Glass composite windows can be considered the glazing of the future. Experts claim that glass composite as a structural material for window profiles has no disadvantages and exceeds the technical parameters of other materials used for this purpose. The WINDOWS MEDIA portal will tell you about the advantages of fiberglass composite windows.
Today, June 29, 2016, is the 10th International Industrial Design Day. Glass composite windows can be considered among those products that highly reflect its essence. Window frames are made of fiberglass composite material (Fiberglass). It is used wherever special technical characteristics are required from the structure, in particular, in the manufacture of boats, airplanes, thermal partitions, and so on.
Fiberglass windows: advantages
Glass composite is made from thermosetting polyester resin and glass filaments, so it is chemically resistant, fireproof, hypoallergenic and environmentally friendly. The window structure does not respond to temperature changes in summer and winter, and is not affected by intra-day temperature changes. Frost resistance, durability, stability in operation, as well as a good combination with glass and double-glazed windows, which contributes to the absence of condensation. There are no restrictions on colors, including veneering, which means that the design possibilities of fiberglass windows are endless.
Important criteria for using this material in window structures are the unique thickness and complexity of the profile. Fiberglass windows, compared to other structures, have surprisingly thin profiles, which creates the impression of exceptional aesthetics and lightness of the object.
The aesthetics of the window are also a result of the unique characteristics of this material. With complete resistance to permanent deformation, as well as high thermal insulation, the profile does not require reinforcement and is quite warm even in the case of a single-chamber structure.
Thanks to the elegance of the profile, interesting structural glazing can be achieved. The narrow frame creates the impression of lightness, while at the same time allowing more light inside by increasing the glass unit area to the total window area.
Installation and operation
Installation of fiberglass windows is carried out vertically in a rigid opening with fastening around the perimeter at intervals of 500–600 mm and a distance of 100 mm from the corner to the fastening point. The voids around the frame are filled with a heat insulator, followed by protection from moisture.
Due to the almost identical coefficients of thermal expansion of glass and composite material, when there are temperature changes between the profile and the seal, no gaps are formed, which eliminates the need for seasonal adjustment of the fittings.
Maintenance consists of periodically cleaning the structure with non-abrasive detergents. Severe scratches on the profile can be removed with touch-up paint; if necessary, the decorative coating can be completely renewed with your own hands. Thanks to the design principle inherent in the structure of a glass-composite window, in the event of mechanical damage to the sash or impost, the defective part can be easily replaced without dismantling the frame.
The choice of the desired glazing design is made by weighing the pros and cons; often the weighting factor is the price characteristics at the time of solving the problem. But in addition to purchasing and installation, during operation you have to invest in maintenance. All windows should be cleaned and lubricated, and seals replaced. PVC systems are demanding in terms of adjusting the degree of pressure; wooden products require preventive painting.
The cost of glass-composite windows is approximately equal to the price of elite plastic models; the main advantage of the new generation of translucent structures is savings on operating costs.
Windows from the future: fiberglass composite or profile with specified properties
Glass composite is a composite material consisting of glass fiber and polyester resin - in a ratio of approximately 70% to 30%. The technical characteristics of the material place it at the forefront of modern building materials. Fiberglass composite, although it is a plastic material, has nothing in common with PVC, so it is not entirely correct to compare it with it. These are two different types of materials with different performance characteristics. In terms of physical characteristics, it is more appropriate to compare both the material itself and the final product made from it with aluminum windows.
The technical perfection of a glass composite window design is determined by the following factors:
- really implement any level of complexity of the structure,
- adaptation of material properties to specified functions,
- has fewer components.
The choice of window profile material is, as a rule, a task of searching for a technological and economic optimum, because customer requirements often contradict each other. For example, many users want the material to be light, durable and at the same time moderate in price. The answer to this challenge is polyester fiberglass composites, which are 2-3 times cheaper than windows made of wood and “warm” aluminum and can compete in price with PVC windows in the premium segment.
Fiberglass window blocks can be used not only in residential and administrative buildings
for glazing of shopping pavilions, loggias and verandas, but even during the reconstruction and restoration of buildings of historical and architectural value. In terms of strength, fiberglass is close to aluminum. Due to the high strength of fiberglass profiles, they do not require the installation of reinforcing steel stiffeners. The results of thermal engineering tests have shown that, due to the high precision of manufacturing, the air permeation resistance of such structures significantly exceeds the standardized indicators adopted in the current SNiP for windows and balcony doors.
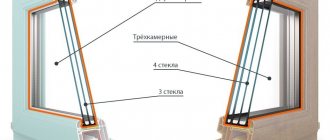
Windows made of fiberglass can withstand temperatures in the range from -70 to +170 °C. Due to their high thermal and strength properties, fiberglass profiles are made with fewer air chambers than PVC profiles (this fact greatly simplifies the design of the frame itself). The frame is assembled using self-tapping screws and sealant. The glazing of fiberglass windows can be single-pane, single-chamber, double-glazed. Fiberglass profiles do not require the installation of reinforcing steel stiffeners. The insignificant coefficient of linear expansion of fiberglass, approximately equal to the coefficient of linear expansion of glass, creates the effect of synchronism with the double-glazed window: the window works as a single whole, that is, glass in glass. This effect ensures reliable operation of all elements of the finished window, since when there are temperature changes, cracks do not form and there is no need to monitor the adjustment of the fittings and the condition of the seals.
What types of windows are composite fiberglass suitable for?
Although glass composite appeared in the middle of the last century, its use in window production was limited by technological difficulties in forming a fairly complex thin-walled profile. The Canadian company INLINE FIBERGLASS coped with this task better than anyone else in the world. The technology it has developed allows not only to produce profiles with very complex cross-sections, but also to achieve economically feasible production speeds. At the moment, glass composite windows have a good and stable position in the European market and awareness of the technical advancement of the product is growing among users.
Fiberglass composite windows first appeared on the Russian market in 1992 and created the basis for the production of a completely new product. During this period, “windows from the future” were tested in practice and gained their admirers, competing with even the most popular PVC structures on the market due to their versatility.
Applications of glass composite profile include:
- Fixed windows, especially panoramic ones;
- Swing, tilt and turn-tilt structures;
- Sliding windows and doors;
- Balcony and terrace doors;
- Glazing of balconies and loggias.
With the advent of the trend towards large-sized glazing in Russia, even greater interest in structures made from this unique material, which can be assigned various properties, has flared up.
Constructive decisions
- Classic windows are equipped with the usual tilt-and-turn fittings, familiar from plastic products.
- Sliding warm systems - light moving parts move horizontally.
- English windows - vertical or horizontal sashes open outward with a handle located at the bottom of the frame.
- The “American” version is a product with a sliding opening in a vertical plane and the ability to tilt up when washing glass.
- Balcony glazing is done with the maximum possible panoramic view using both cold and warm methods.
- Large windows - the mechanical strength of the material allows you to glaze a veranda or terrace up to 3–3.5 m high without additional reinforcing elements.
Ideal material for making windows
Below are some characteristics that indicate that glass composite is an ideal material for making windows:
- At very low temperatures (-40 °C), glass composite does not show the tendency to harden and shrink, which usually leads to brittleness and cracking of other materials due to increased internal stresses.
- At high temperatures (+100 °C), to which the glazing of southern facades is exposed, the profile maintains overall shape stability - it does not plasticize, and demonstrates a very low coefficient of thermal expansion. The thermal expansion of glass composite is minimal (5 × 10-6 / °K), and is close to the thermal expansion of glass. Thanks to this, there is no stress between the frame and the sash, as well as between the glass and the profile, associated with different coefficients of thermal expansion of the two interacting materials. This has a positive effect on the durability of the seal. In addition, in the case of panoramic windows (several meters in length), expansion joints between sections of window frames are not needed.
- Fiberglass composite is a non-flammable material that does not become plastic under the influence of high temperatures. It can only burn in an open fire. In the event of a large-scale fire, where practically everything except concrete can burn to the ground, the glass-composite profile during the process of thermal decomposition does not emit any toxic substances, unlike PVC.
- Impeccable dimensional stability. There is no creep or warping phenomenon. Fiberglass, like any composite material, “remembers” its shape. It is this feature, in addition to the elasticity and mechanical strength of the material with a very high resistance to deformation, that contributed to its choice in the production of vertical supports and high jump poles.
- The chemical resistance of glass composite puts it among acid-like materials that are not subject to corrosion or decay. Thanks to this property, glass composite windows are very popular in Venice.
- The mechanical strength is so high that the resulting profiles do not require reinforcement, and the profile is much narrower than that of PVC structures.
Compared to a PVC profile, a glass composite profile has: • Bending strength is more than 10 times higher.
• Tensile strength – more than 25 times higher • Impact resistance – more than 3 times higher.
- The high level of thermal insulation and its mechanical properties allow the use of glass composite for the construction of heat-saving partitions. One example would be thermal inserts for aluminum windows.
Technical features
Due to its high strength and good heat resistance, a glass-composite profile is designed simpler than aluminum and plastic: it has fewer chambers, does not require metal reinforcement, and as a result, there are no cold bridges in it. Only the locations of the hinges are subject to reinforcement using special steel plates 3 mm thick, inserted inside the frame when assembling the block.
The frame is assembled using corner and mullion connectors, fastening is done with self-tapping screws, and the joints are protected with silicone sealant of the appropriate color. The internal cavity of the profile is filled with thermal insulation - foamed polyethylene, foam glass or expanded polystyrene.
Fiberglass window design:
The surface of fiberglass can be white, painted in any shade or covered with laminated veneer with a wood texture. If desired, the finishing of the profile on the room side may differ from the outer covering.
Excluding the disadvantages of structures made from other materials, fiberglass windows combine their positive characteristics.
Table. Comparative characteristics of window systems made of different materials
| Criterion | Material | |||
| PVC | Tree | Aluminum | Fiberglass | |
| Moisture resistance | + | — | + | + |
| Heat saving | + | + | — | + |
| Strength | — | + | + | + |
| Maintainability | — | — | — | + |
| Fog resistance | different | + | — | + |
| Low Linear Expansion | — | + | average | + |
| Long service life | different | — | + | + |
| Comparative Cost | X | X+75% | X+35% | X+25% |
Warranty for glass composite windows
The warranty on installation of glass composite windows is 5 years, and on the profile itself – 60-70 years. The essence of the guarantee can be expressed in words that for many years the glass-composite window will continue to perform all its functions properly, and for five years, in case of doubt, the company’s specialists are at the disposal of users. The only important condition for obtaining such a guarantee is professional installation.
Bottom line.
Today, buying fiberglass windows is not a problem. There are plenty of companies offering to purchase them, at least in big cities. The most popular sellers are ready to offer window options with different opening methods.
By purchasing products from these companies from distributors, you can be confident in the branded quality of the purchased windows, the availability of all necessary certificates, as well as in the solid warranty period provided for the purchased products, which should not be limited to 1-3 years.
Sources
- https://ElitStekloPlast.ru/katalog/levyj-blok-menyu/steklokompozitnye-okna.html
- https://okno-pro.ru/komplektuyushchie/okna-iz-stekloplastika.html
- https://aniko-gas.ru/plastikovye-okna/iz-stekloplastika.html
- https://CitiOkna.ru/vse-ob-oknah/poleznaya-informaciya/steklokomposit.html
- https://www.WikiStroi.ru/story/windows/okna-iz-stiekloplastika-osobiennosti-kharaktieristiki-pierspiektivy
- https://OknaRaduga.ru/okna-i-aksessuary/okna-iz-steklokompozita.html
A little history
Glass composite was invented in the 50s of the last century in the USA exclusively for the needs of the space industry for the construction of the first solid-fuel underwater launch rocket. The material showed its unique qualities and already in the 60s migrated to the aviation and then to the shipbuilding industry, mainly for military purposes. Low cost in comparison with other materials quickly made fiberglass very popular on an industrial scale in other industries - mechanical engineering, construction and others.
The development of this composite material and the invention of new and new varieties of it began especially quickly with the creation of a very effective and inexpensive technology called pultrusion, when the reinforcing fiber is pulled through (throught) a mold with a heated resin, when the composition cools, a glass composite is obtained. Today, there are horizontal and vertical drawing methods, and production can be batch or continuous. For small volumes of work, either the method of manually spraying fiberglass or the method of manual molding of products is used.
Application
Before characterizing it, it is necessary to tell a little about the profiles themselves, or rather, about the process of their development. These elements are produced by pultrusion, that is, drawing inside a heated die. The glass material is first saturated with resin. As a result of thermal exposure, the resin undergoes polymerization. You can give the workpiece a rather complex geometric shape, and also keep the dimensions very precisely.
The total length of the profile is almost unlimited. There are only two restrictions: the needs of the customer, the possibilities of transportation or storage. Installation costs are kept to a minimum. Specific use depends on execution. Thus, I-beams made of fiberglass become excellent load-bearing structures.
With their help, soil is sometimes secured to the perimeter of a mine shaft. In no case deeper - there the load and responsibility are too great. Fiberglass I-beams become excellent assistants in the construction of warehouses and other hangar structures. With their help, the use of technology is minimized or completely eliminated, since the structures themselves are quite light. As a result, overall construction costs are reduced.
Fiberglass channels are quite rigid. And they transmit this reserve of rigidity to the structures within which they are placed. Such products are suitable for frame parts:
- cars;
- architectural structures;
- utilitarian buildings;
- bridges.
Bridges and pedestrian crossings are often made using fiberglass channels. They are quite resistant to moisture and even exposure to aggressive substances. The same designs are used in the design of stairs and platforms, including at chemical industry facilities. Increasingly, composites are also being used in the construction of hangars. When creating them, an important role is played by increased durability (20-50 years even without prevention and restoration), which is not available for other commonly used materials.
A number of industries use fiberglass corners. In a number of characteristics, they are even better than their steel counterparts. With the help of such corners, rigid frames for buildings are prepared. It is customary to divide them into equal and unequal types. Fiberglass can also be used to equip technological sites where reinforced concrete and steel cannot be used
But this material is also becoming an excellent option for forming building facades and fences. After all, the surface of fiberglass can be painted in a variety of colors. Various textures can also be used. These properties are highly valued by architects and design specialists. As for square pipes, they cope well with both horizontal and vertical loads.
The scope of application of such products is incredibly wide:
- bridges;
- technological barriers;
- stairs on objects;
- sites and platforms for equipment maintenance;
- barriers on highways;
- restriction of access to the shores of water bodies.
The rectangular fiberglass pipe has generally the same purpose as the square models. Round tubular elements are quite versatile. They can be used independently or as connecting links in other elements.
Other possible areas of use:
- energy (insulating rods);
- antenna stands;
- amplifiers inside various structures.
Other areas of application include:
- creation of handrails;
- railings;
- stairs with dielectric effect;
- wastewater treatment plants;
- agricultural facilities;
- railway and aviation facilities;
- mining sector;
- port and coastal facilities;
- noise barriers;
- ramps;
- overhead power line suspensions;
- chemical industry;
- design;
- pigsties, cowsheds;
- greenhouse frames.