In any building, one of the most important elements is the door. Since the construction market offers a wide variety in the choice of models, the designation of doors of different designs on the drawings according to GOST is different, and the same applies to markings. It is very important that the designation of the installed models is correctly marked on the diagram.
Window designation on the floor plan. Conventional images on construction drawings
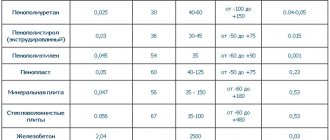
In architectural and construction drawings, in order to give them greater clarity, visibility and readability, conventional graphic symbols in accordance with GOST 5401-50 are used for building materials, building elements, sanitary equipment, etc., which makes it possible to shorten the explanatory inscriptions on the drawings.
Symbols of building materials most often used in the construction of buildings.
The figure shows the symbols of some building materials most often used in the construction of buildings.
Brick or stone masonry is indicated in the section in the drawings by straight parallel strokes with a slope of 45° to the horizon. The distances between strokes depend on the scale of the drawing. In small drawings, gaps of about 1 mm are accepted, in large ones they are increased to 2 - 2.5 mm. The refractory brickwork is hatched into a square check.
In large-scale drawings, the metal parts of structures are shaded in the same way as brick, but a little thicker. On small-scale drawings and in general when the thickness of the cut part in the drawing is less than 2 mm, a solid black fill is made with ink.
Wooden parts in a cross section (from the end) are hatched with circular and radial lines, and in a longitudinal section they are hatched as the fibers go in the wood, and depict the actual arrangement of the layers of wood in nature. Wooden parts that do not fall into the cut are not hatched.
Thin layers of various insulating and cushioning materials (tar paper, cardboard, cork, asbestos, hemp, asphalt, etc.) are depicted as a solid black fill with an explanatory inscription.
Concrete is represented by dots with irregular circles between them. The circles are made by hand with a pen. If two layers of different composition come into contact, they are separated by a horizontal line. The composition of concrete is indicated by inscriptions. Reinforced concrete, i.e. concrete reinforced with iron rods (reinforcement) embedded in it, is indicated by ordinary shading and circles.
Water is depicted with intermittent horizontal parallel strokes, with the spaces between them increasing as they move away from the surface.
Walls and partitions are depicted with two parallel lines, the space between which is shaded with thin oblique lines (at an angle of 45°), sometimes filled with ink, and sometimes left without shading or filling.
Windows and doors are depicted as wall openings of appropriate sizes, which are not shaded, but are depicted as parallel lines for frames and perpendicular for door leaves. The part of the door that opens is called the door leaf. Doors can consist of one or two door leaves
- single-field or double-field. If the canvases have different widths, then the door is one and a half floor.
a - external door; b - internal door; c and d - windows; d - external door; e - monocotyledon door; g - double door; z - window.
Stairs can be internal, if they are located in a special enclosed space called a staircase, external (entrance) and service (basement, attic, etc.). Each staircase consists of inclined parts, called marches, and horizontal platforms.
Marches consist of steps laid along stringers and railings fixed to the steps. The steps are distinguished by their width, called the tread, and their height, called the riser. The slope of the marches is determined by the ratio of the height of the march to its horizontal projection. The steeper the staircase, the more difficult it is to climb.
For residential buildings, slopes are accepted at 1:1.5 - 1:1.75, for attic stairs 1:1, for basement stairs 1:1.25. The staircase is more comfortable if the riser is 15 cm high and the tread is 30 cm.
Sanitary fixtures, i.e. baths, showers, sinks, washbasins, etc., are shown in the figure.
Heating devices
- stoves - shown in plan with the outline of their actual outlines (round, corner, rectangular, kitchen hearths, bathroom column). As a rule, between the stove and the wall a free space is left, called a retreat, measuring 8 - 10 cm, sealed on the sides with 1/4 or 1/2 brick.
Image of heating devices in the drawing
Indicating doors
and
gates
on the drawings used in construction must be carried out in accordance with GOST 21.201-2011. In accordance with this document, it is necessary to use special graphics.
In those drawings that are made on a scale of 1:400 and smaller, the door leaves and the direction of their opening are not shown. If the scale of the depicted doors and gates is 1:50 or more, then when depicting on construction drawings it is necessary to indicate such elements as quarters, thresholds, etc.
| Image | Name |
| Door (gate) outside | |
| Door (gate) double-leaf | |
| Single-leaf double door | |
| Double door | |
| Single-leaf door with swinging leaf (right or left) | |
| Double door with swinging leaves | |
| Single-leaf external sliding door (gate) | |
| Single-leaf sliding door (gate) with opening into a niche | |
| Double-leaf sliding door (gate) | |
| Lifting door (gate) | |
| Door (gate) folded | |
| Door (gate) folding and sliding | |
| Revolving door | |
| Up and over gates |
Doors
One of the most common elements of buildings and structures are doors. They can have a wide variety of designs, but the most common are:
- Single-sex
- Double-field
- Swing
- Recoil
Based on the material they are made of, they are classified into:
- Wooden
- Metal
- Glass
To install doors, frames are installed in doorways. If wood is used for this purpose, then such structures are made from bars and then attached to the wall. Wooden panels are usually made from a material such as laminated boards. Often, chipboard is used for this purpose, which is finished with facing materials.
Metal door frames and their frames are made from galvanized cold-formed steel profiles, which are subsequently painted to give the structure an aesthetic appearance and protection against corrosion. The door leaf of metal doors consists of one or two steel sheets, a frame and stiffeners.
The structural elements of glass door leaves are a frame made of aluminum or steel profile, and a leaf made of so-called “stalinite” (that is, tempered glass, characterized by increased strength).
According to current norms and standards, all entrance doors to buildings and apartments must open outward, that is, in the direction of movement to the street. This is necessary in order to facilitate the evacuation of people from buildings in the event of various emergencies (for example, fires).
Wooden plugs treated with antiseptics are used to secure door frames in openings. They are installed directly into reinforced concrete panels at the manufacturing stage of these structures. If the doors are external, then they are installed together with thresholds, and if internal, then without them.
To hang door panels on door frames, hinges are used. If the door is wide open, it is very easy and simple to remove it from its hinges. In order to avoid doors being open or slamming, special devices called “diplomat” are used. They serve to keep the door closed, and if they open, then return it smoothly, without blows. In addition, the doors are equipped with mortise locks, latches and handles. Entrance doors are often equipped with combination locks.
Gates
Gates are functional building structures that are used to restrict access to a particular territory.
They can play both a strictly utilitarian and decorative role. In the latter case, they often do not have doors and are simply an arch. If the gate is intended for the passage of vehicles, then its dimensions are taken into account during their development and production.
According to their design, gates can be swing, rotary, sliding, sliding, up-and-over and lift-up. The simplest in design and most common are swing and sliding gates. There are also swinging gates, in which the leaves are made of sheets of rubber or elastic transparent plastic. They are most often installed in industrial buildings and can significantly reduce heat loss.
Door
and
window openings
of buildings simultaneously perform two functions: utilitarian and aesthetic. From a practical point of view, they are the elements that provide access to the building for people, light and air. At the same time, door and window openings largely determine the architectural appearance of buildings.
According to GOST 21.201-2011, special symbols must be used on construction drawings to indicate openings and openings.
Usually, when drawing an opening that is supposed to be made in a ceiling or partition, a broken line is drawn inside, which otherwise may not be done if it is clearly clear what exactly is being displayed.
In cases where a hole or opening, as planned by the designers, should be sealed, dotted lines are used to depict them, and when depicting these elements of buildings in sections, shading is used. The explanatory notes indicate the material of the bookmark.
A simplified method of depicting window openings in prefabricated structures (for example, reinforced concrete slabs) is used when the drawing scale is 1: 200 or smaller. In this case, the quarters are not depicted.
Openings and openings in rooms are mainly divided into window, door and ventilation.
Holes and openings are made in walls made from a wide variety of materials: stone, concrete, wood, brick, foam and aerated concrete, etc.
When placing all kinds of window and door openings, designers must take into account such a factor as the convenience of furniture placement for any type of planning solutions.
In order to correctly position the holes through which air is removed or supplied, it is necessary to take into account their spatial position relative to each other. It should be such that air flows freely through them, both into and outside the premises.
When constructing the walls of modern buildings, the manual masonry method with vertical and horizontal bandaging of seams is used. Door and window openings of the walls are made with quarters adjacent to the outside along the vertical, as well as the upper edges.
The quarters enable reliable and tight installation in the openings of window frames. They allow the use of various modern sealing materials. In addition, the presence of quarters looks very good based on the results of the work.
The purpose of windows as elements of buildings is to ensure the penetration of natural light into the premises and their ventilation. Doors are necessary to provide access to the building and communication between rooms isolated from each other.
The windows of modern buildings are usually double glazed. They can be single, double or tricuspid. In addition to them, drains made of galvanized steel sheet, as well as window sill plates, are also installed in the openings. Cement-sand mortar is used to construct slopes.
Doors installed in modern buildings are glazed and solid. Door glazing is usually used to ensure uniform illumination of different rooms, as well as to decorate interiors.
Recently, plastic has been widely used for the manufacture of windows and doors. The windows are equipped with sealed double-glazed windows, which are installed between PVC profiles. Inside these profiles there are cavities, the number of which may vary. They provide good heat and sound insulation. To make it even better, the windows must be equipped with double-glazed windows.
According to GOST 21.201–2011, to indicate on construction drawings such structural elements of buildings as window sashes
facades, special symbols are used. However, the number of bindings themselves is not shown graphically.
To indicate those bindings that open outward, a thin solid line is used in the corresponding images, and those that open inward are used a thin dashed line.
If a binding is not hung on the binding shown on the construction drawing, then the top of the corresponding sign should be directed towards it. As for architectural drawings that depict window blocks, they must be part of the design documentation or the documentation of the order for the manufacture of a particular product.
On those construction drawings that are made on a scale of 1: 200 or less, quarters are not shown.
A window frame is a building structure necessary to strengthen and divide the glazing field and decorate it. It consists of several elements: transoms, windows, sashes. The window frame, in turn, together with the window frame, makes up the window block.
Window units are designed in such a way that during their operation it is possible to replace glass, double-glazed windows, sealing gaskets, window devices, while maintaining the integrity of these parts.
All opening elements of windows installed in residential buildings must open only to the inside of the premises. For individual structures (for example, windows that are installed in the premises of the first floors of buildings or overlook balconies), modern standards, building codes and regulations provide for the possibility of opening outward.
In order to ensure ventilation of the room, in the windows with which they are equipped, either transoms, or casement windows, or regular windows are installed, or special supply valves are installed in them. Transoms can be either openable or blind; they are usually mounted above the sashes, in the upper parts of window frames. To secure an openable transom in the window frame, a horizontal impost is used.
If the box is wide enough, then a vertical impost is installed in it so that the edges of the vertical bars of the sashes adjoin it. Based on the number of sashes in one row, windows are divided into:
- Single leaf
- Bivalve
- Multi-leaf
As for the design of window frames, they are:
- Single
- Paired
- Separate
- Separately paired
In window blocks with paired sashes there are two of them: external and internal. They are connected to each other, and the inner one, in addition, is hung on the box using hinges. Thus, the sashes, connected to each other by fastening elements, form a binding with a fairly high rigidity.
The design of a separate window block includes a frame, vents, transoms and sashes that open either in one direction or in different directions. Separate-paired window units are a combination of windows with separate and paired sashes. In these windows, the outer sashes are single, and the inner sashes are double. In addition, a term such as “split-pair window sash” is often used to refer to a structure that divides a window into separate parts.
Windows are important elements of the interiors and exteriors of buildings. Often those of them that have an original, non-standard shape are their decorations, while simultaneously playing their utilitarian role. Windows are necessary in order to create comfort in the house; they must have a design that ensures savings in money spent on heating the interior.
Standard wooden doors
The main document on the basis of which doors from its derivatives and wood are made for installation in public and residential buildings is the state standard number 6629-88 (see GOST wood doors - GOST guarantees the level of quality). We will see right away that when making soundproofing, evacuation or special-purpose doors, there is no need to rely on it.
In addition, this document does not provide recommendations for the manufacture of door blocks made from useful rocks, since they do not belong to the category of standard products. Door blocks for internal installation are divided into a couple of types.
For clarity, let’s present any of them in the form of a table:
| Door type and appearance | Explanation and Symbol |
| Type "G" . This version of doors is installed in buildings: they can have one or two leaves, with lattice filling. The execution options are as follows: with and without a box; with and without a threshold; with and without covers. | |
| Type "O" . Interior doors with glass inserts. This is the only difference from the previous version. The execution options are the same. | |
| Type "K" . The photo shows the so-called pendulum doors, the doors of which do not pretend, but swing. They are also interior, but differ from types “G” and “O” in design and principle of operation. They are invariably two-floor, with a box, without overlap and, in addition, without a threshold. The presence or absence of coverings is at the discretion of the manufacturer. | |
Type "U". Reinforced doors fall into this category. They are installed in buildings, at the entrance to an isolated room - for example, to an apartment. They are invariably single-floor, without facings or overlap. The leaves of such doors must have a continuous filling. However, it is up to the manufacturer to decide whether such a door will have a frame or not.
|
So:
- The standard regulates the manufacture of doors of all types, in accordance with clearly defined standard sizes. The marking of doors according to GOST must reflect the height and width of the opening for which the product is intended. For example: DK 24-19 indicates: the door is swinging, height 24dm (2.4m), width 19dm (1.9m), taking into account the thickness of the frame.
- Double-leaf doors of types “O” and “G” can have leaves that are unequal in width. The letters “P” (right) or “L” (left) are also added to the marking of a single-leaf door. The additional letter “P” indicates that the door has a threshold - for example: DG 24-15PP.
- As for not markings, but graphic images of doors on the drawings of designed buildings, they are carried out in accordance with standard 21*201-2011. Clause 4.7 contains a table with examples of graphic images of doors that designers should adhere to.
The manufacture of doors of all types must be carried out in accordance with the working drawings presented in this standard, and only in accordance with the permitted standard sizes. Then, a short excursion into the development will be offered to your attention - it may be necessary for those who want to make a wooden door with their own hands.
Designation of windows in drawings
Competent and professional design is the key to the success of any construction project. The correctness of the preparation of technical documentation plays a dominant role in this case. Any construction work must be accompanied by engineering documents completed in accordance with current construction standards. Qualified information about the material of manufacture, technology and stages of work will ensure a high-quality result upon completion. The designation of windows on drawings and construction diagrams makes it possible to install them in accordance with the planned plan and work schedule.
Technical documentation is used both for capital construction of large buildings and facilities, and for private development or renovation. Depending on the complexity of the work, the necessary packages of documents and drawings are prepared. As for the depiction of windows in the drawings, here you need to know the basics of engineering design so as not to make mistakes in reading and interpreting technical documentation.
For customers who are not adept at reading blueprints, standard designations for window structures have been introduced. Below are the most common types of conditional windows in drawing documents.
These window designs can be present in various combinations, depending on the complexity of the project. During the ordering process, the client can see his design in the work contract. Therefore, in order to speak the “same language” with the manager, you need to know how the doors and windows are marked on the drawing. This is necessary to avoid misunderstandings when coordinating window and door structures.
For capital construction, there are standards for designating plastic windows on drawings and assembly diagrams. The plan for construction (or repair) work must be interpreted unambiguously and unambiguously. When implementing these types of projects, there is not one organization of contractors, but several. To better coordinate all joint actions, a simple schematic window type, as shown above, is not enough.
When constructing new buildings, work to implement the project is carried out simultaneously in several directions at once in order to save time. The choice of material for manufacturing window structures is determined at the design stage. The main parameters are operating conditions, desired data on the coefficient of thermal conductivity and noise absorption, as well as the appearance and color of the profile.
In order for the window structure to fit into the new opening according to its dimensions, the construction contractor must provide the following information.
- Frame profile parameters. Each profile system has its own installation depth, ranging from 60 to 80 mm. Based on these parameters, an opening for window installation is designed.
- Glass unit formula. Depending on the formula of the glass unit, the number of chambers in it varies. The area of the glass unit is 80-85% of the total volume of the structure, and the weight in some cases can reach up to 90% of the total weight of the window. Knowing these parameters, engineers of a construction organization will be able to calculate the required total load on the building and on each opening in particular.
- Complex designs. Recently, the demand for structures of increased complexity and size has increased. It is not possible to produce a single, monolithic structure for every design task. In this case, a breakdown occurs into component elements, each of which, in combination with the other, forms the required structure. For correct calculation and correct installation of these types of structures, drawings of plastic windows are used, which schematically indicate the assembly and installation process.
There are drawings of profile systems and layout diagrams of window structures on the plan of a building or room. The drawing of the profile systems (Fig. 1.) is largely necessary for the installation team to correctly install the window, depending on the geometric parameters of the structure.
For designers, other types of window designation are accepted, where each structure is shown conditionally, without details. An important factor in such drawing diagrams is the location of the window on the building plan (Fig. 2.)
In conclusion, it is worth clarifying that the average customer does not need to know how windows are indicated on the drawings. It’s just worth knowing that the more complex the type of construction work, the more requirements there should be for the accompanying documentation, which is the guarantor of a high-quality completed project.
Marking of double-glazed plastic windows
The labeling of plastic windows contains comprehensive information about the products. If you know how to use it, no seller will be able to deceive you, you will be able to choose the product that best suits all your requirements, without overpaying for it and knowing exactly what features it has. This knowledge can be useful if you buy windows secondhand without any documentation.
What does the label include?
Correct marking of plastic windows carries the following information:
- What kind of glass is used and how thick is it.
- What is the width of the air chamber (distance between the glasses).
- What type of gas is the glass unit filled with (argon, air, etc.).
The types and thickness of glass are designated as follows:
- M - these are ordinary glasses that do not have any additional properties.
- K - this type of glass has a harder coating, is protected from minor damage, and its coating is low-emissivity.
- F – products are produced using a special float technology; they are considered more durable and hold heat better.
- I – marking of double-glazed plastic windows, the glass of which has a soft low-emissivity coating.
- PI – energy-saving film applied to the glass.
- S is body-dyed glass.
The distance from glass to glass can be up to 36 mm. The minimum value is 6 mm. In order to find out what gas is in the air chamber, markings of double-glazed plastic windows are applied to the frame. You can find out what gas is inside using the following values:
- If there is dry air inside the glass unit, a space is placed.
- Ar - occurs quite often and means that there is argon in the double-glazed window
- Less common are the designations Kr - this is krypton and SF6 - sulfur hexafluoride.
The marking may look, for example, like this - 4 M - 16 - 4 M: this means that you have a single-chamber double-glazed window with two ordinary glasses located at a distance of 16 mm from each other. The structure is filled with dry oxygen. If the double-glazed window is two-chamber, but with the same parameters, its marking will look like this: 4M -16-4M -16-4M. If the chamber is filled, for example, with argon, the markings of PVC windows will look like this: 4M - 16Ar - 4m.
Insulating glass markings inside
How is a double-glazed window marked according to GOST?
There are other types of designation besides the one above. The marking of double-glazed windows according to GOST has different meanings:
- Ud - impact-resistant structures.
- C – covered with sun protection film.
- Ш – designed for noise protection.
- M - frost-resistant, suitable for use in the northern regions of the country.
- E – marking of energy-saving double-glazed windows.
The number of chambers in a double-glazed window and its type are indicated by the following letters:
- SPO – double-glazed window with one chamber.
- SPD – two-chamber.
Each type of double-glazed window has its own special designations:
- M 0,1,2 indicates the brand of glass. The lower the number, the better the glass.
- U - if the glass has a pattern.
- A – reinforced glass.
- If it is polished, the letter p is added, for example, Ap is a reinforced polished structure.
- P1A-P5A means how strong the glass is in relation to impacts. The higher the number, the stronger the material.
- Р6В – shock resistance.
- Sm-6 - indicates the level of security, the higher the number, the better.
The letter designation depends on whether you have GOST or an imported glass unit marking, the decoding of which is also logically simple. In addition, the designation is often written on the plans and may include which direction the doors open and other useful information.
What can the notation be used for?
The designation of window openings on the drawings is quite useful: it helps to calculate in which direction and how the structure will open, to think about where furniture can be placed and where it will get in the way. If the scale is small, then these values are usually dispensed with; if the scale is less than 200 to 1, they can be used, being needed more often not by builders, but by designers.
Modern technologies make it possible to achieve four opening methods, these include tilting, tilt-and-turn, rotary and parallel-sliding methods. Depending on which opening method is chosen for the structure, the designation will also be displayed on the plan. In addition, a certain type of window requires certain fittings, since it determines how the sash will move and what additional functions the structure as a whole has.
Types of window openings
According to GOST, fittings may have the following designations
- UE – for rotary.
- UPO – tilt and turn.
- UO - folding.
- PS – parallel-sliding.
Tilt-and-turn fittings
Marking fittings for plastic windows helps determine which fittings are suitable and what functions they have. Labels may vary from manufacturer to manufacturer, so you need to take the brand into account when selecting products. There are fittings designed to protect windows and plastic doors from burglary; they are distinguished by their design and strength, and have separate designations:
This is the European standard DIN V ENV 1627, you can read it in more detail separately. Depending on the numbering, the degree of reliability of the fittings varies.
WK1 does not allow you to press the sash by hand, but cannot resist a crowbar. WK2 has more advanced anti-burglary structures, which makes it impossible to press the sash using a crowbar or other metal tools. WK3 – the highest degree of protection. Windows with such fittings are almost impossible to open from the street side.
Fittings may differ in class depending on the weight it is designed for:
- Class I – can withstand a sash weight of up to 50 kg.
- Class II – up to 80 kg.
- Class III – can withstand loads of up to 130 kg. It is most often used for large massive structures.
Marking windows on the plan may include not only marking the windows themselves that need to be installed, but also what fittings should be on them, since they are installed separately and can be purchased in addition according to the requirements for a specific room.
Window opening symbol
GOST requires that windows that open in one way or another have strictly defined values. This helps not only to understand from the drawing what products are in front of you, but also to use the designations for drawing up technical documentation. The window opening symbol looks like this:
- The dashed line indicates that the sash opens inward.
- A solid line means that the sash opens outward.
Different designations for opening windows in the drawings
It is worth noting that for projects, marking windows on the drawings is very important, as it helps to navigate the layout, calculate what arrangement of furniture will be most convenient, and where it is better to direct the opening of doors. Typical projects usually involve opening window structures into the room. Only those windows that are located on the ground floor, facing the fire escape or overlooking the balcony can open to the outside. If the window is equipped with sashes, transoms, vents, this should also be displayed on the plan, including which side they will open to.
Knowing how to read the markings, you can easily navigate any plan; in addition, when buying a plastic window, you will always know exactly what kind of product is in front of you, what kind of glass unit it has and what technical characteristics it has.
oknanagoda.com
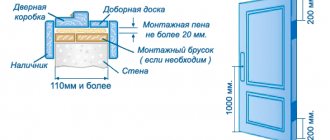
Dismantling the old product and preparing the opening
Before you begin installing a new window, you need to get rid of the old one. This must be done on the day the replacement is performed. If saving the frame is not necessary, you don't have to be very careful. Remove the doors or tear them out with the holding screws. File the frame and frame of the window in several different places.
Take a crowbar or nail puller, pry up each part and remove it from the opening. In some situations, it’s easier to immediately find the two-hundredth nails that hold the box in place and pull them out. Under the box you will find thermal insulation and sealing material. It needs to be removed. At the same time, using a hammer drill with a so-called spatula attachment, dismantle the slopes or some part of them. At this stage, it all depends on what slopes you plan to install in the future.
Pry up the window sill and remove it. Take a hammer drill and destroy the cement backing under the window sill and at the bottom of the opening. Collect construction waste in suitable sized bags and take it to a designated place. Take the remains of the old window there. You won't have to do any more dirty work. Level the ends of the window opening and clean them of dirt. The surface should be primed if possible. Although if window installation is carried out by company representatives, primer is usually not used, but it is better to do it anyway.
Metal doors: standard
The standard size of such a door is 203 x 90 cm. At least, many domestic manufacturers are guided by it. It should be taken into account that doorways in old and new buildings differ in size. Moreover, in the old ones the doorway is framed by a wooden frame, which does not need to be taken into account when taking dimensions. She's cleaning up. But in modern ones there is a metal “edging”. Therefore, if you want to expand the doorway, this will be difficult to do.
According to the nomenclature of goods subject to mandatory confirmation of conformity, entrance and interior doors (wooden and metal) are not subject to mandatory certification.
It should be added that the standards also stipulate standard section sizes for each type of door, installation methods and type of fastening material for various protective and design elements, and much more.
When choosing a particular door, you need to take into account the fact that large items will have to be brought in or taken out through the doorway. Experts recommend a minimum width of 90 cm. If the doorway is narrower, then it is just an emergency exit, and not a full-fledged door.
Conventions used in architectural and construction drawings - Med Dr
In architectural and construction drawings, in order to give them greater clarity, visibility and readability, conventional graphic symbols in accordance with GOST 5401-50 are used for building materials, building elements, sanitary equipment, etc., which makes it possible to shorten the explanatory inscriptions on the drawings.
Symbols of building materials most often used in the construction of buildings.
The figure shows the symbols of some building materials most often used in the construction of buildings.
Brick or stone masonry is indicated in the section in the drawings by straight parallel strokes with a slope of 45° to the horizon. The distances between strokes depend on the scale of the drawing. In small drawings, gaps of about 1 mm are accepted, in large ones they are increased to 2 - 2.5 mm. The refractory brickwork is hatched into a square check.
In large-scale drawings, the metal parts of structures are shaded in the same way as brick, but a little thicker. On small-scale drawings and in general when the thickness of the cut part in the drawing is less than 2 mm, a solid black fill is made with ink.
Wooden parts in a cross section (from the end) are hatched with circular and radial lines, and in a longitudinal section they are hatched as the fibers go in the wood, and depict the actual arrangement of the layers of wood in nature. Wooden parts that do not fall into the cut are not hatched.
Thin layers of various insulating and cushioning materials (tar paper, cardboard, cork, asbestos, hemp, asphalt, etc.) are depicted as a solid black fill with an explanatory inscription.
Concrete is represented by dots with irregular circles between them. The circles are made by hand with a pen. If two layers of different composition come into contact, they are separated by a horizontal line. The composition of concrete is indicated by inscriptions. Reinforced concrete, i.e. concrete reinforced with iron rods (reinforcement) embedded in it, is indicated by ordinary shading and circles.
Water is depicted with intermittent horizontal parallel strokes, with the spaces between them increasing as they move away from the surface.
Walls and partitions are depicted with two parallel lines, the space between which is shaded with thin oblique lines (at an angle of 45°), sometimes filled with ink, and sometimes left without shading or filling.
Windows and doors are depicted as wall openings of appropriate sizes, which are not shaded, but are depicted as parallel lines for frames and perpendicular for door leaves. The part of the door that opens is called the door leaf. Doors can consist of one or two door leaves - single-leaf or double-leaf. If the canvases have different widths, then the door is one and a half floor.
Representation of windows and doors on drawings
Pictures of windows and doors in the drawings:
a - external door; b - internal door; c and d - windows; d - external door; e - monocotyledon door; g - double door;
z - window.
Stairs can be internal, if they are located in a special enclosed space called a staircase, external (entrance) and service (basement, attic, etc.). Each staircase consists of inclined parts, called marches, and horizontal platforms.
Marches consist of steps laid along stringers and railings fixed to the steps. The steps are distinguished by their width, called the tread, and their height, called the riser. The slope of the marches is determined by the ratio of the height of the march to its horizontal projection. The steeper the staircase, the more difficult it is to climb.
For residential buildings, slopes are accepted at 1:1.5 - 1:1.75, for attic stairs 1:1, for basement stairs 1:1.25. The staircase is more comfortable if the riser is 15 cm high and the tread is 30 cm.
Sanitary fixtures, i.e. baths, showers, sinks, washbasins, etc., are shown in the figure.
Representation of sanitary facilities in the drawing
Heating devices - stoves - are shown in plan with the outline of their actual outlines (round, corner, rectangular, kitchen hearths, bathroom column). As a rule, between the stove and the wall a free space is left, called a retreat, measuring 8 - 10 cm, sealed on the sides with 1/4 or 1/2 brick.
Image of heating devices in the drawing
Furnaces located in wooden walls or partitions are cut into one brick.
“Handbook for assistant sanitary doctor and assistant epidemiologist,” ed. Corresponding Member of the USSR Academy of Medical Sciences
Designations for metal models
Doors and windows in the drawings are therefore prescribed by GOST to be marked with standard icons. State standards and labeling of such structures regulate. The symbols for metal doors on the diagrams are usually the same as for wooden ones. However, the labeling of such products usually contains additional information. In this case, the letter “D” also comes first. The second shows the dimensions of the opening. However, for such doors they are marked in dm, and in mm. Also, the marking of metal entrance structures usually contains designations of strength and burglary resistance classes. In this case, the consumer thus has the opportunity, even in the store, to determine the degree of reliability of the product in terms of penetration of unwanted guests into the home.
Fireproof steel doors are also marked in a special way at enterprises. Their designations contain, among other things, the letter “P”. Typically, such models are marked with the letters “DMP” or “DPM” (metal fire door).
How to make window openings on a house plan in AutoCAD (algorithm)
To create window openings in AutoCAD, I used the following algorithm (you can use any convenient method for creating window openings on the plan):
Call the Line command in AutoCAD and draw the first wall of the window opening.
Select the segment and activate the handle. Select the “Move” option from the context menu for editing objects in AutoCAD using handles. Next, to make a copy of it when moving a segment a specified distance, select the “Copy” option. Copy the segment to a distance of 910 mm, i.e. the width of the window opening. To track perpendicular angles and polar angles in AutoCAD, you will need polar snapping or ORTO mode.
Select two segments on the house plan in AutoCAD, indicating the window opening, and group them for ease of working with the window opening and placing it in positions according to the plan of the first floor of the cottage. You can group objects in AutoCAD from the context menu. Click the right mouse button and select the line “Group” – “Group” in the context menu.
Using the “Copy” and “Rotate” commands in AutoCAD, copy the window openings and place them according to the drawing of the house plan.
Doors in the building plan
06.05.2011 09:24
Every room must have a door. The opening part of the door is called the door leaf. Doors can be single-leaf or double-leaf. Door leaves are hung on hinges in door frames, which are arranged in the same way as window frames. The width and height of doorways are selected depending on the purpose of the room.
Doors in accordance with GOST 6629-65 have the following widths: in pantries, bathrooms and restrooms (D-1) - 600 mm, in kitchens, single-floor (D-5) - 700 mm, in rooms, single-floor (D-2) - 800 mm , external, double-field (D-9) - 1390 mm, or (D-10) - 1790 mm.
The height of all internal doors can be 2.00 m, the entrance door 2.30 m (Fig. 14). Doors from apartments to the staircase, to the common apartment corridor or to the floor lobby must open into the apartment. With double doors, they can open in different directions.
Doors to the stairwell, as well as common corridors in public buildings, must open towards the exit. Doors in public buildings intended for evacuation (spare) must also open towards the exit. On drawings at a scale of 1:400 and smaller, the opening of doors and gates no need to show.
The angle of inclination of the door leaf to the plane of the wall, if there is not enough space in the drawing, can be taken equal to 45 or 30°. The doorway marked on the plan must be tied to one of the nearest walls, so that during construction the door will be made in the place where it designed. In this case, you need to indicate the door size and brand (D-1, D-2, etc.). The location of the door panels must be marked on the drawing in accordance with GOST 11691-66 “Construction Drawings”. For the exercise, suggest finding all the doorways on the building plan and determine their size and brand.
You can also suggest that in the process you determine the brand and dimensions of window openings on one of the drawings of a standard project.
< Previous Next >
stroiki-master.ru
What other rules must be followed when drawing up diagrams?
Doors on conventional drawings, like, for example, windows, are supposed to be depicted as wall openings. In this case, such elements on the diagrams are not shaded, but are drawn in the form of perpendicular lines (sashes). Among other things, when depicting doors on drawings, the following rules are observed:
- the main lines are set to 0.8 mm thick;
- inscriptions above the designations are drawn in font No. 7;
- For explanations, font No. 5 is used for symbols.
You can, among other things, determine the characteristics of the door - the opening side of the leaf, the presence of a threshold, the type of construction - by its markings. Such information, according to current regulations, must be present on interior and entrance structures. It can also be placed on design drawings next to the door icon.
What documents regulate
You might be interested in: Idle around: phraseological units for the word. How can you say otherwise?
In our time, manufacturers must produce standard wooden doors intended for installation in residential and office premises, guided primarily by the standards provided for by GOST 6629-88 and GOST 475-78. The exception in this case is structures assembled from valuable wood species. Such doors do not belong to the group of standard ones. Manufacturers also assemble special-purpose structures using other regulatory documents. These could be, for example, evacuation models, fire models, etc.
In our country, door designations on drawings are regulated according to GOST 21.201-2011. Moreover, according to the standards, such elements are usually not marked on diagrams made at a scale of 1:400 or less. Doors are indicated only on drawings 1:50 and larger. In this case, according to GOST, the diagram is supposed to indicate not only the design itself, but also the direction of opening of the leaf, as well as the presence of a threshold.
In addition, the door type is often marked on diagrams using special symbols. Of course, such door designations on drawings are also regulated according to GOST. All design organizations in our country must comply with such standards.
You may be interested in: Research teaching method: purpose, process and essence
Standards for designating doors and windows on drawings in accordance with GOST 11214-86 can also be used in Russia. This document specifies, among other things, the design requirements for such building elements. This GOST also regulates the dimensions and methods of joining standard windows and doors.
What other designations can be used
We have thus found out how interior doors installed directly in buildings can be marked. The second position for such models indicates the type of construction.
However, in various types of buildings, of course, external doors are almost always used. In the marking of such products, the second position may contain, for example, the following designations:
- “N” – entrance doors or tambour-type models.
- “C” – service doors.
- “L” – hatch doors or manhole models.
If there are such letters in the marking, the letters indicating the actual type of construction “G”, “O”, etc., can be transferred further - behind the numbers.
Unlike internal doors, entrance models are manufactured according to the standards provided for by GOST 24698-81. The same document also regulates their designations.
The numbers in the marking of internal doors, as already mentioned, usually appear in the third position. In the same place they are located for the entrance structures. For all types of doors, the numbers indicate the size of the openings in the house. Very often, after them in the door marking, in addition to the type, there are also additional letters displaying some secondary characteristics. In this place, GOST for doors may provide, for example, the following letters:
- “P” – threshold or right wing;
- “L” – left opening;
- “N” – with influx;
- “B” – moisture-resistant door;
- “C” – continuous filling of the canvas;
- “T” – fire-resistant door;
- “Ш” – panel door;
- “C” is a model with an internal solid filling made of wooden slats, equipped with a threshold and a cylinder lock, as well as a compacted rebate.
The last position in the door marking is usually marked with the designation GOST 24698-81.
Classification and labeling
Steel doors are classified according to such characteristics as: design; mechanical characteristics; operational requirements; type of finishing. Structurally, they are distinguished by the box: it can be U-shaped; U-shaped with a threshold; closed.
- Another way of constructive differences is the number and option of opening the canvases. They can be single-sex, including right and left. They can have two canvases: both the same and different widths - including one that does not open. Doors can also open inside or outside the house.
- Depending on the number of contours placed in the vestibule, there can be only two manufacturing options. The door usually has one circuit or two - more is extremely rare, although GOST also allows this.
- The finishing of metal doors can be very diverse. In addition to paint and powder coatings, these are all kinds of cladding: leather and leatherette with insulation; glued PVC films; wooden slats and tiles; veneer; glass; decorative metal elements. In addition, doors manufactured in accordance with GOST 31173*2003 can also be combined.
- Metal products are marked according to the same principle as wooden ones, only the dimensions are indicated not in decimeters, but in millimeters, and a strength class designation is added. For example, the marking DSV DKN 2100-1270 M3 stands for: internal steel door, double-leaf, with a closed frame, opening outwards. Height 2100 mm, width 1270 mm - strength corresponds to class M3.
Complete door blocks made of metal must be delivered to the customer assembled, including with installed locks. By additional agreement, the door can be equipped with a closer, a viewing eye or an opening limiter.
A complete set of keys must be sealed in an envelope and handed over to the buyer against signature. They are accompanied by a product passport, plus installation instructions from the manufacturer.
Outdoor structures
In the previous chapter we talked about internal wooden doors. External standard doors are manufactured according to a different standard, number 24698-81. It does not apply to doors for cultural buildings, shopping and sports centers, train stations, as well as to structures whose area exceeds 9 m2.
So:
- This document regulates the production of three types of doors: under the letter “H” - vestibule and entrance doors, under “C” - service doors. The third type is designated by the letter "L". This is not even a door as such, but a hatch (manhole) - for example, for exiting the entrance to the attic. Everything is similar here: the requirements for door designs, their standard sizes and markings are also set out, taking into account the purpose.
A wooden door at the entrance is an excellent option for a private home
Requirements for metal structures
According to GOST, such models must be made of steel with a flat and smooth surface, free from cracks and chips. The permissible curvature of the material used to assemble the canvas is 0.5 mm.
The sealing gaskets in such doors must be installed evenly, without gaps around the entire perimeter of the frame. Of course, metal doors produced by modern enterprises must, among other things, also be resistant to various types of adverse environmental factors. That is, during operation they should not appear rusty spots, fungus, scratches, chips, etc.
Hinges on such doors can be secured using both welding and mechanical connections. At the final stage of production, doors of this type should be coated with an additional protective layer with a preliminary primer. GOST, among other things, allows the use of wood as a finishing material in the manufacture of such doors. At the same time, parts made of timber and boards used for this purpose, according to the standards, must have a roughness of no more than 60 microns and a humidity of no more than 8-12%.
Sources
- https://dveri-inform.ru/bezopasnost/markirovka-dverey-po-gost.html
- https://o-dveryah.ru/bezopasnost/oboznachenie-na-chertezhakh-po-gostu/
- https://dveri-ultimatum.ru/stati/markirovka-protivopozharnyh-dverey
- https://zao-gefest.ru/dveri-dpm-rasshifrovka-i-markirovka.html
- https://FB.ru/article/467729/oboznachenie-dverey-na-chertejah-po-gostu-primer-markirovki
- https://aniko-gas.ru/plastikovye-okna/otkryvanie-okon-na-chertezhah.html
- https://sdelaidver.com/gost/gost-dveri-337
- https://atel-e.com.ua/okna/metal-plastic-windows/window-help/opening-windows-drawings.html
[collapse]
Post Views: 5,773
Metal blocks
Today, wooden entrance doors are installed mainly in private houses. In multi-storey buildings, preference is often given to metal doors - and they are manufactured according to a different standard: 31173*2003. This document sets requirements for the manufacture of steel blocks with devices embedded in them that prevent unauthorized entry into the premises.
So:
- As for the mechanisms of these devices, they, in turn, are manufactured in accordance with GOST 51242 98. Doors and gates, windows and shutters, blinds and safes - all structures on which protective mechanisms are installed must meet all the requirements defined by this standard .
As for the standard for the doors themselves, it applies only to steel blocks installed in civil buildings for various purposes, including residential ones. As for special-purpose doors, which must be, for example, bulletproof, or resistant during an explosion or fire, they are manufactured according to completely different regulatory documents.
Main types of products
The marking of doors of various designs on the drawings according to GOST has the following meaning:
- "G". It consists of one or two canvases and is mounted inside the building. The product can be assembled with a box, threshold and covers;
- "ABOUT". Similar in type to the previous version, but may additionally have glass inserts;
- "TO". Pendulum type, where the door swings. The design mainly consists of two panels and no threshold;
- "U". Entrance type of product with reinforced frame and canvas. Installed at the entrance to a private house or apartment.
Types of signs
Fire safety diagrams contain various symbols.
They are regulated by a specially developed state standard. In accordance with existing standards, fire safety signs are divided into 2 groups: green or red. Green signs refer to the category of directions in which it is necessary to evacuate building employees.
The red symbols of the evacuation plan make it possible to indicate the places where the means of primary fire extinguishing are located. Every employee must familiarize themselves with them.
Fire safety signs that indicate exits are installed in special places. They are usually recommended to be mounted on the wall, and special arrows are placed next to them. Such signs help to indicate the path of movement in the event of a fire. The symbols in question are usually placed near exits or above the doors themselves.
Preface
The goals, basic principles and general rules for carrying out work on interstate standardization are established by GOST 1.0 “Interstate standardization system. Basic provisions” and GOST 1.2 “Interstate standardization system. Interstate standards, rules and recommendations for interstate standardization. Rules for development, acceptance, updating and cancellation"
Standard information
1 DEVELOPED by the Open Joint Stock Company “Center for Methodology of Standardization and Standardization in Construction” (JSC “CNS”)
2 INTRODUCED by the Technical Committee for Standardization TC 465 “Construction”
3 ADOPTED by the Interstate Scientific and Technical Commission for Standardization, Technical Regulation and Conformity Assessment in Construction (MNTKS) (Minutes dated December 8, 2011 N 39)
The following voted for adoption:
| Short name of the country according to MK (ISO 3166) 004-97 | Country code according to MK (ISO 3166) 004-97 | Abbreviated name of the national standardization body |
| Azerbaijan | AZ | Gosstroy |
| Armenia | A.M. | Ministry of Urban Development |
| Kazakhstan | KZ | Agency for Construction and Housing and Communal Services |
| Kyrgyzstan | KG | Gosstroy |
| Moldova | M.D. | Ministry of Construction and Regional Development |
| Russia | RU | Department of Architecture, Construction and Urban Development Policy of the Ministry of Regional Development |
| Tajikistan | T.J. | Agency for Construction and Architecture under the Government |
| Uzbekistan | UZ | Gosarchitectstroy |
| Ukraine | U.A. | Ministry of Regional Development, Construction and Housing and Communal Services |
4 By Order of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology dated October 11, 2012 N 481-st, the interstate standard GOST 21.201-2011 was put into effect as a national standard of the Russian Federation on May 1, 2013.
5 INSTEAD GOST 21.501-93 in part of Appendix 1 and ST SEV 1633-79, ST SEV 2825-80, ST SEV 2826-80, ST SEV 4937-84
6 REPUBLICATION. July 2022
Information on the entry into force (termination) of this standard and amendments to it on the territory of the above states is published in the indexes of national standards published in these states, as well as on the Internet on the websites of the relevant national standardization bodies.
In case of revision, modification or cancellation of this standard, the relevant information will be published on the official website of the Interstate Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification in the catalog “Interstate Standards”