80-90 cm, and the upper lintel of the window should be no higher than 15-25 cm from the ceiling, it is easy to calculate the maximum height of the window and apply the light ratio to it parties - these calculated parameters will comply with the requirements of SNiP.
Calculation of window height from floor and ceiling
According to SNiP, with a total glazing area corresponding to 10-12% of the floor area of the room, a minimum amount of natural light will enter it. In this case, the optimal width of the window opening is considered to be corresponding to 55% of the width of the room.
The aspect ratio of the window plays more of a visual significance than a constructive one. Also, the correctly chosen aspect ratio makes it more comfortable to use the transoms. Therefore, the correct proportions are usually taken as standard ratios, for example, 8:13. There are computer programs to calculate window sizes; you can also use an online calculator.
In addition, there are rules that must be followed when making any calculations. For example, before calculating the parameters of the window and luminous flux, it is assumed that for one living space the angle of incidence of natural light through the glazing should be 18-30 0, and the glazing area should be in the range of 14-17% of the total floor area in the room .
When calculating the parameters, it is necessary to take into account neighboring buildings - the angle of incidence of the natural flow of light depends on the height of the window opening and the proximity of buildings adjacent to the dwelling. The natural flow of light will decrease as the distance between houses decreases, and vice versa. The same applies to the angle of incidence of illumination - the higher the nearby buildings, the higher the angle of light flux.
An example of finding design points
In building design, a window is considered the most vulnerable surface in terms of heat and energy exchange, therefore any standard calculations require minimizing the size of the window, which leads to a decrease in the natural light flux through the glazed area. To avoid a conflict between the desire to increase lighting and heat losses, the corresponding SNiPs have been drawn up and are in effect. Using the same recommendations, coefficients and formulas, designers carry out calculations of illumination and natural light fluxes for different rooms.
Emergency lighting angle calculation
Popular questions when calculating windows
How to calculate correctly?
Despite the availability of multifunctional calculators, they are limited in several parameters, especially when calculating windows and window frames. If you order it entirely in non-standard sizes, you must take into account additional problems that may arise during operation.
In other words, non-standard windows require additional parameters, because of this you will have at least one question: “how to calculate the weight?”
Metal-plastic window with two movable sashes
Formula for calculating window weight
An accurate weight is necessary to determine the load that will act on the hinges. If this is missed, the window may bend under its own weight, especially in areas of movable elements and sashes.
These parts should not weigh more than 60 kg, so the average is around 50 kg. In the photo you can see the main point that is affected by the mass of the sash.
Movable sash window hinge
In order to calculate the required weight, it is necessary to take into account 3 standards used by most manufacturers:
- Thickness 4 mm;
- Weight of 1 m2 of single-chamber glass with frame 25 kg;
- Weight of 1 m2 double-glazed window with frame 35 kg.
Based on these data, we can calculate the mass based on the dimensions using a very simple formula: multiply the window area by the standard 1 m2 of the selected glass unit. Don't know how to calculate the window area? You just need to multiply the width by the height.
For example, you chose a single-chamber double-glazed window with a height of 140 cm and a width of 90 cm. Let’s find out the area by converting the indicator into meters: 1.4*0.9= 1.26 m2 – the area of our window. Now we calculate the mass: 1.26 * 25 = 31.5 - we get the required weight.
Basic parameters of a plastic window
For fixed-type windows, you do not need to carry out a weight calculation, since they do not have movable parts.
Accurate area calculations
The larger the structure, the more difficult it will be to accurately measure it. Therefore, the question of how to calculate the window area in square meters on a large scale is very relevant. But everything is not as difficult as it seems at first glance:
- First, you need to divide the entire structure into the metal-plastic sections of which it will consist.
- After this, you need to find out the area of each section, including both fixed and movable windows.
- Then all you have to do is add up the entire area, and you will get the total area of the entire structure.
Large metal-plastic windows
Standards and rules
There are practical and scientifically proven standards that determine the calculation of window area, which affects other parameters of the room. Below are the fundamental extracts from several SNiPs for developers:
- SNiP 31-01-2003 determines the ratio of glazing to the total floor area for kitchen and living areas in the house - they must maintain a range of 1:5.5 - 1:8. In addition, a broader understanding of this parameter is indicated here: in low-rise buildings for the upper floors with inclined glazing (attics, attics, terraces), the ratio of the window light opening to the floor of the room should be ≥ 1:10. Also, the glazing area may vary depending on natural light and the characteristics of the window itself;
- SNiP 31-02-2001 defines the requirements for the flow of natural light through window openings in kitchens and living rooms. The optimal value of the natural light flux will be ensured by the ratio of glazing to floor area as 1:8, for attics and attics with inclined windows - as 1:10, but not less;
- SNiP 2.08.01-89 and SNiP 23-05-95 standardize the requirements for a larger group of premises for natural lighting. These are living and kitchen premises, bathrooms without sewerage, corridors and halls not directly connected to residential premises, staircases, corridors and passages in “tram” type buildings, public residential premises. In all of the listed premises, the ratio of the glazing of window openings to the floor area should be ≤ 1:5.5, taking into account that the minimum ratio is allowed as 1:8, and for attics and attics with inclined windows - 1:10.
An example of a quick calculation of glazing area
When calculating the glazing area to the floor area, we start from the following necessary steps:
- It is necessary to calculate the area of the window opening and determine the dimensions of the frame in order to find out the volume of light flux and glazing area;
- It is necessary to decide on the size and pattern of the window frame if it is not possible to use a standard pattern;
- It is necessary to work out drawings of each window indicating the exact dimensions if it is impossible to use a standard window. At the same time, the minimum glazing area is regulated by lighting standards - from SP 31-110-2003 to MGSN 2.06-99;
- The ratio of room glazing to floor area should not depend on the climatic and geographical region of the residential property, as well as on the orientation of the building to the cardinal points;
- When planning a room using windows to illuminate secondary rooms with additional light, the glazing area is calculated taking into account all areas of the rooms that will be illuminated by these light openings.
Geometric coefficient when determining luminous flux
Requirements for luminous fluxes for a room with natural light, but additionally illuminated artificially, are determined by the area of the window opening, which should be:
- In bathrooms - 0.5 of the total floor area of the room;
- In showers and bathrooms - 0.25 of the total floor area of the room;
- In halls, vestibules and corridors - 0.16 of the total floor area of the room;
- In entrance rooms with natural light, the window opening area can be within 0.4-0.5 of the floor area of the room.
Also:
- If there are windows in a long corridor, any place on the wall opposite the window should not be closer to the window than 750 cm;
- If a long corridor is illuminated only by a window at the end of the room, then the distance of the farthest point of the wall from the window should not be greater: for northern regions 20 meters, for southern regions - 25 meters;
- If the corridor is illuminated at both ends by natural light, then its length should not exceed 55 meters.
Sizes of window openings and room illumination
In frame buildings with strip-cut walls and strip lighting, the width of window openings determines the width of individual inserts along the axes of the supporting structure of the frame.
When designing buildings, the dimensions of window openings are set taking into account the required illumination of the premises, depending on their purpose, size, natural light in specific geographical conditions, the light characteristics of the window for a given ratio of the dimensions of the room and the window opening, the light transmittance of the window block, etc.
The area of window openings as a percentage of the area of the room is regulated by the “Building Norms and Rules” (SNiP P-A862) and is determined by the formula. SNiP P-A862 gives the normalized value of k.e.o. in the main premises of residential and public buildings located north of 45° and south of 60° northern latitude, taking into account the mandatory regular cleaning of glass at least 2 times a year for rooms with insignificant emissions of dust, smoke and soot, and four times for rooms with significant emissions.
When buildings are located south of 45° north latitude, the normalized value of k.e.o. multiplied by a factor of 0.75, and when the buildings are located north of 60° north latitude by a factor of 1.2.
For example, with side lighting in buildings located north of 45° and south of 60° north latitude c.e.o. it is 0.5 for residential premises, 1 in locker rooms and medical offices, 1.5 in school classrooms and laboratories, classrooms, assembly and sports halls, group rooms of kindergartens, dressing rooms and laboratory rooms of medical institutions, wards of maternity hospitals and 2 in hospital operating rooms.
SNiP allows deviations of ±10% of the calculated values of k.e.o. (average or minimum) from the normalized value when assigning the sizes of window openings. SNiP provides the values of the total light transmittance of the light opening t0. These values take into account the shading of the opening by supporting structures, the material and design of the binding. For example, for single binding t0 = 0.4, for double binding T0 = 0.25, for double binding t0 = 0.3.
Related article: How to check energy-saving windows
Thus, the light transmittance of a window opening, under all equal conditions, is affected by the distance between the panes and the number of panes. Naturally, with an increase in the number of glasses and the distance between them, the light transmittance of windows worsens due to the absorption and refraction of part of the light rays. The reflectivity of walls, ceilings and floors is taken into account by the coefficient G (SNiP). With medium tones of wall decoration G = 3.0.
The effect on the illumination of the room of the darkening of window openings by opposing buildings is taken into account by the coefficient k. In new construction, if the required gaps between buildings are observed, the darkening coefficient is practically equal to 1 and can not be taken into account. The light characteristic of windows c0 depends on the ratio of the width and depth of the illuminated room B and on the ratio of its depth to the elevation H of the upper edge of the window above the conventional working plane (for example, in educational premises) or the floor (in residential premises), the value of the light characteristic c0 is given in SNiP (with a window sill height of no more than 1.2 m).
Using these values in accordance with the data of the illuminated room, it is possible to determine the value of the light characteristic of the window opening with rounded relationships between the width and length of the room and between its depth and the elevation of the upper edge of the window. To more accurately determine the intermediate values of the light characteristics of a window, the interpolation method should be used.
How to calculate window area
For multi-apartment multi-storey buildings, as well as for standard individual construction projects, the window area in a living room is a parameter calculated by specialists in advance, and for the apartment owner it does not matter, since it already meets all norms and standards. But for developers who build their own housing from scratch, according to their own design, window area is as important a parameter as the grade of cement or the strength of concrete. The calculated glazing area helps not only to provide the correct lighting in the room - it also means the correct arrangement of furniture, and the correct calculations of the floor beam of the opening, and much more.
Window area calculation table
How to calculate the area of windows so that the house is not dark
When designing and constructing a residential building, you must be guided by the contents of SanPiN 2.1.2.2645-10. According to this regulatory act, all residential premises are required to have light openings in the external walls of the building. The number of windows in living rooms and kitchens must be such that the coefficient of natural light is not lower than 0.5. Insolation standards are established by regulatory documentation taking into account:
- geographical latitude of the object's location;
- calendar period;
- functionality of the premises;
- planning zone of the city.
General principles for calculating glazing area
The light opening is perhaps the most vulnerable area of the building envelope. On the one hand, heat escapes through it, so it is desirable that the opening be minimal. On the other hand, for sufficient illumination it must be larger. This contradiction is resolved thanks to specially developed regulatory documents.
The glazing area is calculated according to the methods set out in SNiP. In particular, all the necessary formulas and coefficients are given, as well as a list of lighting standards for rooms of different types. The ratio of the areas of the opening and the floor is taken as the main initial data for simplified calculations of illumination. The data was obtained experimentally and has been tested for many years in various parts of the world. They are summarized in a table quite convenient for use.
For example, in civil buildings located in the middle zone, provided that nearby buildings are slightly darkened, this ratio is equal to:
Glazing parameters
Any of the parameters necessary to ensure the best glazing of the room are calculated at the design stage, and they are individual. Independent calculation is quite complicated for a non-professional, so as an example, let’s look at ready-made results when light rays fall at an angle of 18–30° for various types of rooms. Comfortable lighting can be achieved provided that the glazing area is related to the floor area as 1 to 8 - 1 to 5. In other words, the window opening should make up 14–17% of the floor surface. Depending on the location of the house and its number of storeys, the angle of incidence of light changes, therefore, the illumination also changes. Therefore, with nearby tall neighboring houses, the decrease in illumination is compensated by large light openings.
As for its location, two factors are taken into account:
- convenience and safety of looking outside; the presence of free space above the top edge, sufficient for attaching blinds, curtains, etc.
The choice of window sill height depends on the type of room:
- for residential – 0.7–0.9 m; workers – 0.9–1.0 m; dressing rooms - 1.75 m; in the kitchen -1.25 m.
Glazing area is an important component of proper room lighting
Comfort in any room is largely determined by its lighting. The best source is sunlight, which can be obtained from windows. With proper glazing, the room will not only be light, but also warm and cozy.
According to SNiP, in order to ensure a minimum amount of light penetrating into the room, the glazing area is about 10–12.5% of the total. In addition to the linear dimensions of the window, their ratio is also important. For better visual perception, it is recommended to bring the width to height ratio as close as possible to the parameters of a harmonic rectangle, say, 80 to 130.
Insolation requirements
Artificial lighting, even of the highest class, cannot compare with natural lighting. Lack of sunlight can quickly affect your health.
SNiP, regulating this area, imposes quite stringent requirements.
If shielding control systems grow with or without sufficient subject knowledge, complications are inevitable
It is also important to note that the external solar control elements driven by the motor and system, particularly the irradiation, screens and awnings, are equipped with automatic protection against destruction. In daylight conditions, these devices are parked in a resting position, provide no sun protection, and cannot be controlled by local user controls
It is therefore advisable to consider such eclipse of additional internal shading elements.
- In multi-apartment residential buildings, the ratio between the area of living quarters and kitchens and the area of window openings should be no more than 1:5.5 and no less than 1:8.
- For private houses, the floor area of all living rooms and kitchens and the area of window openings should be in a ratio of 1:8.
- In attic rooms with a sloping roof, a ratio of 1:10 is allowed.
This means that the size of the window opening, based on the proportion, will be equal to: 12/8 = 1.5 square meters. m. These are the minimum window sizes that are acceptable in such a room.
Daylight significantly influences the perception of the interior and affects the psyche and health of the person in it
Pay special attention to the choice of shape and size of windows and other transparent structures and their placement. This should already be associated with the project documentation
Another situation arises when a window design is given and the interior must be adapted to the lighting conditions.
Many body functions, as well as the human psyche, depend on natural daylight. Natural light and the regular daily cycle of changes are closely related to human biorhythm. The lack of light is depressing, whether we want to admit it or not. Well-chosen artificial lighting can alleviate the effects and consequences of a lack of natural light for people, but cannot replace it equally. If a person is to feel comfortable in a room, they must be in good condition, which means that the space where they stay longer must be provided with a reasonable amount of daytime natural light.
Windows are necessary to provide sufficient lighting during the day.
Rice. 1. Types and overall dimensions of windows in residential buildings (USSR and Russia)
Rice. 2. Types and overall dimensions of balcony doors in residential buildings (USSR and Russia)
Visual well-being is mainly related to the intensity of lighting without significant distractions. The quality of lighting also affects the direction of light in space, the color rendering of the interior and the color of light. However, this is a very general solution that does not take into account the orientation from different sides, the shape of the room, external shading elements - balconies, loggias, the proximity and height of surrounding buildings, plants or terrain. However, the owner's subjective feelings must enter into these figures. The shape, size and placement of windows must be decided by the architect because other factors such as the layout, character of the house or proportions and its overall architectural design also come into play in the design.