We measure and change windows
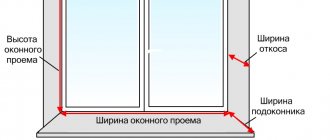
Window opening measurement
Changing windows in an apartment is as easy as shelling pears.
Firms involved in this provide a full range of services in this matter.
The client just has to pay everything.
But before ordering a window, we need to figure out how much it will cost.
At the same time, thoughts about how to calculate the square meter of a window stimulate us to solve this problem.
For the window area, you need:
- Measure height
- Measure the width
- Multiply width by height
- Measure the balcony door separately, the window separately, then add up
The windows themselves are not measured in square meters, we simply calculate the size of the window opening. And this can only be done approximately in order to know the approximate size of the window and its estimated cost.
Specialists separately calculate the size of the frame and the size of the glass unit, but all these are subtleties. The main thing for us is to know how to measure the height (from the window sill, or including the window sill) and width. And when multiplied, we get the desired square meters.
Measurement of plastic windows
Based on the needs of our clients, as well as the demand for plastic window systems of various sizes, the company has developed an exclusive offer: small plastic windows in Moscow at an affordable price. We specialize in the manufacture of high-quality products, which are accompanied by appropriate documentation and certification.
Scope of work performed
To date, we have produced about 200 thousand products for premises in different parts of the capital and region. Buyers choose us thanks to our modern service, which includes the following services:
- consulting professionals to select the optimal window system, components and fittings;
- calculation of the approximate cost of the product;
- accurate measurements using a professional measurer;
- careful delivery;
- high-quality installation of window systems, slopes, window sills, etc.
Metering
Step 1. Measure the opening. Calculating the size of a plastic window.
| Rice. 1: Window opening without quarter. | Rice. 2: Window opening with a quarter. |
Measuring the opening without a quarter.
First, we measure the width of the opening (Wpr), i.e. distance between side walls. To calculate the window size (Wо), it is necessary to subtract the gaps for the mounting seam (Wm) from the obtained value of Wpr. As a rule, 20-30 mm are left under the mounting foam on each side.
Rice. 3: Calculation of the window width for a quarter-less opening.
Then we proceed to measuring the height of the opening (Hpr), i.e. distance between the lower and upper wall.
From the resulting height we subtract gaps of 20-30 mm at the top for the installation seam (Nmv) and 40 mm at the bottom for installing the window sill (Nmn).
As a result, we get the window height (Ho):
But = Npr – Nmv – Nmn
Measurement of the opening and a quarter.
Unlike the quarter-less version, in this case measurements are taken both from the street and indoors.
We measure the opening from the street side (Wul) and the opening width in the apartment (Wkv). The width of the plastic window (Wo) should be 20-50 mm more than Wul and 40-60 mm less than Wsq.
Rice. 5: Calculation of window width for a quarter opening.
We also measure the height of the opening from the street side (Nul) and indoors (Hkv).
If there is a quarter at both the top and bottom, then the height of the window (Ho) is calculated using the formula:
But = Zero + (10…30 mm) – 15 mm
If the quarter is only at the top, then the height (Ho) is calculated using the formula:
But = Zero + (10…30 mm) – (40…60 mm)
| Rice. 6: Calculation of window height for a quarter opening | Rice. 7: Calculation of window height for a quarter opening (without lower quarter) |
Step 2. Measuring the ebb and window sill.
The length of the ebb is determined by the width of the opening on the street side. Allowances of 30-40 mm on each side are added to the width of the opening. The size of the flashing is measured by the depth of the external wall (from the frame to the edge of the wall), plus 20 mm of penetration under the frame, plus 30-40 mm of the projection of the flashing from the edge of the wall.
The length of the window sill is measured by the width of the opening on the side of the room. To this value, allowances of 100 mm are added on each side. The width of the window sill is determined by the depth of the inner wall (from the edge of the wall to the frame), plus 20 mm of overlap under the frame, plus the amount of protrusion of the window sill from the edge of the wall.
When measuring the window sill, it is very important to take into account that it should not cover the heating radiator by more than 1/3. Otherwise, obstruction to the free circulation of warm air may result in the formation of condensation on the glass.
When measuring the tide and window sill, you need to remember that the frame of the new plastic window will be narrower than the old wooden frame. Therefore, the window sill and ebb will be larger in width.
Step 3. Measuring the width of the internal slope.
The width of the slope is determined by the depth of the inner wall from the frame to the edge of the wall. A minimum of 20mm must be added as a trim allowance.
When measuring the slope, you need to remember that the frame of the new plastic window will be narrower than the old wooden frame. Therefore, the resulting slope will be wider.
These measuring instructions will help you determine the preliminary parameters of the window and components to calculate the approximate price.
You can find out the price by calling (multi-channel).
Window calculator
Of course, first of all we will be interested in the final price. For this purpose, a program was invented - a window calculator. What is this?
Most performing companies provide their clients with a unique automatic calculation system - a “window calculator”. With its help you can find out the approximate cost of the structure.
I note that the calculator for plastic windows from one company may differ significantly from another. However, in general the programs are very similar. They look something like this:
Example of calculator functionality for plastic windows
Please note:
- Selecting a window type. This action is the very first in almost any calculator. You are given a choice of many different types, which include the number of sashes, the type of internal structure, etc.
Main types of windows
- Window size. The PVC window calculator is based on the size of the future window. You should use a tape measure and take the necessary measurements. Don't forget to consider slopes as well as compaction.
Measuring the window with a tape measure
- Selecting the country of origin. This point is the second key factor that will determine the future price. Before choosing a manufacturer, study information about it, and in particular, consumer reviews.
- Selection of double-glazed windows. The type of double-glazed window directly affects the cost, and naturally, the single-chamber option is the cheapest. But this solution will not be successful in all cases.
Math for blondes
Mathematics is very simple, even simpler than we can imagine. Complex mathematics is made by mathematicians themselves.
Pages
- Home page
- New mathematics
- Dictionary
Friday, September 17, 2010
We make repairs
Blondes sometimes do renovations too. And here it is impossible to do without the use of mathematics. You need to pay money for repairs. At the same time, the question inevitably arises: how much and for what exactly do they take money from me? Did the builders calculate the cost of repairs correctly? How to calculate the amount of work when renovating an apartment? This is where your knowledge of mathematics comes in handy. And so, if we are doing repairs, then we need to at least approximately know the volume of upcoming work. Calculating the volume of work is a rather tedious task, but necessary. How much wallpaper should I buy? How many tiles do you need to buy? These figures are also taken from the scope of work.
The volume of work is calculated very simply, mainly by the area of the rectangle - the length is multiplied by the width and the area is obtained (in full accordance with the multiplication table). If this is the floor, then the length and width of the room are taken. Measurements are taken with a tape measure between opposite walls above the baseboard. As a measuring tool, you can use a meter, which you use to measure the volume of your hips, waist, and chest. For example, if we have a room measuring 5.0 by 3.0 meters, this room has 15 square meters of flooring.
This is the amount of work involved in laying tiles, laminate, linoleum, screeding, priming the floor, etc. in this room. Additionally, the floor area in the doorway and radiator niche can be taken into account. This area is added to the area we have already obtained. Builders can use work complexity coefficients when calculating estimates, but craftsmen must prove that the work was not performed as standard. For example, in the bathroom, tiles of two colors were cut along a curved line, which, naturally, is more difficult than simply laying tiles. Even choosing a tile pattern may increase the cost of the work.
If the room has a complex shape, then the floor area is calculated from the areas of simple geometric shapes into which you need to mentally divide the room and the formulas for finding the areas for which you know. In my practice, I very often used Heron’s formula to find the area of a triangle based on the lengths of three sides.
If some work is priced in linear meters (for example, installing a baseboard), then this is simply measured with a meter or tape measure around the perimeter of the room. In a room measuring 5 by 3 meters, the perimeter is 16 linear meters.
To calculate the amount of plinth, you need to subtract the width of the doorway, usually 0.8 - 0.9 meters, and add plinth on the door slopes (if the room has one). Let in our case the door be 0.9 meters long, and the door slope be 0.3 meters wide. In total, we will get 15.7 linear meters of plinth installation.
If some work is priced per piece (installation of corners on baseboards, installation of sockets, etc.), this is calculated by poking a finger into the product. The same product twice does not count. You need to keep in mind that installing a socket box and installing a socket are different jobs that are paid at different rates, although they are performed sequentially in one place. By the way, socket boxes are also installed for switches. The check is simple: the number of switches plus the number of sockets is equal to the number of socket boxes. If the numbers do not agree, then we consider the builder’s finger pointing method (now the builder must calculate everything himself in your presence) and listen to his arguments, because there are different situations (telephone socket, television socket, computer socket - they are all placed in socket boxes). The socket box is cheaper than the mounting box and can be used at the junctions of wires - a kind of homeless version of a European-quality renovation.
The ceiling area is calculated in the same way as the floor area - the dimensions are measured from wall to wall. The area of the niches is added, and the area of the columns is subtracted from the area of the ceiling. Typically, the ceiling area is equal to or less than the floor area (remember, the area in doorways and radiator niches can be added to the floor area).
The area of the walls is calculated by multiplying the length of the wall by the height of the room minus the area of door and window openings. Let us have a room height of 2.5 meters, a window measuring 1.4 by 1.5 (height) meters, a door 0.9 by 2.1 (height) meters. Then the area of the walls is equal to the perimeter of the room (we already calculated the baseboard this way) multiplied by the height of the room minus the area of the openings and is 36.0 square meters:
What determines the cost of walls?
Calculation of the cubic volume of plaster solution for walls depends on several factors:
- Wall material - the consumption will be greater when plastering an adobe wall than a brick one.
- Irregularities - the presence of cracks and bulges plays an important role, the sealing of which will require several working layers and priming. According to regulatory standards when using building materials for construction, when putting housing into operation, the level of the walls is checked. It should be the same, without deviations.
In old houses this is not easy to achieve, so they resort to plaster for leveling. Consumption will increase if there are more deviations and cracks.
- Type of mortar - each type of plaster has its own consumption standards per square footage of the room. The calculation is carried out for a specific type of work.
How is a linear meter of slope calculated?
Often, to calculate the cost of finishing window slopes, it is not the area of the slopes that is used, but the length of the slopes, which is measured in linear meters. The length of the slopes is equal to the perimeter of the window and in this case is linear meter(s).
How to count slopes correctly?
The door slope is equal to 5.1 linear meters: If the price for slopes is in square meters, then we multiply the resulting linear meters separately: the length of the window slope in linear meters by the width of the window slope, the length of the door slope by the width of the door slope.
How is a linear meter calculated?
A linear meter is a meter equal to 100 cm in length. ... A linear meter is a value, a unit of measurement of the length or distance of something in meters. Linear meter = meter. Certain segments of surfaces are counted in linear meters for clarification, measuring lengths and distances.
What are slopes in construction?
Slopes are the section of wall between the window and the wall, i.e. the window opening. Slopes can be both external (located outside the window) and internal (located inside the room).
What is considered a slope?
The company that did the interior work states that any wall less than 50cm is a slope.
What is considered a slope when plastering?
if the slopes are plastered, then they are considered linear meters and are subtracted from the area of the walls. It’s another matter if the doorways are in a hard-to-reach place... then the master may ask for a premium for the complexity of the work.
How many linear meters are in 1 meter?
How many mm in a linear meter
As already mentioned, one linear meter is equal to one standard meter. It turns out that there are 1000 mm in 1 linear meter.
How to calculate a linear meter of plinth?
In the store you can easily calculate the price per linear meter of the product. To do this, you need to divide the price per strip by its length in mm and multiply by 1000 mm. For example, one plinth 2.5 m long costs 300 rubles. Next, we calculate the linear meter of the plinth: 300/2500*1000= 120 (rub).
How to correctly reduce a linear meter?
| Code | Unit name | Symbol (national) |
| 018 | Linear meter | linear m |
| 019 | One thousand linear meters | 103 linear m |
| 020 | Conventional meter | conventional m |
| 048 | Thousand conventional meters | 103 conventional m |
How many linear meters are in 1 sq. m?
Or another option is a meter, and the width is 10 centimeters we get 10_100 = 0.1 sq. m. It's simple, to find out how many square meters are in a linear meter, you need to multiply the length by the width. To do this, we need to know the width of the material that needs to be measured in linear meters.
What is the difference between a linear meter and a square meter?
A square meter is a square 1 meter long and 1 meter wide. A linear meter is a rectangle 1 meter long across the entire width of the roll. So how many square meters are in one linear unit? Depends on the width of the linoleum.
How is 1 square meter calculated?
The calculation formula is simple, S = a*b, where S is the area, a and b are the length and width of the room, respectively. In our example (drawing with measurements), instead of small letters, the length is A and the width is B, and the opposite walls are G and B.
What is a door slope?
Door slopes are the walls on the sides of the doorway, decorated with tiles, wallpaper or PVC panels. Door slopes are the walls on the sides of the doorway. ... However, modern trends, especially if this space is not closed by a second door, require a creative approach to the design of slopes.
Plastic
Experts consider finishing slopes with plastic the most successful choice. Especially if plastic sandwich panels, which have good thermal insulation, are used. Moreover, when installing plastic panels, you can install an additional layer of thermal insulation between the slopes and the surface of the plastic.
Finishing window slopes using PVC materials can significantly improve the functionality of the entire window unit by increasing the thermal insulation properties. And special sealants make it possible to achieve complete tightness of the joints of slopes and window profiles. The appearance of plastic slopes is in perfect harmony with the appearance of PVC windows, creating a single, complete structure. In addition, plastic slopes are highly durable and easy to maintain.
How is slope plaster considered?
if the slopes are plastered, then they are considered linear meters and are subtracted from the area of the walls. It’s another matter if the doorways are in a hard-to-reach place... then the master may ask for a premium for the complexity of the work. But this may not apply to all openings.
How to calculate the slopes of windows and doors?
The door slope is equal to 5.1 linear meters: If the price for slopes is in square meters, then we multiply the resulting linear meters separately: the length of the window slope in linear meters by the width of the window slope, the length of the door slope by the width of the door slope.
How much does it cost to plaster door slopes?
Cost of plastering slopes.
The cost of plastering slopes is 350 rubles per linear meter excluding material and 600 rubles per linear meter including material. If it is necessary to plaster radius and other complex slopes, the cost of work is 700 rubles/m. P.
How is a linear meter of slopes calculated?
Often, to calculate the cost of finishing window slopes, it is not the area of the slopes that is used, but the length of the slopes, which is measured in linear meters. The length of the slopes is equal to the perimeter of the window and in this case is linear meter(s).
How to correctly calculate slopes?
Don't know how to calculate the window area? You just need to multiply the width by the height. For example, you chose a single-chamber double-glazed window with a height of 140 cm and a width of 90 cm. Let’s find out the area by converting the indicator into meters: 1.4*0.9= 1.26 m2 – the area of our window.
How to count door slopes?
To calculate the amount of plinth, you need to subtract the width of the doorway, usually 0.8 - 0.9 meters, and add plinth on the door slopes (if the room has one). Let in our case the door be 0.9 meters long, and the door slope be 0.3 meters wide. In total, we will get 15.7 linear meters of plinth installation.
How much is 1 linear meter?
Linear meter is a unit of measurement of the number of long objects (so-called molded products, materials, etc.), corresponding to a piece or section 1 meter long. A linear meter is no different from a regular meter; it is a unit that measures the length of a material, regardless of the width.
How to make slopes on windows from the street?
The best option is a ready-made dry mixture such as Typhoon Master. In addition to cement and lime, it contains polymer additives that make the mixture plastic and resistant to temperature changes. It costs a penny and lasts for years. As for consumption, on average, the external slope of one plastic window requires 2-3 kg.
What is the best way to cover a doorway?
Jambs To avoid covering the door jamb, you need to cover it with masking tape. If there are gaps between the jamb and the walls, they are sealed with mortar or felt, tow, cotton wool, and then with foam and plaster. A layer of solution is applied several times.
What are slopes in construction?
Slopes are the section of wall between the window and the wall, i.e. the window opening. Slopes can be both external (located outside the window) and internal (located inside the room).
How is a linear meter calculated?
A linear meter is a meter equal to 100 cm in length. There is a version that supposedly in the old days the length was measured from the tips of the fingers to the middle of the shoulder strap on the shoulder of an average-sized man, this was a meter, that is, an shoulder strap, a linear meter.
How to calculate the area of a road slope?
the ratio of height and width is 1:1.5) you get a slope width of 2*1.5=3m. If you multiply the length of the slope by the width, you get the projection area. If we calculate the perimeter of the site as the length of the slope, we get: 20*3=60m. sq.
How to calculate the price per linear meter?
It is necessary to calculate as follows: divide 1 square meter of edged board by 120 mm (product width), we get a value of 8.33. This is the number of linear meters.
How to calculate the volume of a pit with slopes?
Calculation of the volume of a pit with slopes
V = (F1+ F2) / 2 ∙ h, where: F1 - bottom area; F2—sectional area at the top of the excavation (zero level of the section); h is the depth of the recess.
What is a linear meter of a window?
Linear meter - measurement of the length of a product. Linear meters measure window slopes, door openings, room perimeter, and roll lengths.
We insulate the inside
Having decided how to insulate the slopes, we move on to practice. Sometimes it happens that when a plastic window is installed, despite good treatment with foam, the glass gets wet and there is a strong blow from the slopes. This is often the result of careless installation, as a result of which the structure will have to be put in order yourself.
Before gluing the foam, it is recommended to scratch its surface
Having figured out in practice how to insulate the slopes of plastic windows inside, we move on to external work.
How to calculate the area of door slopes
Renovation is a troublesome task, but at the same time pleasant, because after it, a private house or apartment becomes cozy, relaxing, and modern.
How to calculate the area of a room is perhaps one of the main questions that often arises before starting renovations. You don’t have to deal with the calculations yourself, but entrust it to a special team of finishers who will deal with the repair itself. What should you do if you have already decided that you will do all the work yourself? In this case, you will have to carry out calculations in a particularly careful manner, since the lack of experience is the result of an overabundance and shortage of one or another material.
Taking wall measurements
Quite a few calculators have appeared on the World Wide Web, which can be used to calculate absolutely all construction values, such as: geometric volumes, dimensions, weight, as well as usable area. It is not always possible to calculate a square meter using programs. In such cases, you have to use the usual calculation method.
To calculate using the usual method you will need: a pen or pencil, a building level or a long rod, a tape measure and, accordingly, a calculator.
1. Before you start measuring, you should clear at least two walls of obstructing furniture. This is necessary, since when calculating the area of a room, including the ceiling, walls, and floor, you can only find out their exact sizes.
2. In order to calculate the area of the walls, you need to take a tape measure and, using it, apply it to the wall along the baseboard and measure the value. To ensure the accuracy of the data obtained, when measuring, you should use a special line, which must be drawn evenly, using a level (staff). The results obtained must be recorded immediately.
3. Then, strictly vertically from the ceiling to the floor, you need to draw a line. In order to successfully measure it with a tape measure, it is best to use a stool, stepladder or table.
How to correctly calculate the area of a rectangle is clear: the width is multiplied by the length. If, at the same time, the length of the room is 5.5 meters and the height is 3 meters, then the wall area will be equal to: 5.5 * 3 = 16.5 square meters.
4. In the same way, it is necessary to calculate and measure all other walls. If there are curves or other complex configurations, you need to divide the wall into several separate areas, and make calculations for each separately.
In most cases, finishing the walls in apartments involves painting or wallpapering them. The available figures for wall areas will be necessary when calculating building materials.
Knowing the area of the walls, how to correctly calculate the wallpaper? It is quite possible that the total area of the walls will differ from the actual area that is subject to wallpapering, since the rooms have doors and windows. They must be subtracted from the total amount.
How to find out the total area of doors and windows?
The area occupied by windows must be measured by its slopes and window sill. The height of a window opening is determined by its side slope, and the width by its upper slope or window sill.
For example, the height of the window is 1.65 meters and the width is 1.55 meters. 1.65*1.55=2.56 square meters.
Plastering technology
Before performing the main work, you should install the window sill, seal the window frame with masking tape, and cut off the mounting foam. After this, it is recommended to moisten the surface with a primer for better adhesion to the plaster solution. It is advisable to apply a frost-resistant sealant to the gap that is filled with polyurethane foam. It will prevent the penetration of moisture from the environment into the room. Only after this they begin to apply plaster. It is distributed over all surfaces using a spoon to form the desired shape of the slope.
vote
Article rating
What is a “linear meter”
To calculate the cost of repair and finishing work or consumable finishing materials, the unit of measurement is often used not “meter”, but “ linear meter ”.
A linear meter is a unit of measurement in meters of the length of an object without taking into account other parameters that characterize it (width and height).
The combination of the words “ running meter ” may have come from the words “drove” and “meter” (“drove” - unrolled or presented something to measure in meters only its length, for example, to measure they unrolled a roll of wallpaper and measured the length of the wallpaper with a tape measure on a roll).
GESN-2001 Finishing work. Calculation of work volumes
ST-SMETA PIR
A program for determining the cost of design work and engineering survey results
MDS ESTIMATED 2020
Program for drawing up construction estimates and checking estimate documentation
STATE ESTIMATED STANDARDS
STATE ELEMENTAL ESTIMATED STANDARDS FOR CONSTRUCTION AND SPECIAL CONSTRUCTION WORKS GESN-2001
State estimate standards. State elemental estimate standards for construction and special construction work (hereinafter referred to as GESN) are intended to determine the need for resources (labor costs of construction workers, machinists, operating time of construction machines and mechanisms, material resources) when performing construction and special construction work and to draw up based on them, estimates (estimates) for the production of the specified work using resource and resource-index methods. GESN are the initial standards for the development of other estimate standards: unit prices at the federal, territorial and sectoral levels, individual and consolidated estimate standards. Approved and entered into the federal register of estimate standards to be applied when determining the estimated cost of capital construction projects, the construction of which is financed with funds from the federal budget by Order of the Ministry of Construction and Housing and Communal Services of the Russian Federation dated January 30, 2014 N 31/pr (as amended Order of the Ministry of Construction of Russia dated 02/07/2014 N 39/pr).
II. Calculation of work volumes
Finishing work
2.15. Calculation of work volumes when using GESN Part 15 “Finishing Works”.
2.15.1. The scope of work on surface cladding with natural stone is determined by the surface area of the cladding. Wherein:
a) the dimensions of walls and columns are taken taking into account the fracture in the plan along the outer contour, i.e. along sections including facing slabs;
b) the area of facing with profiled stones and parts is taken without taking into account the relief of stones or parts (according to the projection of the larger side);
c) the amount of extension of the profiled rod (eaves, platbands, etc.) greater than its height (width) is taken on the larger side.
2.15.2. The scope of work for facing steps and laying window sill boards is determined taking into account the ends of the slabs embedded in the masonry or plaster.
2.15.3. The scope of work on surface cladding with artificial slabs is determined by the surface area of the cladding without taking into account its relief.
2.15.4. The scope of work on covering the surface with artificial marble is determined by the unfolded surface.
2.15.5. The area of plastered walls is determined minus the area of the openings along the outer contour of the boxes. In the area of improved and high-quality plaster of facades, the area occupied by architectural details (cornices, corbels, platbands, other drawn parts), as well as columns and pilasters adjacent to the building, is not included and must be determined separately.
2.15.6. The area of window slopes and ebbs, door slopes, as well as side surfaces protruding from the plane or protruding into the thickness of the walls of architectural and structural parts is determined separately and divided into two groups: width up to 200 mm and more than 200 mm.
2.15.7. The scope of work on plastering columns adjacent to the building or free-standing, as well as pilasters, is determined by the area of their unfolded surface.
2.15.8. The scope of work for pulling out cornices, rods, belts, platbands and other drawn parts for high-quality plastering of facades is determined by the area they occupy on the surface of the facade (as projected onto the wall), and for pulling out cornices with a slope exceeding their height - by their area horizontal projection.
2.15.9. The area occupied by molded parts installed on a plastered surface is not excluded from the total plastering area.
2.15.10. The scope of work on interior plastering is determined by individual premises depending on the type of finishing (simple, improved, high-quality) or by apartment, floor, section, etc. in general, if the type of finishing for all rooms is the same.
2.15.11. The scope of work on plastering internal walls is determined minus the area of openings along the outer contour of the frames and the area occupied by stretched platbands; the height of the walls is determined from the finished floor to the ceiling; the area of the sides of the pilasters is added to the area of the walls.
2.15.12. The scope of plastering work: ceilings (including coffered ceilings with a horizontal projection area of up to 12 m2) is determined by the area between the internal edges of walls or partitions; ribbed ceilings and coffered ceilings with an area of their horizontal projection of more than 12 m2 is determined by the unfolded surface.
2.15.13. Scope of work for plastering side and top window caps and slopes, heating niches in standards 15-02-015-01, 15-02-015-03, 15-02-015-05, 15-02-015-07, 15- 02-015-09, 15-02-015-11, 15-02-016-01, 15-02-016-03, 15-02-016-05, table 15-02-017 and 15-02- 018 taken into account; The volume of work on the installation of lower window plugs is determined additionally by their area, and the consumption of resources for their implementation should be determined according to standard 15-02-031-03.
2.15.14. The scope of work for plastering window and door slopes inside buildings should be determined additionally by their area, and the consumption of resources for its implementation should be normalized according to standards 15-02-031-01, 15-02-031-02.
2.15.15. The scope of work on installing rods for internal platbands should be determined by the area they occupy on the wall surface (as projected onto the wall).
2.15.16. The scope of work for plastering staircases and landings should be determined by the area of their horizontal projection (floor by floor).