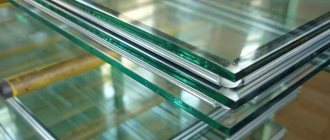
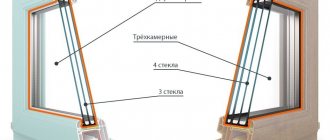
Most often, single-chamber or double-chamber double-glazed windows are installed in the window profile. The most budget solution is single-chamber. A two-chamber one is more expensive, but other things being equal (glass characteristics, filling of chambers) is superior to a single-chamber one in a number of operational characteristics.
It is a more complex and massive design, there are more possibilities for different combinations of elements, and its thickness varies over a wider range.
What does a plastic double-glazed window look like?
Actually, a blind PVC double-glazed window, not yet inserted into the profile, is a glass block usually in the shape of a parallelepiped, the width and height of which significantly exceed the thickness. There are also double-glazed windows of more complex shapes.
Visually, the third glass, located in the middle of the glass unit, is practically indistinguishable. Therefore, from a distance, a double-glazed window gives the impression of an all-glass monolith inserted into a window block.
Up close you can see that this design has glass at the front and back, spacers around the entire perimeter inside, and sealant along the entire contour outside (at the ends, top, bottom).
If the glass unit is already installed in the sash, the sealant and the main part of the spacer frame are hidden from view, only the glass and the side of the spacer (dividing frame) facing the inside of the glass unit are visible, which is visually perceived as a metal (less often polymer) strip with small perforations - diffusion holes.
Without a profile, in the edge zone of the glass unit, the sides of the spacer frame are visible, glued to the glass with a thin layer of sealant.
The easiest way to visually distinguish a double-glazed window from a single-chamber one is to turn off the overhead light in the evening and go to the window with a lighter or flashlight.
The number of reflections of the light in the double-glazed window must correspond to the number of glasses. That is, if you see 3 lights, your double-glazed window really is two-chamber.
Double-glazed windows: main types and features of choice
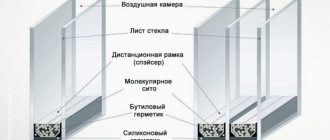
A double-glazed window is a large part of a window, which is a sealed block of two or more sheets of glass. The term appeared due to the peculiarity of the technology used in production for connecting several glasses together into a single hermetic structure. A double-glazed window typically consists of two or three sheets of glass sealed with a high-strength sealant. The space located between the glasses is called the chamber. These chambers in double-glazed windows are filled with ordinary air or inert (rarefied) gas. The second option provides higher sound and heat insulation.
In order to maintain a certain distance between the glasses, spacer frames containing moisture-absorbing material are used. It is important that the frames are made of polyvinyl chloride or aluminum and not steel. The use of such elements makes it possible to protect the glass unit from freezing at the edges.
Thus, a kind of sandwich structure is created in which air chambers are located between the sheets, alternating with each other. The design of the package prevents dirt and dust from entering the space between the windows. The double-glazed window, along with the profile, determines the noise and heat insulation properties of a PVC window. At the same time, this part of the light-transparent structure may have a number of additional options, such as: shock resistance, tinting, design, stained glass.
Double-glazed glass design
Some elements of the glass unit are hidden from view. The composition of a two-chamber double-glazed window includes:
- glass – 3;
- chambers (interglass spaces) with air or gas filling – 2;
- distance (dividing) frames – 2;
- desiccant;
- internal (primary) sealant;
- external (secondary) sealant.
Glass can differ in production and processing technology, PVC profile, composition, coating, color, thickness, and it is on their characteristics that the properties of a double-glazed window largely depend.
It is also important to fill the chamber between the glasses; regular moist air must be pumped out of it; the inside of the glass unit must contain a minimum of moisture, otherwise condensation will negate its heat-protective properties.
The spacer frame is a hollow tube with a cross-section close to rectangular, lightweight but durable. Initially, spacer frames were made of aluminum, less often of steel; later, a technology for producing frames from polymers with lower thermal conductivity than metal was developed.
The frame can consist of four straight segments connected by corners, or bend at the corners. In the second case, the structure has only one joint and the likelihood of depressurization through the joints is significantly reduced.
The spacer is filled with a desiccant (absorbent, desiccant - a substance with a large number of pores), and there are small diffusion holes along the top of the frame. Through them, moisture molecules penetrate from the air in the chamber into the frame and are absorbed by the absorbent. The following are used as a desiccant:
- molecular sieve;
- silica gel;
- a mixture of them.
Primary sealant - butyl mastic or tape, which retains elasticity after hardening, is used to firmly connect glass and frames into a single structure and to protect against water vapor contained outside.
After gluing the glass and frames, a secondary, external sealing is carried out to give the structure additional strength and moisture-vapor resistance. For external sealing, plastic masses based on:
- polysulfide;
- silicone;
- polyurethane.
Read: which double-glazed window is better: single-chamber or double-chamber.
Main technical characteristics
The double-glazed window occupies up to 80% of the entire window and largely determines the noise and heat insulation properties of the light-transparent structure. According to building regulations, in the Moscow region it is recommended to use packages with a heat transfer resistance of 0.55 m2*C/W for glazing. These requirements are fully met by windows with double-glazed windows with a thickness of at least 36 mm, while the profile width should be from 76 to 82 mm.
Thickness. Warm double-glazed windows, as a rule, include three sheets of glass, two air chambers, spacer frames made of polyvinyl chloride, energy-saving glass (marked “I”), which has a higher resistance to low temperatures. The thickness of the entire product is at least 32 mm, and the thickness of one glass is at least 4 mm.
Cold double-glazed windows, intended for installation in well-heated rooms, can consist of two sheets of glass and one air chamber. The permissible thickness of these products is 24 mm.
Thermal protection. When choosing the type of double-glazed window, you should take into account the location and purpose of the room. Single-chamber ones are suitable for loggias, balconies, and rooms where there are no significant requirements for the thermal insulation properties of the product. Double-chamber ones are designed to provide maximum thermal protection. Higher thermal insulation characteristics can be achieved if krypton or argon is used in the chambers, or glass with a special heat-reflecting coating is installed. The use of inert gases between sheets of glass makes it possible to increase the thermal insulation properties by up to 5%. The thermal protection function of a double-glazed window also depends on the thickness of the product, the number of chambers, and the absence of cracks.
Seal. The quality of the seal largely determines the tightness of the double-glazed window and the fixation of the position of the glass sheets inside the PVC profiles. To produce these elements, rubber, rubber, and silicone are used. Silicone products have a longer service life and are installed in expensive transparent structures. The seal allows you to ensure the thermal insulation properties of the window due to its characteristics. Thus, such elements have soft material, elasticity, and the ability to withstand temperature changes. The seal is laid along the joint between the window sash and the frame.
Soundproof. The sound insulation properties of a double-glazed window are affected by the number of air chambers between the sheets of glass, the distance between the glasses, the combination of light-transparent products of various thicknesses, and the presence of additional coating. Therefore, to ensure the required heat and sound insulation properties, various types of double-glazed windows are used.
Source: oknaotk.ru
Double-glazed window: formula, thickness and advantages
Compared to a single-chamber double-glazed window, the formula for a double-chamber double-glazed window is more complicated, it consists of 5 elements, 1, 3 and 5 - glass characteristics (thickness, category), 2 and 4 - chambers (width, filling).
You can calculate the thickness of a two-chamber double-glazed window using this formula by adding all the numbers - the thickness of three glasses and the width of two chambers. A double-chamber double-glazed window can be symmetrical or asymmetrical; different design options for glazing are possible:
- all glass is the same thickness, and the chambers are of equal width;
- the width between the glasses is the same, but the thickness of one of the glasses differs from the thickness of the other two, or all three have different thicknesses;
- different glass thicknesses and different chamber widths.
Thicker glass not only absorbs noise better, but if the thickness of the glass in a double-glazed unit does not match, the resonance that occurs between them is dampened, so that the sound insulation characteristics of the double-glazed window are increased.
The different widths of the chambers also contribute to noise absorption; the best performance will be with an asymmetrical double-glazed window with different thicknesses of all three glasses. The width of the chambers and the thickness of the glass also affect the thermal insulation characteristics, but it is more effective to increase them by replacing standard glass with low-emissivity glass in combination with filling with argon.
The standard thickness of the glass used in double-glazed windows is 4 mm; to improve heat conservation and noise protection, 1-2 glasses are replaced with thicker ones - 5 or 6 mm; glasses of smaller and larger thickness (3 or 7-8 mm) are used much less frequently, on order.
The width of the chambers in double-glazed windows often varies in the range of 6-16 mm. Double-glazed windows with a width (mm) available on the Russian market are:
- 24, with 6 mm chambers between 4 mm glasses;
- 32, along with the formula (4-10-4-10-4), the options (6-8-4-8-6), (4-10-4-8-6) are used;
- 36, 12 mm chambers, 4 glasses;
- 40, 14 mm cameras.
Double-chamber windows of greater width - 42, 44 mm - are still a new product, the standard formula of the latter (4-16-4-16-4), its sound insulation and heat transfer resistance are the maximum among all of the above, but the weight is also the heaviest.
In terms of performance characteristics, taking into account the price, the thickness of the double-glazed window is considered to be 40 mm; another popular solution is a double-glazed window of 32 mm.
Theoretically, the thickness of a double-glazed window can reach 72 mm if the interglazing spaces are widened to 24 mm and thickened glass of 8 mm is used. And the minimum width, based on technical conditions, is 24 mm.
Main varieties
Depending on the type and design features, double-glazed windows come in the following types:
- single-chamber - products include two glasses with one air chamber between them;
- two-chamber - consist of three different sheets of glass with two independent air chambers.
When choosing a product, it is necessary to take into account the degree of illumination and the practical purpose of the room. Single-chamber double-glazed windows are more affordable, but have lower light transmittance and thermal insulation properties. Double-chamber packages provide high light transmission, heat and sound insulation characteristics.
Single-chamber structures in our weather conditions can only be used for glazing loggias, balconies, warehouses and industrial premises. But here it is worth considering that special single-chamber double-glazed windows consisting of low-emissivity glass are currently being produced. This is a special type of glass containing silver, which retains thermal radiation and selectively transmits ultraviolet rays. Such products can compete with conventional two-chamber ones in their properties, but at the same time they have a more affordable price.
Double-glazed windows differ from each other in quality characteristics, their composition, and the thickness of the structure. Thus, a special coating prevents the penetration of infrared rays, which makes it possible to reduce the heat loss rate of the structure. At the same time, the translucent properties of the glass unit remain unchanged. In summer, such products provide the necessary coolness; in winter, they make it possible to retain heat in the room. Coverings can be either hard or soft. The former have high moisture resistance and are used in practice more often than the latter. Sun protection on double-glazed windows is created by spraying a thin layer of metal oxide coating, or by installing specially painted products.
Double-glazed windows may have fire-resistant properties. This is achieved by installing a metal mesh that securely holds the glass even when exposed to an open flame. There are shockproof packages consisting of laminated glass and covered with triplex, a special film that provides high noise insulation and does not allow direct sunlight to pass through. There are double-glazed windows with tempered sheets of glass, like in vehicles. Such products, upon impact or mechanical impact, break into small pieces with blunt edges. Double-glazed windows are also produced, inside of which an inert gas (argon or krypton) is used instead of air. Such packages are distinguished by high heat and noise insulation properties, but at the same time they are significantly more expensive than standard analogues.
Parameters of gas-filled double-glazed windows.
Results of experimental studies of double-glazed windows
(lab. G.G. Farenyuk, NIISK, Kyiv)
| No. | Number of cameras | Glazing options | Gas composition, % | Heat transfer resistance, R def. m2 K/W | |||
| Air | Krypton | Argon | Xenon | ||||
| 1 | 1 | 100 | 0,32 | ||||
| 2 | 1 | 100 | 0,38 | ||||
| 3 | 1 | 100 | 0,53 | ||||
| 4 | 1 | 100 | 0,67 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 100 | 0,7 | ||||
| 6 | 1 | 100 | 0,59 | ||||
| 7 | 1 | 100 | 0,78 | ||||
| 8 | 1 | 100 | 0,83 | ||||
| 9 | 1 | 75 | 25 | 0,73 | |||
| 10 | 1 | 50 | 50 | 0,7 | |||
| 11 | 1 | 50 | 50 | 0,79 | |||
| 12 | 1 | 25 | 75 | 0,67 | |||
| 13 | 2 | 100 | 0,45 | ||||
| 14 | 2 | 100 | 0,51 | ||||
| 15 | 2 | 100 | 0,47 | ||||
| 16 | 2 | 100 | 0,59 | ||||
| 17 | 2 | 100 | 0,91 | ||||
| 18 | 2 | 100 | 1,16 | ||||
| 19 | 2 | 75 | 25 | 0,88 | |||
| 20 | 2 | 50 | 50 | 0,82 | |||
| 21 | 2 | 50 | 50 | 0,89 | |||
| 22 | 2 | 25 | 75 | 0,81 | |||
| 23 | 2 | 100 | 0,73 | ||||
| 24 | 2 | 100 | 1,48 | ||||
| 25 | 2 | 100 | 1,54 | ||||
| 26 | 2 | 100 | 0,64 | ||||
| 27 | 2 | 100 | 1 | ||||
| 28 | 2 | 100 | 1,34 | ||||
| 29 | 2 | 75 | 25 | 0,94 | |||
| 30 | 2 | 100 | 0,93 | ||||
| 31 | 2 | 50 | 50 | 0,9 | |||
| 32 | 2 | 50 | 50 | 0,92 | |||
| 33 | 2 | 25 | 75 | 0,81 | |||
| 34 | 2 | 100 | 1,58 | ||||
| 35 | 2 | 100 | 1,93 | ||||
| 36 | 2 | 75 | 25 | 1,48 | |||
| 37 | 2 | 50 | 50 | 1,36 | |||
| 38 | 2 | 50 | 50 | 1,48 | |||
| 39 | 2 | 25 | 75 | 1,3 | |||
Example: 4M1-(Kr75/Ar25)16-4I – On the street side, uncoated glass 4 mm thick, a gas layer 16 mm thick, filled with a mixture of 75% krypton and 25% argon, glass with a soft low-emission coating 4 mm thick.