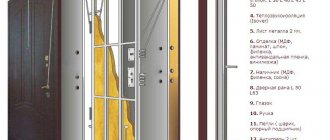
General information about glass and fused materials
Depending on the source raw material, three types of fused materials and products are distinguished:
- glass and glass products;
- slag cast products;
- fused stone products (rocks).
Glass is the most widely used material. Among slag products and materials, cast paving stones for paving roads and crushed stone for concrete have become widespread. Special acid-resistant, fire-resistant and facing materials are made from fused rocks.
In structure, fused materials can be amorphous (transparent or opaque), such as glass, or partially crystalline (fused products from rocks or slag, all opaque). In terms of chemical composition, these fused materials are various silicates, aluminosilicates, in particular magnesium silicates, less commonly borates, phosphates, etc.
How to make it opaque?
You can achieve a matte glass texture:
- chemical and mechanistic methods;
- using a sandblaster.
Follow the instructions below and you will learn how to make glass opaque.
It is easier and safer to use a mechanical method based on the use of abrasive paste or sand.
You need to take polished glass with a thickness of 4 to 6 mm, place it on a flat surface, placing a thick cloth under it.
Thin spatulas need to be nailed to the sides of the glass so that it does not slide on the table.
Prepare sand (river sand or corundum sand is best: it scratches glass more smoothly), then sift it through a sieve until smooth .
Then apply sand to a board measuring 20 by 30 cm and moisten it with water. Place glass on top of the board, and any weight on top of the glass so that it presses it tightly to the surface.
Move the board parallel to the side edges of the glass. Do not make circular movements under any circumstances.
Moisten the sand as it dries.
Periodically check whether the matting process is successful by removing sand from the surface and holding the glass up to light. Continue the procedure until you get the expected result.
Characteristic features of different types of glass
Window glass
Machine-made window glass is made with a thickness of 2-3-4-5-6 mm, most often glass with a thickness of 2 mm is used. Window glass is produced in the form of sheets ranging in size from 250x250 to 1600x2200 mm. Deviations from the specified dimensions are allowed: width and length +2 mm and -6 mm, thickness +2 mm. Glass is produced in two grades, for which the standard: limits the degree of curvature, stripes and waviness, the number of bubbles, scratches, pebbles, etc. Ordinary window glass transmits at least 84% of the rays of the visible part of the solar spectrum. In addition to it, other types of glass with other light transmittance values are manufactured and used, as well as special glasses described below.
Decorative glass
Decorative glass, one or both surfaces of which have some kind of pattern obtained by sandblasting, etching, engraving, etc.; This glass transmits, depending on the pattern, from 20 to 80% of the rays of the visible part of the spectrum
Uviol glass
Uviol glass is best - quartz, with a content of Fe2O3 < 0.01%), transmitting, in addition to the rays of the visible part of the spectrum, at least 25% of ultraviolet rays; it is used for glazing individual premises of kindergartens, medical institutions, greenhouses, etc.
Heat-absorbing glass
transmitting up to 60% of the rays of the visible part of the spectrum and absorbing at least 60% of solar thermal rays; it is used for glazing shop windows, windows of special warehouses, refrigeration units and individual premises of medical institutions.
Reinforced glass
Heat-absorbing glass with a smooth or patterned surface, plain or colored, with a metal mesh inside; it is used for glazing skylights, staircase openings and rooms where increased bending and impact strength, as well as fire resistance, are required; When such glass breaks, it does not produce fragments.
Tempered glass
Tempered glass (transparent and tempered, colored and clear), which has increased strength and thermal resistance; this includes safety glass - “Stalinite”, which does not splinter, but disintegrates into small cellular particles without cutting edges; These glasses are used for glazing shop windows, doors, etc.
Semi-tempered glass
Semi-tempered glass with increased strength. Bent glass (annealed and tempered) - for glazing curved surfaces.
Light-scattering glass
Light-diffusing glass (frosted clear or colored, dimmed colored or milky white), giving diffused light in the complete or partial absence of visibility; it can be corrugated, smooth, single-layer and overlaid, i.e. two-layer; used for glazing industrial premises that require diffused light, exhibition premises, medical and children's institutions, etc.
Colored glass
(decorative) transparent of all colors and shades can be single-layer (smooth and corrugated, reinforced and patterned) and overlay, consisting of layers of clear and colored glass.
Showcase thick glass
Thick display glass, 5-12 mm thick, is made on a continuous rolling mill, then slowly cooled, then ground and polished. This glass is used for large window openings. Residential, cultural and industrial construction, the construction of high-rise buildings, requires more and more high-quality polished mirror glass.
Shelf
Glass shelves are popular because they can easily fit into any interior . In addition, they can withstand significant loads, although they seem fragile.
Glass furniture looks good in small rooms - because of its transparency, it seems less noticeable, so it does not visually take up space in the room.
The location should be accessible to adults, but inaccessible to children (so that the child cannot hang on it).
To make a shelf you will need:
- glass cutter (it is more convenient to use an oil cutter);
- belt-type sander with abrasive sandpaper (grit value should be 120 units);
- respirator, gloves and other protective equipment;
- rulers (you will need to periodically check whether the layers are even).
It is created in the following order:
- You need to prepare a template , knowing in advance the exact dimensions of the shelf, as well as measuring the angles between the walls where it will be installed. The task is to take the most accurate measurements so that in the future the glass structure fits perfectly against the wall.
- Cut and process glass of suitable size. This can be done using a glass cutter. You need to make one cut and then break the glass along a pre-designated line. In case of an error, it is better not to make repeated cuts to the glass, otherwise scratches or cracks may form. To begin with, you can practice and cut several pieces of unnecessary glass.
- Glass sections also need to be processed. Otherwise, when using the shelf and using it carelessly, there is a risk of injury. When performing grinding, periodically wet its surface (this will remove dust, which can get into the lungs when cutting, and also make the surface of the glass transparent).
- All that remains is to fix the glass structure. The fastening itself must be reliable and aesthetically pleasing. Holders or an aluminum profile are suitable for this.
Glass making methods
Glass materials used in construction include: sheet window and other glass, structural products, architectural and decorative products, thermal insulation materials and pipes. The high technical and architectural advantages of glass (especially polished and colored) and glass products provide great prospects for the use of glass in our construction.
Glass is a supercooled melt of complex composition, consisting of a mixture of silicates and other substances, with a gradually increasing viscosity, which solidifies upon cooling. It is amorphous, homogeneous and isotropic. The process of transition from a liquid to a glassy state is reversible.
The chemical composition of the most common window glass is as follows:
- Si02 - 71-72%;
- CaO - 7.5-8.5%;
- MgO - 3-3.5%;
- Na2O - 15-15.5%;
- А12О3 - 1.5-1.6%;
- Fe2O3 up to 0.2%.
The main raw materials for glass production are: pure low-iron quartz sand, limestone and soda or sodium sulfate.
Glass melting is carried out mainly in bath furnaces at temperatures up to 1500°. During the glass melting process, silicates are formed, the glass melt is clarified, it is given homogeneity, and it is partially cooled to acquire the viscosity necessary for molding products.
Molded glass products undergo a special heat treatment - stress-relieving annealing or tempering (see below, tempered glass). The production of window and other types of glass is mechanized.
The usual method of making window glass on vertical drawing machines is to lower a fire-resistant float (boat), which looks like a long rectangular beam with a through longitudinal cutout that turns into a narrow slit at the top, into the molten glass mass, cooled to approximately 1000°. The glass mass is squeezed through a slot, formed into a ribbon of a certain thickness and cooled as the ribbon passes between refrigerators. The tape passes between several pairs of transport rollers and is then cut into sheets.
In addition to this conventional method of producing sheet glass, another method of glass drawing, boatless, is used, which produces glass of higher quality.
Photo frame
A more difficult operation will be decorating frames, panels and paintings.
Before making a frame with glass, you will need to prepare:
- a sheet of fiberboard of a suitable size (dimensions are selected based on the intended design);
- broken glass (transparent and colored);
- acrylic paints, gouache or ink;
- glue.
A thick layer of acrylic paint is applied to the fiberboard sheet. If desired, you can cover it with one or more shades . This is necessary to prepare the background. When everything is dry, the sheet needs to be inserted into the frame of the future product.
Then, on the future panel or painting, you need to apply the contours of the planned design using a stencil or by hand.
This is why ink or gouache was needed - to circle the outlined lines twice and glue the fragments along them.
Having pasted them in the background area, you need to let the product dry.
Properties of glass
Glass has the following properties:
- the bending strength of ordinary (annealed) glass is at least 450 kg/cm2,
- semi-hardened - not less than 1000 kgcm2,
- tempered glass “Stalinite”—2500 kg/cm2;
- hardness (on the hardness scale) - 5 and above;
- volumetric weight - 2500 kg/m3;
- When heated, the glass softens.
Hydrofluoric acid (hydrofluoric) acid corrodes glass, so it is used for etching designs on glass and for giving it a matte surface. Sulfuric acid acts much weaker, other acids act very weakly. Alkali solutions and even water, especially warm water, although very slowly, spoil glass. Water extracts some of the alkalis from it, and the released silica is released to the surface in the form of scales, and the glass first begins to cast all the colors of the rainbow, then becomes cloudy and rough.
Mirror
The easiest way is to decorate mirrors using shards (colored or transparent). This can be done with vases, candlesticks, and trays.
Since the essence of the decoration is gluing pieces of glass, be sure to wear rubber gloves before starting work; they will protect your hands from cuts and allergies to substances contained in the glue.
On the surface of the object you must first apply pattern markings along which the fragments will be laid out. Only ceramic glue is suitable, layers of which must be applied using a special tool - scrapers.
If transparent pieces of glass were used, they can be painted with acrylic paint designed for working on glass.
After the layer with the fragments has dried a little, the holes between them can be sealed with tile putty or mosaic cement. You need to act carefully, but there will still be excess. You can remove them using a damp cloth.
This is what mirror frames made in this style look like.
You can decorate in a similar way:
- frames for photographs, mirrors, paintings;
- flower pots;
- caskets;
- drawers;
- countertops and other items.
Main:
- accurately calculate the number of pieces of glass (prepare paint to finish painting the transparent pieces);
- apply clear markings and indicate where and what layer will need to be laid.
Technology
To enhance or weaken the properties of compounds, amplifiers, opacifiers, dyes, decolorizers, etc. are added to the melting process. After cooking, the mass is quickly cooled, which avoids the formation of crystals. Of all the components, the largest percentage in the recipe is sand - from 60 to 80%. The sand acts as a framework around which a glassy material is formed. Glass production technology has remained unchanged for centuries.
Lime is another component without which glass cannot be produced. What is calcium oxide in the ingredients? This component gives the material chemical resistance and enhances shine. Glass can be melted only from sand and soda, but without lime it will dissolve in water. The third player in the charge is metal oxide - sodium or potassium (up to 17%). It is added to the mixture in the form of soda ash or potash. These components reduce the melting point, allowing individual grains of sand to completely melt and combine into a monolith.
Atriums
An ancient Roman invention, the atrium, is especially popular. Previously, this was the name for the covered courtyard, into which other rooms opened. About ten years ago, atriums were erected mainly in shopping centers and train stations; subsequently, this architectural element began to appear in hotels, business centers, banks and private homes.
From an architectural point of view, an atrium is a spacious room, the height of which is several floors. The atrium can have a direct connection to the rooms located on the floors of the building, or be completely isolated. Sometimes it forms a kind of “light well” for adjacent rooms, from which it is separated by windows. Atriums play a special role in public and residential development: they serve as decoration for houses and perform useful functions. Sometimes the atrium air space is used for forced air circulation.
ShareLikeClass TweetPinSubscribeWhatsappTelegram
How to make a hole?
A hole in the glass can be drilled using:
- drills with flexible shaft;
- dental burs.
The structure itself can be machined , but the fragility of the glass must be taken into account. Therefore, it is necessary to calculate the force and impact points, as well as the operating procedure.
The processing should not lead to cracks, breaks and chips on the main surface, otherwise the entire product may break.
Before making a hole, you need to prepare the glass for processing. The working surface must be cleaned and leveled. Watch for defective areas - under mechanical stress they can chip and damage the workpiece.
First, make markings: mark the lines of future holes so that surface flaws are located inside the circle and do not extend beyond its limits. Additionally, you can treat the surface with chemicals , ridding it of oil traces.
Determine where the work will be done. You need to prepare the fixing equipment.
The method of glass fixation itself is determined based on the chosen technology for creating the hole.
damping soft materials are placed under the areas that will be affected .
What if you need to make a small hole?
Miniature holes can be drilled using a drill and drill. A drill is required first:
- heat up;
- immerse in sealing wax and hold until the substance begins to melt;
- moisten the tip in turpentine.
After this you can start working.
The second option is:
- Grind camphor and coarse sandpaper particles.
- Pour the resulting elements into a small container and then dilute them with turpentine. Place this paste on a clean glass surface of the workpiece.
- Prepare a small piece of copper wire. It will need to be clamped in the drill chuck. This type of equipment needs to be guided, so prepare a guide jig (plywood).
- The preparation is completed. You can start drilling.
Large holes in glass are made in a different way. If the required diameter exceeds 10 cm , household equipment will not help.
You can still drill, but you must first make a small through point in the center of the future hole.
Any small-format glass of small diameter (up to 1 cm) can handle this. Extraneous chips will occur, but this is not a big deal: they form in areas that will later be removed.
Having received a small through opening, you need to insert and secure a piece of wire into it.
One end is fastened with a glass cutter. After checking whether the elements are securely fixed and whether the tool moves smoothly in a circle , you can cut a circle.
If you can't drill a hole, you can melt it. You will need to prepare equipment in which liquid tin or lead will be prepared. The glass blank is treated with gasoline, acetone or alcohol.
Having made the markings and formed the area for the future hole, the resulting area is sprinkled with moistened sand.
It should be enough to create a funnel, the bottom of which will be comparable in size to the edges of the hole, then metal is poured into it.
After 1-2 minutes it will cool down, and the sand equipment can be removed along with the mold.
As a result, a hole with smooth edges is formed . The risk is only in the melting process itself: it is impossible to control the diameter that is formed after the interaction of glass and metal.
The last option is to cut the hole using a soldering iron. You need to start by creating risks using a needle file.
Carefully mark the zones in which the melt will be made with a soldering iron in depth.
Then you need to warm up the tip and start cutting. Proceed slowly and carefully.
It is better to melt small sections , periodically cooling the glass (this will reduce the risk of deformation in nearby areas).
The result will be exactly the opposite of the above method:
- the boundaries of the intended diameter of the hole will be maintained;
- the edges will turn out uneven.
Construction
Glass bottles can be effectively used in households and construction:
- create from them fences for front gardens and small fences separating garden or garden paths from plants;
- use in the drainage layer of paths;
- create a foundation from them for small buildings, such as a barn;
- apply in masonry walls.
Read more on this topic here.
Modern developments
The twentieth century can be called a time of widespread use of glass. After the development of technology for mechanical methods of obtaining the material, it began to be used in a variety of fields - as the finest fiber in the field of telecommunications, and with no less success it is used in large multi-ton blocks in construction technologies.
The properties of glass are diverse; they continue to be studied in scientific institutes, and craftsmen find new uses and invent new types. In 1940, glassmakers introduced foam glass to the world. Its qualities are:
- Lightweight - does not sink in water, has a cellular structure, the specific gravity is slightly higher than the weight of cork.
- Moisture resistance, durability.
- Environmental friendliness (coke is added to the classic batch recipe).
- Fireproof (does not burn) and suppresses fire.
- The material can be sawn into pieces without compromising quality.
The scope of application is insulating materials for hazardous industries, refrigerators, etc.
Solar cells use glass with a conductive coating of a thin layer of metal oxide. Coated panels operate at temperatures around 350 °C. In addition, such glass is installed in aircraft cabins to avoid ice and retain heat inside the cabin.
An important achievement of modern times has been the possibility of producing glass ceramics. The material is made using conventional glass technology, but at the last stage of cooling the process slows down and crystallization occurs in the mass of the material. Catalysts are special additives that do not affect the external state of the glass in any way, but form small crystals. The material can withstand high temperatures without deformation and is more resistant to all types of damage. Used in rocket science, home appliances, laboratories, engine parts and many other fields.
Where to get raw materials for processing
Recycled glass can be purchased:
- at a glass collection point, or open your own;
- at a distillery or window manufacturing plant; they usually have special containers where rejected products are dumped.
- at landfills; in many regions of the Russian Federation you can get it there for a nominal fee.
You can get raw materials by installing special garbage containers for glass on city streets. Municipal authorities are usually only happy about this. You can also organize a collection point for glass containers yourself.