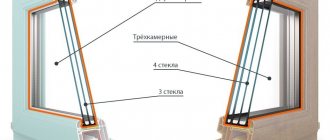
Windows from the Russian manufacturer Kaleva are known both in our country and abroad. Since its founding, the company has been manufacturing products of the highest class, performing a full cycle of work: from independent production of profiles to assembly of elements into a finished structure.
The production process is as automated as possible, and the quality laboratory controls all stages of production. Kaleva specialists are constantly working to create new models, the characteristics of which allow them to withstand the capricious climate of Russian regions without consequences and withstand significant temperature fluctuations (from -30°C to +30°C) for a long time depending on the season. Domestic manufacturers have more stringent requirements for their products than companies manufacturing windows in Europe.
It is worth noting that the Kaleva company sells windows only to private individuals and, in principle, does not cooperate with contractors and construction organizations. This is explained by the fact that wholesalers and large builders are not interested in purchasing and installing high-quality windows in buildings. They strive to buy cheaper and more for a minimum cost, without caring about the comfort of future residents (the so-called economy option). For this reason, the flow of standard designs is standard size, and works with each order individually.
An individual approach has virtually no effect on the cost of the final product, since high automation of most processes can significantly reduce its cost.
Let's figure out how the production of plastic windows works.
Where and how?
Modern metal-plastic windows have a modular design (a construction set, like Lego), which some craftsmen manage to assemble even in a garage or basement. High-quality window production involves the preparation and processing of all components in an automated or semi-automatic mode on special production lines. Most workshops today use Austrian, Italian or German-made equipment with built-in electronic control (CNC).
For the manufacture of windows, PVC profile blanks are used, which are supplied to the factory or workshop in the form of 6-meter long rods. The profile first undergoes quality control for evenness and clarity of edges, grooves, structure density and correct geometry. Subsequently, they are cut in accordance with the sizes specified in the order. This means that when you order windows, the measurer enters all the measured parameters of your openings into the specification and sends it to the workshop. This is how your products are made. Therefore, the correctness of taking dimensions directly depends on what kind of structure will be manufactured in the end.
In the same workshop where profiles are cut, reinforcing elements are also cut. They can be closed or another (open) shape, but must be galvanized or coated with an anti-corrosion layer. After reinforcement, parts of the window are welded, double-glazed windows and fittings are installed in them.
All components must comply with the requirements of individual GOSTs:
- Fittings - GOST 30777-2001.
- PVC profiles - GOST 30673-99.
- Glass - GOST 30698-2000.
- Double-glazed windows - GOST 24866-99.
Finished PVC windows are checked for quality against GOST 30674-99.
A certain microclimate must be maintained in the production and warehouse premises. The air temperature must not be lower than +18℃ to avoid deformation and changes in the properties of PVC.
The production process of plastic windows
The process of producing plastic windows begins with the production of glass of the required quality and size, assembly of double-glazed windows, production of PVC window profiles and steel reinforcing inserts. Let's call all this blanks for the production of double-glazed windows and plastic windows and leave them outside the scope of this article. The technology for producing double-glazed windows was described earlier in a series of articles about double-glazed windows. Therefore, we will consider the production process of plastic windows separately from the rest, assuming that double-glazed windows, profiles, fittings and other materials are already in stock.
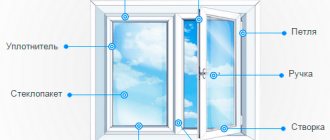
Rice. 2. Window block design
When finished double-glazed windows and blanks arrive at the production of double-glazed windows, they are assembled into window blocks, which are then installed at the customer’s site.
During the production of plastic windows:
- Based on the measurements, an electronic drawing of the future window is created;
- Blanks of PVC profiles for sashes, frames and imposts are cut;
- Holes are made in the blanks to remove moisture and fittings;
- Reinforcing profiles are cut, installed and secured in PVC;
- PVC profiles are fused on a special machine;
- Welding seams are polished;
- Imposts are milled according to a template and attached to the window block;
- Strapping, counter fittings, handles are installed;
- Rubber seals are attached to the frame and doors;
- The sashes are fixed in the frame;
- Double-glazed windows are installed in frames and sealed;
- Before release, the glass unit is checked for quality.
It seems quite simple, but let's look at each stage separately.
Preparation of PVC profile
Cutting of PVC blanks is carried out according to a given program in accordance with the specifications of each order. The profile is cut with two-head miter saws: for mullions at an angle of 90 degrees, and for frames at an angle of 45 degrees. In this case, an allowance of 3 mm is left for welding the connecting sides. On fully automated lines, the machine itself measures and cuts profiles in accordance with a given program.
Next, holes for drainage and fittings are milled. In workshops with not the most modern equipment, this process is carried out manually using a drill.
The reinforcing profile is also cut into pieces of the appropriate size and inserted inside plastic blanks, securing them with metal screws. The impost and support profile are installed manually.
Next, the finished frame is welded at the corners on a four-head welding complex at a temperature of 250 ℃. After welding, the corners and seams are processed on another machine to obtain a smooth surface without plastic sagging. Arched or round windows are made by bending a heated profile at the desired angle. Subsequently, it is fixed to harden in a given shape.
Assembly area
Assembly shop
In addition to the plastic profile, steel profiles play an important role in the design. They make the window strong and rigid. Using a band saw, the metal blanks are given the required length and installed inside the plastic profile. Almost all frame windows are strengthened in a similar way. A lighter truncated profile is placed in the sashes.
In some modern models, a double-glazed window is glued directly into a plastic profile to increase the glazing area. In this case, it is an additional strengthening element.
Cutting individual elements of the future window
Cutting the finished profile into blanks of the required length and installing the steel profile into it at the factory is almost completely automated.
All window elements are marked - they are marked with information about the size and the customer. A special display receives data for the operator, informing him about the sequence of movement of the workpieces and their sizes. In the photographs you can see stickers with information glued to the products, as well as the sequence of laying out the elements for their further delivery.
The machine lays the profile for subsequent distribution to departments
Automated systems themselves calculate the required window dimensions and weld the parts simultaneously on four sides. This ensures perfect evenness of corners and ideal shape of the product.
Operator's place of work for cutting plastic profiles
The line operator only makes sure that the parts of the structure are present on all sides and are correctly laid out there. The smart machine produces heating and compression of parts independently.
Automatic heating of the end sides of the profile and its compression
The conveyor transfers the glued frame to an automatic platform for cleaning the seams.
Get ready for the cleanup!
The same workshop produces imposts - vertical profiles installed in window openings. They can perform a purely decorative role or be useful and functional elements: increase the reliability of closing the valves, increase the rigidity and strength of the structure.
Making an impost - a partition between sashes in windows
Imposts in windows are installed manually.
Fitting and installing the impost
After the imposts, the window is equipped with a seal - this work is also done manually.
Fastening the seal around the perimeter of the frame takes a worker no more than a minute
The final stage is equipping the product with fittings and locking devices. The operation is fully automated.
The final stage is installation of fitting mechanisms
This completes the production of the frame.
Installation of double-glazed windows
Glass boxes are often supplied to the window production plant from other enterprises that specialize specifically in the production of double-glazed windows. However, there are full-cycle factories that produce their own double-glazed windows.
To make double-glazed windows, the glass is first cut and washed, then spacer frames are prepared and the glass is glued to them using a primary sealant, and at the last stage the structure is sealed a second time. The chambers can be filled with inert gas. This creates a completely insulated glass box with the specified parameters.
Double-glazed windows are installed in frames on straightening plates in a frame that is thoroughly cleaned of dust and shavings. The seals are wiped before installation, and the glass on the outside is wiped as well. In a level position, the glass unit is fixed using glazing beads. These plastic blanks have a specific shape with a latch for clamping. The glazing beads are inserted into the grooves, snapped together along their entire length and the tightness of the clamp is checked.
Cutting steel reinforcement
At the second stage, which is carried out parallel to the first, the steel reinforcing profile is cut. This profile is necessary for installation inside the PVC profile chamber intended for it in order to strengthen the future window structure. As an alternative to the reinforcing profile, PVC profiles with composite or fiberglass are extruded to strengthen the window structure.
The reinforcing profile is cut individually or in batches, to size or in increments. For cutting, circular or band saws, guillotines or plasma cutting centers are used. The plasma cutting center allows you not only to cut reinforcement, but also to cut grooves and locking cylinders in the metal.
Hanging sashes
This is the final stage of window production, when finished sashes with double-glazed windows are carefully hung on hinges and fixed. The hinges can be masked with decorative plastic overlays. After assembly, the master checks the operation of the fittings for opening and closing and fixing all elements.
The window is ready for transportation and installation!
The assembled structures are sent to the finished product warehouse and subsequently transported on specially equipped vehicles to customers at the delivery point.
Processing the ends of the impost
The next operation is milling the ends of the impost. An impost is a vertical window element that divides a window or doorway. The ends of the impost are milled with special type-setting cutters, which follow the contour of the profile to which the impost is joined, for their tight fit. For these purposes, an impost machine is used, single-headed or double-headed, with the ability to mill several imposts simultaneously on one side, or a milling module in a sawing and processing center.
Milling an impost
The finished window experiences many loads: squally winds, rain, temperature expansion, the weight of the window itself with double-glazed windows, and when the sash is opened, the window frame is subject to force from the weight of the sash.
Production stages
The production of PVC profiles and the assembly of the structure are preceded by a subtle but very important stage - design. Design engineers create drawings and diagrams of future windows, in which:
- outline the structure down to the millimeter;
- provide mechanisms to ensure window safety;
- select fittings and accessories for noise, hydro, and thermal insulation;
- design the placement of insulation, an opening mechanism, a metal profile that strengthens the structure, etc.
Then, based on the project, plastic windows and doors are created, the production of which consists of several stages. Let's take a closer look at each stage of manufacturing plastic windows.
Order completion
In parallel with the production of windows, the complete order is completed: cutting to size window sills, slope panels, production of drainage systems, mosquito nets, formation of the full volume of necessary materials for high-quality installation, including polyurethane foam, silicone, fasteners, etc. and so on.
Cleaning and milling corners
The next step is to clean the corners of the welded profile from weld deposits. Cleaning machines are used for these purposes. The machines can be manual, with pneumatic units, or with CNC control. These machines can be free-standing or as part of a line along with a welding machine.
Currently, there is only one revolutionary solution that allows you to completely abandon the stripping machine. This technology is popularly called “seamless windows,” although it would be more correct to call this technology welding without the need for subsequent stripping.
Drilling holes for handles
The next operation is to drill holes for the handle and mill the fitting groove if it has not been milled before. In some cases, the combination of profile and reinforcement makes it possible to avoid the operation of drilling through the reinforcing profile, and such holes are drilled only in the PVC profile. These operations are performed on a copy-milling machine or machining center.
Using a template, the copying unit of a manual machine allows you to make a hole in the profile for the lock cylinder and a groove for the lock. Machines are produced that perform only two operations, but in automatic mode: drilling under the handle and simultaneous milling of the fitting groove.
Welding of the structure
Next, the cut BEKA plastic profile is supplied to a semi-automatic 4-head welding complex, where the corners of the future window structure are welded at a temperature of 250°C.
Installation of seals, fittings, imposts.
The next step is to install the seal. This operation is carried out manually. If the window is made from the Veka Euroline Pro system, installation of a seal is not required, since the profile already comes with all the sealing contours.
Fastening the reinforcing profile
In order to strengthen and maintain the geometry of the profile during thermal expansion, metal reinforcement is inserted into the cut and milled workpieces. The reinforcement is inserted into a special chamber inside a plastic profile. Metal reinforcement is approximately 10-30 mm shorter in length than the workpiece. This distance is necessary for subsequent welding of the workpieces.
The reinforcement is inserted into the workpiece manually or using a manipulator and then screwed onto the PVC profile. The workpieces are screwed together with special screws and a drill using a hand-held screwdriver, a screwdriver with automatic screw feeding, or in a machining center.
Automated centers for screwing and finishing in metal include from one to three screwing devices simultaneously. In addition, these centers carry out drilling for a handle on a sash through metal, drilling for an impost or drilling for dowels. Make-up screwdrivers can be air or electric driven.
Make-up and metal processing center
List of feature articles
Technologies for manufacturing PVC windows
The demand for PVC structures is constantly growing. Two factors contribute to this. The first is the need to replace old wooden windows with modern energy efficient ones. The second is large-scale residential construction. For example, in Russia in 2006, the PVC profile market increased by almost 50%. The trend, according to experts, will continue in the next 3-4 years. During this time, they predict the growth of this segment of the construction industry by 30-35% annually. As a result, the number of companies operating in this area is increasing. In our country, the number of manufacturing companies and sellers of plastic windows today is more than 10,000. Such rapid growth rates in the industry are helping to attract more and more manufacturers of window systems. In a highly competitive market, product quality comes first. And it is determined by compliance with the manufacturing technology of PVC window systems. First of all, during production it is necessary to be guided by regulatory documents and standards. These are two main GOSTs: • GOST 30674-99 “Window blocks made of polyvinyl chloride profiles. Technical conditions"; • GOST 23166-99 “Window blocks. General technical conditions". As you know, a translucent structure consists of three main components - a profile (or frame), a double-glazed window and fittings (a set of mechanisms for opening/closing the window). Each component must meet the quality standards accepted for it. The profile is in accordance with GOST 30673-99 and GOST 30973-2002, the glass unit is in accordance with GOST 24866-99 and GOST 111-2001 and the fittings are in accordance with 30777-2001 and GOST 538-2001. Often the properties of the finished system depend on the quality of the window components. Thus, the production of translucent PVC structures is a complex technological process, including the production of a profile, double-glazed windows, fittings and final assembly of structures. Let's look at each stage sequentially. Profile
This is the basis of the window structure.
Initially, the mixture is prepared. In addition to the main PVC component, as a rule, it includes a strength modifier (giving plasticity and frost resistance), stabilizers and lubricants (for the extrusion process), hydrophobic chalk (for product strength), titanium dioxide (as a dye for light fastness) and various auxiliary additives (fire retardants, plasticizers, etc.). The ratio of these components determines the physical and mechanical characteristics of the profile. Each company has its own unique material recipe. For example, the profile systems of the PROPLEX Group of Companies, the largest Russian manufacturer of PVC profiles using Austrian technologies, are manufactured on the basis of mixtures developed by Chemson (Austria). The company’s specialists have created a recipe that takes into account the peculiarities of our climate: sudden temperature changes and cold winters. The basic element for the production of PVC profiles is an extruder. It comes in different types - single screw, twin screw, multi screw or disc. When producing PVC window profiles, extruders of the second type are most often used. The design of the screws can be conical or cylindrical. As specialists from Technoplast (Austria) note, the latter have a number of advantages. In particular, compact drive, low cutting (shear) loads, resistance to high output pressures, high torques, ease of dismantling, etc. The augers can either be engaged or not; rotation is carried out in one or different directions. The best performance is found in extruders with tight meshing and screws rotating in different directions. In a standard twin-screw extruder, the technological process goes as follows. First, the mixture is captured, and due to friction (and heat transfer), it is preheated. Then, under intense shear deformation, the material is plasticized. Precise supply of raw materials is realized using a doser (usually with a dosing screw). Optimal plasticization occurs at a temperature of 180-200ºС (pressure - 150-300 bar). In the degassing zone, gaseous products, including trapped air, are removed from the plasticized (agglomerated) material. To do this, there is a large empty space between the turns of the screws. Next, the material is forced through a die, where the polymer melt is shaped. The performance of an extruder largely depends on the throughput of the device. Today it can reach about 700 kg/hour. This is equivalent to approximately 10 m/min. According to experts, double-strand dies provide the highest productivity. The final stage of manufacturing PVC profiles takes place in a calibrator. It consists of two modules - dry and wet. In the first, the mass leaving the extruder is subjected to molding and initial cooling. At the initial 50-100 mm, the profile is given the desired shape. After which, due to special water channels, heat is removed from the internal surfaces of the products. Modern dry calibrators are characterized by longitudinal cooling channels, a sequential cooling scheme, a system for quick replacement and centering of calibrators, and a minimum number of water and vacuum supplies. Final cooling is carried out in a wet module, where the entire profile is irrigated with water. In this area, we can note the development of Technoplast. These are wet calibrators with whirlpool baths. They can reduce the water consumption required for cooling by approximately 50%. All blocks of calibrator tanks are standardized, which makes it possible to use the same tank for different standard sizes of profiles. Thus, profile production is a fairly high-tech production. Today, the leading suppliers of extrusion lines on the world market are Austrian companies. Their products have already proven themselves to be reliable, efficient and economical. Therefore, almost all the largest manufacturers of PVC profiles for windows use equipment from Austrian companies. For example, the PROPLEX plant uses extrusion lines and related tools from Greiner, Gruber and Technoplast. One of the most important stages in the technological chain of PVC profile production is its painting. There are four dyeing methods: co-extrusion, bulk dyeing, lamination and varnishing. The first two methods are used in the profile manufacturing process. Co-extrusion is the joint extrusion of PVC and plexiglass. Dyeing in the mass occurs at the earliest stages of production by adding color pigments to the initial mixture (later, the resulting products are usually laminated). Lamination refers to the final stage of profile manufacturing. Durable films resistant to climatic influences are glued to the material. Coating products with acrylic varnish is called varnishing. This is followed by cutting, packaging and transportation of the finished product to processing companies (direct assemblers of window structures). Double-glazed window
The process of producing another window component, double-glazed glass, is quite labor-intensive and requires the use of modern equipment.
For example, CJSC Siberian Glass Company (Russia, Krasnoyarsk) uses automated high-tech lines from Lenhardt Maschinenbau GmbH (Germany) and Frontech Machinery and Technology sa (Switzerland). First, glass is cut on special tables covered with thick fabric. Then the distance frames necessary to create the frame of the double-glazed window are measured. They are made mainly from aluminum. The glass must be washed and cleaned (since after sealing the inside of the glass unit will be inaccessible). This is done using machines (using brushes). Then a desiccant (desiccant) is poured inside the perforated spacers to absorb water. It consists of molecular sieves, silica gel, or a mixture of these substances. The next step is the assembly of the remote circuit. The frames are connected manually with corners. After which the primary sealing layer is applied (butyl cord, liquid butyl, etc.). This operation can be done manually, but it is more efficient to use automatic butyl extruders. Next comes the assembly of the glass unit. Glass is glued to the distance contour on both sides. And on the table for crimping the component, the resulting structure is crimped (to impart tightness and the required thickness). The final phase of production is the application of a secondary sealing layer (silicone, polysulfide two-component sealant, etc.) to the end of the assembled structure and drying of the products. As a rule, a finished high-quality double-glazed window has a continuous primary sealing layer. There should be no leaks of sealant inside the remote contour of the product, and no dust in the space between the glass. This is important to consider when choosing a supplier of this type of component. Fittings
It is made from high-quality, specially hardened steel using automatic casting machines.
An anti-corrosion coating is applied to galvanic treatment areas. According to experts, it is mainly the quality of the protective layer of the fittings that determines its service life. For example, products from the Turkish company Kale have a three-layer coating. Using the new alkali-zinc technology, zinc is first applied, then trivalent chromium, after which the fittings are painted with varnish. Manufacturers pay great attention to product quality control. In particular, when manufacturing Kale fittings, the incoming raw materials are first checked (the surface of the steel, its thickness, the chemical composition is analyzed). Then, during the production process, at each stage, every 15 minutes, a random selection of semi-finished products is made, they are inspected, geometric parameters are measured, and the quality of the coating is monitored. The standard kit consists of hinges, handles, limiters, fuses, clamps, tilt and turn mechanisms (non-plastic parts must be used as fastening power elements). Along with it, the assembler of window structures is supplied with a manual for installing fittings. When installing it, the weight and dimensions of the opening/closing elements of the products are taken into account, and the permissible loads specified by the supplier are taken into account. The holes for the rotary lower and upper hinges are drilled using a drill (the drill size is about 0.7 of the screw diameter). The distance between them and the locking points should be less than 700-800 mm. The hinges are fastened with stainless steel screws through two walls of a PVC profile (at least 4.5 mm thick). Another option is through one surface and a reinforcing amplifier. Moreover, if the mass of the sashes is more than 60 kg, reinforcing elements are used to increase the fastening strength. In particular, Kale fittings can support a sash weighing up to 130 kg. Experts recommend using products that have adjustable hinges, tilt-and-turn opening/closing mechanisms, equipped with devices for both slot ventilation and adjustable opening angles. It is desirable that the fittings have safety locks and locks to prevent accidental opening. Reliable fittings provide more than 20,000 opening/closing cycles. Assembly
Manufacturing of the window structures themselves is carried out by processing companies. The most common option is to purchase all the necessary components. However, there are also companies that, before assembling finished windows, manufacture double-glazed windows. As for the direct production of the window structure, first the necessary parameters of the profile products are established in accordance with the future dimensions of the window (with a margin for welding (5-6 mm)) and the profile is cut. It is performed, as a rule, using two-head saws. During the cutting process, you should control the angles of inclination and rotation of the cutting discs (for frame and sash profiles - 45º, for the impost (middle part of the frame) - 90º), the cleanliness of the surfaces and the length of the workpieces. In addition to the PVC material, reinforcing rods necessary to enhance the rigidity of the profile system are cut using metal cutting saws. The next stage is milling a number of different holes in PVC blanks (using a special machine or drill). They are necessary for draining water, organizing ventilation and compensating for wind pressure. So, for example, at least two drainage holes must be made in the lower profile of the window frame, and two (up to one meter) or three (more than one meter) in the upper part, depending on its length. The maximum distance between the slots is 600 mm, their diameter is at least 6 mm. Next, the profiles are reinforced, that is, they are reinforced with galvanized steel rods. Reinforcing liners are installed either using a machine or manually (using a screwdriver and self-tapping screws (at least two per reinforcing rod with a pitch of no more than 400 mm)). They should be located with a gap towards the outside and fit snugly against the walls of the profile chambers. This is followed by the stage of connecting the sash and frame profiles using welding. It is performed on a one-, two- or four-head welding machine. Temperature, pressure, surface cleanliness, cycle time, as well as the dimensions of frames and sashes are monitored. Profile blanks are welded along the entire contour. The seams should not have any defects. At the end of the process, the strength of the fillet welding joints is tested. The resulting structures are cooled (for 5-10 minutes) and proceed to cleaning the external and internal welds. To remove weld deposits, automatic (cleaning machine) or manual equipment (pneumatic drill, chisels) is used. The next technological phase is milling the impost for a more precise fit to the frame profile and its installation. The latter is carried out in accordance with the technical documentation of the profile system supplier. Markings are made and the impost is attached to the box using system (metal or plastic) connectors. However, in the PROPLEX-Optima profile system, metal-plastic connectors are used along with conventional ones. The results of tests carried out in Testing showed that these connectors are superior in strength to analogues made from zinc. The connection must be tight and have no gaps or voids. Next, seals are installed around the perimeter of the sashes and frame. Laying is done manually, not in sections, but with a whole piece of rubber (with a compression deviation along the length of one percent). The joint must be tight and prevent the penetration of water. At the ends, the seal is secured with a special waterproof glue. According to PROPLEX specialists, the most effective is a double-circuit seal, which is performed in the frame and sash. The sealing material must be resistant to climatic influences. Artificial rubber (EPDM) and silicone have proven themselves well. Then the symmetry of the sashes (no curvature), the uniform fit of the sealing gaskets in the rebates, and the distance between the front plane of the frame profile and the sashes (about 16.5 mm) are checked. All mechanisms and devices must be set in motion without any effort - easily and smoothly. Now you can move on to the final stage of manufacturing window systems, namely their glazing. When installing a double-glazed window, it is necessary to correctly distribute its weight in the frame or sash, prevent direct contact of the frame with the double-glazed window, and also ensure easy movement of the sash. Installation takes place using base (to align the rebate bevels), distance (to create the necessary gap between the sash rebate and the edge of the glass unit) and support (to optimally transfer the mass of the glass unit to the entire structure) pads. Their dimensions depend on the product and the features of the sealing system. As a rule, the width of the linings should exceed the thickness of the glass unit by 2 mm, and the length should be about 100 mm. They are made from weather-resistant polymer materials. After the gaskets are installed, the double glazed windows are inserted. They are secured with glazing beads, which are cut using specialized equipment. They are cut using a special saw at an angle of 45 degrees. The beads are driven in with a plastic or rubber hammer with gentle blows (first short ones, then longer ones). After that, the vertically placed sashes are adjusted on a special stand. Finished products are securely packaged to protect them from mechanical damage and atmospheric influences during loading, unloading and transportation. Before packing, the doors should be closed with all locking mechanisms. It is not recommended to stack ready-made window blocks on top of each other. Between them it is necessary to make inserts from elastic materials and store them in an upright position on wooden pallets or special containers. So, the production of modern PVC window structures is high-tech in nature. As you can see, there are two main factors that should be taken into account by processing companies. First of all, this is the quality of window components, the manufacture of which requires significant recovery and an effective organization of production. In addition, it is necessary to correctly establish the assembly process itself, automating all the links of the technological chain as much as possible - from cutting the profile to installation of double -glazed windows.
Return to list
What else is needed for production?
We have considered only that part of the activity that directly covers the production of profiles, but this is not all. The plant has a special laboratory that controls the quality of products, mixtures for their manufacture, and also develops new compositions for those window models that will be used in specific conditions.
In the laboratory, each batch of finished profile is tested, they are carried out several times a day. There they check the strength of the seams, the profile, and how high-quality the welds are. There is special equipment that checks the whiteness or color of colored elements.
Quality Control Laboratory
German plastic windows are probably the most popular. Read our article “German plastic windows, features of choice.” Don’t know which profile to choose? Read on our website about how to choose a plastic window profile.
You can see the rating of plastic window manufacturing companies at https://oknanagoda.com/okna/plastik/profili/brendy-plastikovykh-okon.html.
Manufacturing of arched structures
Arched windows are made by hand according to a fairly simple principle. The profiles are heated to a state of elasticity and fixed:
Go ahead.
How are glazing beads made?
It became clear what plastic windows are made of, but how are glazing beads produced, the task of which is to hold the double-glazed window in place?
This process is divided into two parts. First, the part of the bead that bears the main load and is hard is made, then pads made of soft PVC are stuffed onto the edges of the product. This is also done using automation, with its own mechanism installed for broaching.
Bead production line
Stages of glazing bead production