The invention of low-e glass has revolutionized energy conservation. What is i-glass, is it really 80% warmer than regular glass, is discussed by the WINDOWS MEDIA portal.
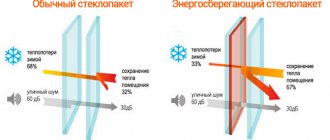
Before the advent of energy-saving technologies, the largest heat loss in a building occurred through windows (about 40%). The bulk of the heat escaped through the glass, and its area in the window occupies up to 85%. With the advent of modern “Euro-windows” - with double-glazed windows and fittings, the situation improved, but the double-glazed window still remained an energy “hole” in the window. Ordinary float glass, even as part of a 2-chamber double-glazed unit, was cold and let a lot of heat into the street. Therefore, the emergence of low-emissivity glass, in particular I-glass, has made it possible to raise the heat efficiency of modern windows to a new, previously unattainable level.
Low-E glass – a revolution in energy saving
Low-emissivity glass is glass with a special coating that is invisible to the eye and low emissivity - the ability to transmit heat, which is why it is called low-emissivity. In winter, glass reflects heat from heating objects back into the room, reducing heat loss.
Photo: I-glass retains heat indoors in winter The advent of low-e glass has changed the architectural appearance of modern buildings. Panoramic floor-to-ceiling windows, all-glass facades, glass skyscrapers - all this became possible thanks to a new breakthrough technology.
Definition
Low-emissivity glass
- These are glasses that have high light transmittance and transparency and at the same time provide fairly high thermal insulation coefficients. In other words, due to their transparency, they allow sunlight to penetrate into the room, and the heat and thermal energy accumulated inside the premises from heating objects to be reflected into the room.
From a technical point of view, such glasses are polished glass, on which a special coating of metal oxides is applied, which reduces the proportion of energy emitted by the glass in the direction of this coating. That is, if in the case of ordinary glass, the energy accumulated by it is radiated with the same intensity both inward and outward (which means heat loss), then in the case of low-emissivity glass, the intensity of radiation outward decreases many times, and heat loss decreases accordingly.
Types of Low-E Glass
There are 2 types of low-e glass: K-glass and I-glass (I-glass). They differ significantly from each other - in terms of heat saving level, production technology, type of coating and possibilities of use.
K-glass – “warm” glass with a hard coating
Low-emissivity glass with a “hard” coating is so called because it is resistant to mechanical damage (scratches) and weathering.
Features of K-glass production. During the glass manufacturing process (“on-line” method), a transparent layer of indium-tin oxides is applied to its surface using pyrolysis. The coating reflects heat 4 times better than ordinary glass (the emission coefficient of K-glass is 0.2; ordinary glass is 0.85).
I-glass – “warm” glass with a soft coating
Low-emissivity glass with a “soft” coating is so called because it is susceptible to mechanical and atmospheric influences, while at the same time it has the best heat-saving characteristics (emissivity coefficient is only 0.04).
How I-glass is produced. A silver-based coating is applied to the glass after its production - “off-line” method. The thickness of the nanolayer is only 0.08-0.012 microns, so it is invisible to the human eye.
Photo: technological process for the production of I-glass Currently, K-glass glass is practically not used in the window industry, but I-glass has become widespread.
i-glass produced in Russia must meet the requirements of GOST R54176-2010: “National standard of the Russian Federation, Glass with low-emissivity soft coating. Technical conditions".
Principle of operation
The principle of operation of low-emissivity glass is seen in the mirror. Only it reflects everything and on one side, and glass, thanks to a special thin film, only infrared, they are also called thermal waves, and on both sides. The reflective film transmits electromagnetic radiation of the visible spectrum (light). True, at the same time, the loss of luminous flux increases slightly, up to 10%.
Thanks to this structure, heat does not go outside in winter, and does not enter the room in summer. Sunlight penetrates freely into the home all year round.
The ability of any surface to absorb heat with its subsequent release is designated by the term “emissivity”. This indicator is estimated from 0 to 10 (you can also find from 0 to 1). For ordinary glass, the emissivity coefficient or surface emissivity (E) is 9 (0.89), hard-coated glass (k) is from 1.8 to 4 (0.18-0.4), low-emissivity glass with soft coating is from 0.3 to 1.9 (0.03-0.19).
The given figures show the high efficiency of low-emissivity glass.
Position of I-glass in a double-glazed window
- When installing one I-glass in a 2-chamber double-glazed unit, the glass should be located in position No. 5 (outmost - on the side of the room) with the coating facing inward. I-glass in a single-chamber double-glazed window is installed as in a two-chamber double-glazed window - with the outermost coating inside the double-glazed window. If one I-glass is placed outside (with the coating inside the glass unit), the heat-saving properties of the coating will be preserved, but on the side of the room there will be ordinary glass, on which the likelihood of condensation will be higher.
Photo: location of I-glass in a double-glazed window and position of i-coating (street to the left of the double-glazed window, room to the right) - When installing two I-glasses in a 2-chamber double-glazed unit, the glass covering positions should be No. 2 and No. 5 (the outermost glass on the outside and inside the room).
Photo: location of 2 I-glasses in a double-glazed window and position of the i-coating (in red)
| Attention! Installing i-glass in position 3 (middle glass in a double-glazed unit) is not recommended due to the possibility of thermal shock. This option is possible if the glass is tempered. |
How to determine an energy-saving double-glazed window when purchasing
If in a regular double-glazed window the glass is simply sealed, there is a frame between them, and they are filled with sealant around the perimeter. The glass unit with energy-saving glass contains inert gas. Argon is used most often. It is pumped between the glasses and prevents them from freezing in winter.
You should pay attention to the labeling. It is significantly different for an energy-saving double-glazed window
The regular one is marked 4-16-3, and the energy-saving one is 4-16 Ar-4I.
The marking of energy-saving double-glazed windows in the following example can be deciphered as follows: Ar10-4M1-Ar10-I4, we have a two-chamber double-glazed window filled with argon, the thickness of one sheet is 4 mm, one of them has an energy-saving I-coating applied to it.
In Russian climatic conditions, energy-saving glass allows you to install a single-chamber double-glazed window, instead of the usual two- or three-chamber one, which is also beneficial. And proper care of plastic windows will allow them to last for decades.
To check whether a double-glazed window is energy-saving, you will need to bring a flame to it. To do this, just light a lighter. If the glass is ordinary, then the color of the flame will not change in reflection.
If the double-glazed window is energy-saving, then in the reflection of one of the glare of the flame a reddish tint appears. This is the most affordable way to check a double-glazed window for energy saving.
Checking a double-glazed window for energy saving can also be carried out using other methods. One of them is called the Flare Method. If you look at the glass at an angle, you can easily notice a bluish-violet tint on its surface, like on a car windshield.
The use of the “scientific method” is not accessible to everyone. It requires the use of special expensive devices. High-precision equipment can accurately check whether the glass has an energy-saving coating, what the thickness of the glass is, and even derive the formula for the glass unit.
Today, such devices are available to large construction organizations, whose immediate task is to constantly monitor the quality of work of window companies performing glazing of objects.
When going to a hardware store, you need to take a fire source with you. Now, knowing how to test an energy-saving window with a lighter, you can easily put this into practice.
Advantages of I-glass
I-glass has the following advantages:
1. High heat saving. Emissivity of ordinary glass (emissivity): 0.85, K-glass: 0.2, I-glass: 0.04. The lower the emissivity of the glass, the less heat is lost through it.
Heat saving (reflection of heat back into the room) of various types of glass, Float glass, K-glass and I-glass, %
Source: WINDOWS MEDIA 2. “Warm” glass. I-glass is also called warm glass. In the process of reflecting heat from the low-emissivity coating, the glass itself is additionally heated, reducing the likelihood of condensation forming on it .
| Attention! When purchasing a window with I-glass and an aluminum spacer frame, it is recommended to give preference to a 2-chamber double-glazed window instead of a single-chamber one. In particularly cold regions, it is advisable to use a “warm” spacer, for example, made of plastic and steel. These measures will help reduce heat loss at the junction of the glass and the spacer frame and prevent condensation, and in some cases, the formation of ice. |
What is an issue of securities
This process refers to the issuance of bonds and securities for the purpose of their subsequent sale to individuals and legal entities. A security or bond is a document that confirms the property rights of its owner. Emissions of this type are also controlled by state legislation.
The main purpose of issuing securities is to raise funds. In the vast majority of cases, issuers are included in this process for the following reasons:
- Formation of primary authorized capital.
- Increase the authorized capital.
- Control or splitting of previously issued securities and bonds.
- Change of organizational and legal form of a legal entity.
- Revision of the scope of property rights under previously issued securities and bonds.
- Attracting free investments (replenishment of equity capital).
- Attracting paid investments with subsequent payment of dividends.
After making a decision to issue securities, the company issues them and subsequent state registration. Violation of the procedure for issuing bonds in the Russian Federation provides for criminal liability. Information about bonds is posted on the securities prospectus for free review by all interested parties.
Disadvantages of I-glass
When purchasing windows, you need to consider the following features I -glass .
- I-glass is used only as part of a double-glazed window. The low-emissivity coating of I-glass is not resistant to mechanical and atmospheric influences. If it is installed as a single one, it will oxidize from contact with air (rainbow spots will appear, like from gasoline).
Photo: classic I-glass can only be installed as part of a double-glazed window with the coating inside
Therefore, I-glass is installed with a coating inside the glass unit, where there is no access to oxygen.
- Reduces light transmission. I-glass has a lower natural light transmittance compared to conventional glass by 9% and K-glass by 3%. This is almost invisible to the human eye.
- Impossibility of hardening. Most types of I-glass, unlike K-glass, cannot be tempered (made stronger and safer) due to the destruction of the soft coating.
General information about glass
Energy-saving glass is the simplest double-glazed window in appearance, which reduces heat exchange between the outside air and the room. This technology helps maintain optimal conditions both in winter and summer. At the same time, minimal use of additional equipment is planned. Now there are several options that allow you to improve the quality of glass:
- The space between the windows is filled with argon.
- Sputtered film is applied.
- Part of the outer surface is sprayed.
Regardless of which method is used to obtain the effect, the result will be identical. Here the throughput deteriorates, which leads to small temperature differences. But at the same time, the window can bring results both in winter and in summer. At the same time, such windows now have both their advantages and disadvantages. We need to talk about them, because they will significantly influence your purchasing choice.
Special requirements and errors
When producing double-glazed windows with I-glass, unlike ordinary glass and K-glass, it is necessary to comply with special requirements, which, if violated, may cause problems with the windows over time.
Photo: oxidation of low-emissivity i-coating on glass The most common violations in the production of double-glazed windows with i-glass are:
- Violation 1. If the coating on the edges of the i-glass is not removed (at the junction of the glass with the spacer frame and the sealant), then after some time the glass unit will depressurize and the i-coating will oxidize (stains will appear) from moisture in the air. Such glass will not perform its functions effectively; the glass unit will need to be replaced.
- Violation 2. Incorrect installation of I-glass in a double-glazed window (i-coating outward). Initially, if the glass is installed incorrectly, the difference will not be visible, but over time, the “soft” low-emissivity coating will oxidize and rainbow stains will appear. Such double-glazed windows will have to be replaced.
- Violation 3. I-glass was not placed in the 5th position (when there is only one I-glass in the double-glazed window).
And why do we need gas?
If, instead of ordinary air, an inert gas is pumped between the glasses, heat will be transferred at a lower speed, since these substances are characterized by low thermal conductivity. In addition, the glass filler will be completely devoid of water molecules capable of forming condensation. Water is an excellent conductor of heat, and the less it is, the more efficiently energy is stored.
Is it worth overpaying for window packages assembled using this technology? It is believed that argon reduces energy losses by approximately one tenth, which in reality is very difficult for an ordinary person to notice. Most users note that they did not feel any significant difference. On the other hand, it cannot be denied that the use of special gases improves the performance of window systems, and with a high level of heat retention can provide additional improvement. But when installing a regular plastic window, filling the chambers with argon or krypton does not bring any real benefit - the energy losses are large enough that a tenth does not play any significant role.
Heat saving of various types of windows with I-glass and regular glass
The difference in the heat-saving properties of windows of various configurations is as follows.
Heat saving of various types of windows
Source: WINDOWS MEDIA*The starting point is the level of heat saving of a window made of a plastic profile 70 mm wide with a 2-chamber double-glazed window (3 glasses) with ordinary glass (heat transfer resistance (0.53 m² °C/W). This is the standard configuration of a window for a residential premises in central Russia.
The heat-saving characteristics of windows increase significantly when using a wider profile (80 mm) and two I-glasses in a double-glazed unit.
| Attention! Although the heat saving indicators of a window from a 60 mm profile with a 2-chamber double-glazed unit and a window from a 70 mm profile with the same double-glazed unit differ by only 6%, it must be taken into account that windows with a narrower profile will have additional problems - the appearance of condensation and even ice on the inside slope of the wall near the window. Windows made from a 60 mm profile are considered obsolete and undesirable for installation in residential premises. |
Energy efficient glazing - in every home
Saving energy costs and efficient use of resources is no longer a problem only for the private home owner who counts his expenses, but also an issue that is being considered at the government level. Savings at the regional level can reach millions of rubles just through energy-efficient glazing.
What kind of glazing is called energy efficient?
Glazing that has characteristics of reduced heat transfer resistance and air permeability that exceed the basic requirements of regulatory documents for a given climatic region by more than 10% is called energy efficient. The category of energy-efficient window units includes plastic windows with energy-saving double-glazed windows.
Prices for double-glazed windows from Etkos
| Nomenclature | Formula | Price | Notes |
| SINGLE CHAMBER | 4+16+4 | 1200 | Package thickness from 14 mm to 36 mm |
| 5 mm | 250 rub. | one glass 5 mm to the price with/pack | |
| 6 mm | 300 rub. | one glass 6 mm to the price with/pack | |
| any | Dog. | For sizes over 2,250x1,605 mm | |
| DOUBLE CHAMBER | 24-32 mm | 1500 | 4+6+4+6+4, 4+8+4+8+4, 4+10+4+10+4, etc. |
| 34-40 mm | 1550 | 4+12+4+12+4, 4+8+4+16+4, etc. | |
| 42-44 mm | 1650 |
Specialists will provide you with expert assistance in choosing double-glazed windows. You can order glazing of windows, balconies, entrances, place an order for the installation of glass in private homes or commercial premises. You can get more information by phone in Moscow.
Issue timing
The timing of the issue of securities is influenced by various factors:
- how quickly the decision on the issue will be made;
- how soon will they find an intermediary and conclude an agreement with him;
- deadlines for state registration of the issue.
Deadlines for registering shares in Russia:
- issue upon establishment of a joint stock company – up to 20 days;
- additional issue – up to 20 days;
- issue during reorganization – up to 30 days;
- report on the results of the issue – up to 14 days.
According to Russian legislation, no more than 1-3 months should pass from the moment the decision on the issue is made to the registration of securities.
- no later than 1 month, it is necessary to register the issue when distributing securities among the founders, when issuing bonds or convertible shares;
- up to 3 months in other cases.
Comments: 1
Your comment (question) If you have questions about this article, you can tell us. Our team consists of only experienced experts and specialists with specialized education. We will try to help you in this topic:
Author of the article: Klavdiya Treskova
Consultant, author Popovich Anna
Financial author Olga Pikhotskaya
- Violetta
01/09/2022 at 00:32 Thank you for such a useful and informative article.
Bravo! Reply ↓
Emission policy in Russia
The basic principles of the emission policy in our country are as follows:
- Monopoly. Only the Central Bank regulates the volume of money supply; it injects money supply, and it also withdraws it depending on current tasks.
- The absence of the obligation to provide the gold reserve that we have in our country today is not enough for the ruble to be fully backed by gold. The situation is the same in most other countries.
- The principle of par. The ruble is the monetary unit of Russia; the manufacture of analogues or the introduction of other units is prohibited by law.
- Rubles are accepted for payment throughout the country. Banknotes are interchangeable - a 5 thousand ruble bill is always 5 1 thousand ruble bills or 10 500 ruble bills.