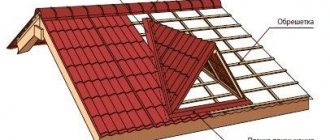
The requirements for window installation are quite high. The structure must have the necessary strength, provide a sufficient level of illumination and ventilation of the room under the roof, and organically fit into the architectural appearance of the structure, making it recognizable.
Dormer windows have been popular for many centuries. The fashion for their appearance has constantly changed, and today dormer and dormer windows can differ significantly in their design features and design.
In addition to window structures mounted directly into the roof plane, windows with vertical glazing are popular
:
- without side walls, with a pediment in the plane of the building;
- with side walls and pediment in the plane of the building;
- with side walls and pediment outside the plane of the building.
Small triangular, trapezoidal and arched openings with glazing of the entire vertical plane are actively used. Among structures with side walls, roof dormer windows differ in the type of roof they have.
:
- single-pitched;
- gable;
- hip;
- arched (with a semicircular or beam arch);
- flat french.
The location and type of windows should be selected taking into account the style of the building and the placement of ordinary windows. Otherwise, they will be perceived as an alien element on the roof.
Window design
The design and installation of a dormer window should be carried out in accordance with the requirements of SNiP (SNiP II-26, SNiP 21-01)
. Regardless of the design features and style of the chosen structure, it is necessary to comply with building rules and regulations. This allows us to ensure the necessary reliability and durability of this structure without weakening the operational parameters of the building’s roof.
The key requirements of SNiP for dormer windows include
:
- installation is permissible if the roof slope angle is 35 degrees or more;
- superstructures must be located at a regulated distance from the external walls of the building;
- sashes opening and located on the dormer window must have a minimum size of 0.6×0.8 m, which means the permissible size of the roof window will be 1.2×0.8 m;
- if a window with a hip roof and a quadrangular opening is provided, its facade cannot be a continuation of the wall of the building.
GOST provides for the use of various materials for cladding. This could be copper, sheet metal, tiles. According to their design features, skylights can differ in the absence or presence of a roof overhang, their own roof, or a gutter. A large opening can have a balcony, which looks especially interesting and attractive. Lucarne windows are distinguished by the presence of side walls and a fully glazed facade.
Types of dormer windows
The requirements for window installation are quite high. The structure must have the necessary strength, provide a sufficient level of illumination and ventilation of the room under the roof, and organically fit into the architectural appearance of the structure, making it recognizable.
Dormer windows have been popular for many centuries. The fashion for their appearance has constantly changed, and today dormer and dormer windows can differ significantly in their design features and design.
In addition to window structures mounted directly into the roof plane, windows with vertical glazing are popular
:
- without side walls, with a pediment in the plane of the building;
- with side walls and pediment in the plane of the building;
- with side walls and pediment outside the plane of the building.
Small triangular, trapezoidal and arched openings with glazing of the entire vertical plane are actively used. Among structures with side walls, roof dormer windows differ in the type of roof they have.
:
- single-pitched;
- gable;
- hip;
- arched (with a semicircular or beam arch);
- flat french.
The location and type of windows should be selected taking into account the style of the building and the placement of ordinary windows. Otherwise, they will be perceived as an alien element on the roof.
Window design
The design and installation of a dormer window should be carried out in accordance with the requirements of SNiP (SNiP II-26, SNiP 21-01)
. Regardless of the design features and style of the chosen structure, it is necessary to comply with building rules and regulations. This allows us to ensure the necessary reliability and durability of this structure without weakening the operational parameters of the building’s roof.
The key requirements of SNiP for dormer windows include
:
- installation is permissible if the roof slope angle is 35 degrees or more;
- superstructures must be located at a regulated distance from the external walls of the building;
- sashes opening and located on the dormer window must have a minimum size of 0.6×0.8 m, which means the permissible size of the roof window will be 1.2×0.8 m;
- if a window with a hip roof and a quadrangular opening is provided, its facade cannot be a continuation of the wall of the building.
GOST provides for the use of various materials for cladding. This could be copper, sheet metal, tiles. According to their design features, skylights can differ in the absence or presence of a roof overhang, their own roof, or a gutter. A large opening can have a balcony, which looks especially interesting and attractive. Lucarne windows are distinguished by the presence of side walls and a fully glazed facade.
Accommodation options
Roof options are divided into 2 types.
Single-pitch
The simplest solution is a flat roof with a slight slope and a slightly larger canopy.
Regarding the requirements for the device, the following can be noted: since its angle of inclination is small, the smaller the degree, the more slippery the coating should be.
Gable
This is a hybrid of a single slope and a triangle, i.e. triangular cap and the presence of side walls. Such options are erected mainly for the sake of creating a certain architectural style, since they are more complex than triangles in execution, and are less functional than single slopes.
Construction stages
- cutting into the roof rafters is unacceptable;
- the foundation must be strengthened;
- the frame is assembled after preparing the elements according to the template;
- the bottom of the window should be at an appropriate distance from the “clean” floor.
Finished frame
After construction, the frame is sheathed and the roof is laid.
Triangular dormer
If you plan to make a dormer window with your own hands, most often a triangular-shaped opening with steep roof slopes is installed
. This common design is characterized by the fact that the gable wall of the opening is installed without recessing into the roof - it must be located in the same plane as the corresponding outer wall.
Triangular openings in the roof should be located in line with windows located lower in the walls of the building, so as not to disturb the architectural proportions of the structure.
The roof slopes of triangular openings are located at a large angle (60-70 degrees), so there is practically no increase in the usable area of the attic. The advantage of triangular windows is their aesthetic appeal and the ability to create an original layout for the attic space.
If you plan to install a triangular dormer window with your own hands, you should take into account that its roof is adjacent to the roof of the building, going down to the place where the valley is formed. Thus, during the arrangement there is no need to waterproof the joints of the side walls and the roof, which greatly simplifies and speeds up the sealing and finishing of the opening and the main roofing of the building.
Structure frame
Before you start building the frame, you need to frame the roof of the house - build gables, mount the rafter system. It is necessary to provide openings between the rafters where windows are installed. The rafter system of a dormer window has its own characteristics: the rafter legs framing such openings must be made double or triple, since they will subsequently bear an increased load.
According to SNiP, the gables of openings located in the roof must be supported by side walls, which are installed perpendicular to the external wall deep into the building and have a height of 1.5 meters
. The frames of the side walls rest on the ceiling beams.
The side wall frame is installed after assembling the roof truss system of the building. After that, you should tie the horizontal crossbars and racks of the gable frames of the openings.
Further work is carried out in several stages
:
- Since the gables of a triangular window are located in the same plane with the walls of the building, the lower ends of the rafters adjacent to the walls should be cut flush with the wall sheathing.
- Jumper beams are mounted between the double rafters of the opening frame. It is recommended to use metal overhead brackets.
The use of notches and tie-ins that weaken the rafter beams is not allowed.
Valley device
The installation of a dormer window on the roof, which has a triangular shape, may be similar in appearance to the installation of a multi-gable roof. But there is a noticeable difference in installation technology. The slopes of a multi-gable roof most often have the same slope, while a triangular opening is equipped with a roof with slopes whose inclination angle is 60-70 degrees. Thus, the connection of the roof slopes of the window with the roof slopes of the building is carried out with the formation of non-standard valleys (valleys).
To arrange the dormer window, slanted rafters are used, into which the spigots, shortened rafter legs, rest (at an angle of 60-70 degrees). To install this structure, it is necessary to calculate the length and cross-section of the grooved rafter beam, the angles at which the side walls and the ridge beam meet. Each triangular rafter opening requires a pair of mirror-symmetrical beams of this type.
It is recommended to make shortened rafters using a universal template; this significantly speeds up the work.
Bottom of dormer window
When considering how to make a dormer window, you need to carefully consider the installation features of its lower part. It must be designed in such a way that the inner part of the soft roof is hidden in it through the side walls and is not visible from the inside. For this purpose, a simplified method of installing the gutter is used.
The valley beam is installed on top of the roof sheathing of the house. The lower ends of the rafter legs of the gable roof of the window rest against this beam. At the final stage, the structure is sheathed with sheets of plywood, on top of which the roofing material is attached. Sheathing with plywood starts from the ridge of the dormer window, installation of the roofing is carried out in the direction from bottom to top.
If you plan to install window openings on your own, it is recommended that you first familiarize yourself with the installation features of these structures. It is recommended to entrust the calculation and arrangement of windows of original shapes, installation of complex roof connections to professionals
.
Installation stages
The installation of dormer windows is a responsible undertaking.
The process resembles the specifics of installing a multi-gable roof, but it has its own characteristics and important nuances.
Important! When arranging an attic structure, it is worth knowing that the angle of inclination of the triangular dormer windows is 64 degrees, respectively, the angle of inclination of the roof will be 40 degrees.
Therefore, difficulties often arise with connecting the corresponding planes. As a result, the grooves turn out to be non-standard, so the design of each component of the structure separately requires an individual approach.
For the upper base, a specific structure is prepared, consisting of slanted rafters. Shortened rafters will rest on it during operation. For the installation to be successful, it is important to have information about the dimensions of the valley rafter beams and to know the angle of contact of the ridge beam with the side wall. The installation process is as follows:
- using a level, the center point is determined, which is selected relative to the ridge beam and the groove;
- a line is measured from the center that leads to the corner of the side wall, and the line of the ridge beam is also drawn;
- the angle resulting from the intersection of two lines is measured, the lower part of the rafters of the valley is sawed off;
- for convenience, a fishing line is stretched between the corners of the side wall and the ridge beam, and then the cutting angle of the upper end of the rafter beam is measured with measuring instruments;
- The workpiece is marked, the end edges are filed taking into account the measured angles of 18 and 72 degrees, respectively.
The second beam is installed symmetrically. To ensure that the process does not cause difficulties, it is necessary to have visual drawings and diagrams.
Dormer window design
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-nG9lO7BNvwAfter completing the installation work on installing the upper part of the structure, we proceed to installing the lower base. To do this, a valley beam is fixed to the top of the roof sheathing of the building, which will serve as a support for the ends of the rafters. The design is carried out according to a single algorithm, after which the length of the rafters must be reduced to the optimal size. After completing the design stage and direct installation, the structure is sheathed with waterproof plywood, and the final roofing covering is laid on top.
Installation of a dormer window
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MWe6H5j9zPkThe installation of dormer windows in attics or attics is invaluable. When constructing dormer windows, you need to take into account several factors: design features, materials, individual dimensions and style. First of all, such structures are an important element of the ventilation system, providing access to natural light and an optimal microclimate in the room.
In addition to high performance characteristics, dormer windows of all kinds can increase the level of prestige and add a touch of elite charm to the architectural style of the building.
Lucarne or dormer window on the roof
Once upon a time, lucars, superstructures above the roof, served only to ventilate the space under the roof, but time “prepared” a new purpose for them. They have become a stylish and unusual decorative detail for the roof with many functionalities, for example, they are used to illuminate residential attics and increase the usable area. The invention of the dormer window is associated with the name of the master inventor who first installed a similar structure on the roof of the Moscow arena. His last name was Slukhov, which is why they are called rumors. This is just one version of the origin of the Russian version of the name lucarna. There is also this: the original purpose of such openings was ventilation, and the word “hearing” once corresponded to the meaning of “vent” and “hole”. The lucarne looks like a small house with a roof, walls and facade made of glass, usually matching the general style of the house with its decoration, architectural details, etc. Often it intersects the roof of the house at the level of the ridge, that is, at its highest point.
Rafter system
Rafters are the load-bearing system of pitched roofs. They consist of rafter legs placed obliquely, vertically placed racks and obliquely mounted struts. If necessary, they can be connected from below with horizontal rafter beams. Rafter systems are divided into hanging and layered.
When a roof is being built, the layered structure rests with its ends on the walls and partitions of the building, and in the middle, if the span is more than 4.5 m, on additional supports.
The arrangement of an intermediate beam makes it possible to increase the width that the rafters cover to 12 m, and the width of two supports to 15 m.
Hanging rafters rest with their ends only on the walls. This system is selected if the distance between the external walls is no more than 6.5 m.
- In wooden log and cobblestone buildings on their upper crowns;
- In frame buildings - on the top frame;
- In brick, block, stone buildings - on a Mauerlat having a thickness of 14/16 cm.
The support beam can be mounted along the entire length of the house or placed only under the rafter leg.
Note! When the legs have a small cross-section, they sag over time. To prevent this, you need to make a special grille, which includes a stand, struts and a crossbar. For this, boards with a cross-section of 15×2.5 cm are used.
To fix the rafter legs, a tie is used that connects their lower sides. If the end of the rafter slides along the tie, it is able to destroy it.
To prevent this from happening, when making a roof, you need to drive your foot into the tie with a spike, a tooth, or both at the same time. In addition, it is recommended to place the rafters at a distance of about 30/40 cm from the edge.
What is a dormer window for? ↑
Perhaps the lucarne would have retained its decorative purpose, but over time, with the increase in the population of Europe, a parallel need for additional living space arose. Thus, the idea arose to use the attic space for this purpose, which could only be illuminated and ventilated through an opening in the roof. Attics are not just a tribute to the past; they are still successfully used today even for residential floors. That is why lucarne has not lost its relevance today.
The need for a dormer window in non-residential attics is beyond doubt. Indeed, if we assume that air does not move in the attic space under the roof, then sooner or later wood structures will begin to rot. The fact is that when warm air comes into contact with the cold surface of the roof, condensation forms, the moisture from which subsequently flows onto the elements of the sheathing and rafter system.
For air to move into the attic, cold air must come from outside; it will accelerate and dilute the warm air that comes from below. In this way, the effect of condensation can be avoided. As a rule, a dormer window with louvres is used for a cold attic.
However, it is not always possible to fully ventilate a cold attic using dormer windows alone. For additional air intake from the atmosphere, ventilated eaves are installed in apartment buildings. If the space under the roof is designed for living space, then they are used for natural lighting. Although, according to experts, the flow of light through a lucarene opening is less than that of an attic, since the presence of side walls significantly reduces the volume of penetrating light. Openings can be located in one or several rows.
And finally, a hatch is a possibility of access to the roof for emergency maintenance, say, in case of fire, flood, etc. Perhaps one could get by with one exit, but imagine how inconvenient this is in the case of a long building. As a rule, stairs in the form of wooden ladders are arranged at the edge of the hatch, which, naturally, should be located in the middle of the entrance. A pair of boards on which the transverse strips are attached is enough to climb up them to the roof ridge. In this case, as a rule, the distance between the lower edge of the opening and the surface of the attic floor is about 90 cm. The upper edge of the opening is placed based on the height of the attic ceiling. It is clear that the higher the hatch structure is placed, the more illuminated the under-roof space will be.
Requirements for fire escapes and roof exits 2022
Requirements for fire escapes and roof exits of buildings and structures are given in:
Here are the requirements of these regulatory documents that relate directly to fire escapes and roof exits:
According to Federal Law-123 “Technical Regulations on Fire Safety Requirements”:
Article 39. Classification of stairs
2. Fire escapes intended for fire extinguishing and emergency rescue operations are divided into the following types:
1) P1 - vertical stairs;
2) P2 - flight stairs with a slope of no more than 6:1.
Article 90. Ensuring the activities of fire departments
1. For buildings and structures the following must be provided:
2) means of lifting personnel of fire departments and fire equipment to the floors and roofs of buildings and structures;
3) fire-fighting water supply, including those combined with utility or special ones, dry pipes and fire-fighting tanks (reservoirs);
2. In buildings and structures with a height of 10 meters or more from the mark of the fire truck passage surface to the roof eaves or the top of the outer wall (parapet), exits to the roof from the stairwells must be provided directly or through the attic or along type 3 stairs or through external fire escapes stairs.
According to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated April 25, 2012 No. 390 “On the fire safety regime”:
24. The head of the organization ensures that external fire escapes and fences on the roofs (coverings) of buildings and structures are maintained in good condition, they are cleared of snow and ice in the winter, and organizes operational tests of fire escapes and roof fences at least once every 5 years. with the preparation of an appropriate test report, as well as periodic inspection of the condition of rescue equipment from heights in accordance with the technical documentation or passport for such a product.
75. The head of the organization ensures the proper maintenance (at any time of the year) of roads, driveways and entrances to buildings, structures and structures, open warehouses, external fire escapes and fire hydrants.
It is prohibited to use turning areas and special areas intended for the installation of fire-rescue equipment for parking vehicles (private vehicles and corporate vehicles).
370. The external fire escapes and fences provided for by the project on the roofs of buildings under construction are installed immediately after the installation of load-bearing structures.
According to SP 4.13130.2013 Fire protection systems. Limiting the spread of fire at protection facilities. Requirements for space-planning and design solutions:
7 Ensuring the activities of fire departments
7.1 For buildings and structures the following must be provided:
— means of lifting personnel of fire departments and fire fighting equipment to the floors and roofs of buildings and structures;
— fire-fighting water supply, including those combined with utility or special ones, dry pipes and fire-fighting tanks (reservoirs).
7.2 In buildings and structures with a height of 10 meters or more, from the mark of the fire truck passage surface to the roof eaves or the top of the outer wall (parapet), exits to the roof from stairwells must be provided directly or through the attic or along type 3 stairs or external fire escapes .
7.3 The number of exits to the roof (but not less than one exit) and their location should be provided depending on the functional fire hazard class and the size of the building and structure:
- for every full and partial 100 meters of the length of a building and structure with an attic covering and at least one exit for every full and partial 1000 square meters of the roof area of a building and structure with an attic covering for buildings of classes F1, F2, F3 and F4;
- along fire escapes every 200 meters along the perimeter of buildings and structures of class F5.
7.4 It is allowed not to provide:
- fire escapes on the main facade of the building and structure, if the width of the building and structure does not exceed 150 meters, and there is a fire water supply on the side opposite the main facade;
— access to the roof of one-story buildings and structures with a covering area of no more than 100 square meters.
7.5 In the attics of buildings and structures, with the exception of buildings of class F1.4, exits to the roof, equipped with stationary stairs, should be provided through doors, hatches or windows measuring at least 0.6×0.8 meters.
7.6 Exits from staircases to the roof or attic are provided along flights of stairs with landings in front of the exit through fire doors of the 2nd type measuring at least 0.75×1.5 meters.
The indicated flights and platforms must be made of non-combustible materials and have a slope of no more than 2:1 and a width of at least 0.9 meters.
7.7 In buildings and structures of classes F1, F2, F3 and F4 with a height of no more than 15 meters, it is allowed to provide exits to the attic or roof from stairwells through type 2 fire hatches measuring 0.6×0.8 meters on fixed steel stepladders.
7.8 On technical floors, including in technical undergrounds and technical attics, the passage height must be at least 1.8 meters, in attics along the entire building and structure - at least 1.6 meters. The width of these passages must be at least 1.2 meters. In certain areas with a length of no more than 2 meters, it is allowed to reduce the height of the passage to 1.2 meters, and the width to 0.9 meters.
7.9 In buildings and structures with attics, hatches are provided in the enclosing structures of the attics.
7.10 In places where there is a difference in roof height (including for lifting skylights onto the roof) of more than 1 meter, fire escapes are provided.
7.11 It is allowed not to provide fire escapes if the difference in roof height is more than 10 meters, if each section of the roof with an area of more than 100 square meters has its own exit to the roof or the height of the lower section of the roof does not exceed 10 meters.
7.12 For ascent to a height of 10 to 20 meters and in places where the roof height differs from 1 to 20 meters, fire escapes of type P1 should be used; for ascents to a height of more than 20 meters and in places where there is a difference in roof height of more than 20 meters, fire escapes of type P2 should be used.
7.13 Fire escapes are made of non-flammable materials, located no closer than 1 meter from the windows and must have a design that allows the movement of fire department personnel in combat clothing and with additional equipment.
7.14 A gap of at least 75 millimeters wide should be provided between flights of stairs and between handrails of railings of flights of stairs, with the exception of two-flight stairs installed in two-story buildings with a height of no more than 12 meters to the floor level of the second floor.
7.15 In each fire compartment of buildings and structures of class F1.1 with a height of more than 10 meters, buildings and structures of class F1.3 with a height of more than 50 meters, buildings and structures of other functional fire hazard classes with a height of more than 28 meters, underground parking lots with more than two floors, Elevators must be provided for transporting fire departments.
7.16 In buildings and structures with a roof slope of no more than 12 percent inclusive, with a height to the cornice or top of the outer wall (parapet) of more than 10 meters, as well as in buildings and structures with a roof slope of more than 12 percent, with a height to the cornice of more than 7 meters, fencing should be provided on the roof in accordance with the requirements of this set of rules. Regardless of the height of the building, the specified fences should be provided for exploited flat roofs, balconies, loggias, external galleries, open external staircases, flights of stairs and landings.
Types of lucarnes ↑
Lucarnes are classified according to the following parameters:
- by design features;
- form;
- material.
Various designs ↑
As an example, let's look at the three most common ones.
Flat
The task of a lucar with a flat roof (slope no more than 15°) is to ensure the flow of the greatest volume of light and air into the under-roof space. Given the fairly small slope, gutters are installed to drain excess water. The same parameter affects the choice of material for covering; for example, tiles are not suitable in this case. Coating with metal, zinc, copper and aluminum would be more appropriate.
Single-pitch
Lucarne with one slope is considered the simplest option. This design has a flat roof with a slope slightly less than the slope of the main roof. In addition to the fact that this is the simplest version of the device, it is also quite cost-effective. This design allows you to get more space than a gable one with the same width. And the smaller the slope of the slope, the larger the space. The only thing that should not be forgotten when designing a lean-to hatch is to ensure proper water drainage. Depending on the decorative tasks set, the roof of a lean-to hatch can have a rectangular or trapezoidal shape.
When choosing the design of such a window, you must take into account that a large lean-to window does not look very elegant.
Gable
This kind of hatch is more complex in design than the lean-to version, and its construction is more expensive. The shape of its roof can be peaked or rounded, and rainwater in this case will drain on both sides. With such a device, the lucarne “eats” the height of the ceiling, that is, the main part of the area formed during its installation cannot be used as living space.
Shape and dimensions ↑
There are no strict restrictions on the design of such structures. The location that dormer windows may have and their dimensions depend more on the individual vision of the designer and the purpose - whether it serves a decorative or practical role. However, since dormer roofing has a long history, certain patterns have emerged over the years. Based on them, a number of requirements were developed. The rules provide, in particular, that:
- their installation is possible on roofs with a slope starting from 35⁰;
- the minimum permissible size of opening doors is 60x80 cm, respectively, the size of the hatch can be no more than 120x80 cm;
- they should not be located close enough to the ridge, eaves and gables;
- the pitch of window openings must be at least 0.8 m, otherwise installation of the roof covering and preventive inspection of the roof become more difficult, and snow bags will form in these places.
Triangular can most often be found in private construction. In this case, the roof slopes of the lucarne act as side walls. The dormer window GOST 12506 81 with a triangular opening has its advantages. Externally very attractive and elegant, they can be located at a fairly high level, and the small number of connections to the main roof reduces the amount of waterproofing work. For these lucarenes, the correctly calculated size is very important; it should not be too small or too large. The slope should be approximately the same as the main roof. The issue of obtaining usable space in the attic in this case is secondary; the main thing is to ensure as much light as possible and an influx of fresh air.
But at the same time, you need to know that if you do not bring the facade of the hatch flush with the facade of the building, then the internal illumination of the attic will suffer.
Lucarnes are not only polygonal in shape. In the Baroque era, the most popular were the dormer round ones, but today they have been replaced by semicircular structures that are more original in design. The semicircular dormer is known by different names:
- “bat” bordered by a smooth “wave”;
- its combination with a hatch with a pitched roof - thanks to the curved silhouette of the side walls, fits perfectly into the main roof;
- “Bull's eye” is an oval-shaped lucarne with a steep “wave”.
These structures look especially beautiful on roofs tiled or slate. Narrow semicircular hatches look like loopholes and are appropriate if the building needs to be given a historical look. Some of their advantages include the following:
- there are no “blind” corners in the design in which snow will accumulate;
- rainwater flows freely from the roof, that is, it can be argued that in such a design the likelihood of leakage is initially minimized
The once popular wooden dormer windows are gradually losing their relevance. Their position today is occupied by plastic ones, which are much more affordable and do not require such care.
GOST 12506-81 Wooden windows for industrial buildings. Types, design and dimensions (590.5 KiB, 1,830 hits)
What are they?
There are different solutions. The window structure can be built into the roof plane or it can be vertical glazing.
The use of small triangular, arched and trapezoidal openings with a fully glazed vertical plane is common.
Dormer windows on the roof, the structures of which have side walls, vary depending on the type of roof:
- flat;
- quadrangular single-pitched;
- quadrangular gable;
- triangular;
- semicircular;
- panoramic trapezoidal;
- light lanterns;
- round.
- Single-pitch
This is the simplest type, characterized by the presence of a flat roof, the slope of which is less than the slope of the roof.
A lean-to window has a flat roof with a slight slope
It is characterized by the presence of sufficient space under the ceiling compared to the gable option. When installing it, attention should be paid to providing high-quality drainage for rainwater and other precipitation. The downside of a slight slope is the reduction in the number of options for roofing materials that can be used.
- The traditional solution is a window located in the wall plane on a gable roof.
The gable window design significantly reduces the space under the roof
The design of the gable roof itself is characterized by a small space above the head. The window can have a pointed or rounded shape. A complex structure will require greater financial costs than a lean-to structure. The downside is that the space under the roof will actually decrease.
- The external design of a hip window evokes an association with a measured and comfortable life. The angle of inclination of the structure and the roof repeat each other.
- The arched design gives the appearance of the house the atmosphere of a mansion. In addition to the horizontal placement of dormer windows, vertical placement is possible.
- A window called “skylight” will add visual lightness and airiness to the exterior of the building.
- Panoramic windows on the roof provide high visibility and maximum natural light.
- The enclosing side surfaces of the trapezoidal window are covered with roofing material.
- A window called a “bat window” is better suited for window designs with a slight slope.
- Dormer windows do not serve to decorate the facade. They perform the practical task of providing the attic living space with sufficient natural light and fresh air. Installation of these windows will not require the construction of auxiliary structures. In terms of waterproofing qualities, modern window systems are reliable and durable.
Calculating the ideal size of roof windows
In modern private houses you can often see residential attics located on the upper floors, roofs and in the under-roof space. Such rooms, like other living rooms, require lighting, with the exception of storage rooms, dressing rooms, and toilets . What sizes of attic windows need to be chosen, how much area to allocate for glazing, how many windows need to be built into the attic can be determined using the regulatory framework and GOSTs, and expert advice will help determine the number of windows and their location. There are high requirements for the design of roof windows. The window must be strong enough to withstand gusts of wind and precipitation. Provide the necessary degree of illumination, maintain ventilation of the room and at the same time not disturb the aesthetics and general architectural appearance of the building.
Russian building codes
The rules and regulations regarding the construction of roofing structures are prescribed in many documents. Some of them are morally outdated, however, they have not yet been cancelled.
Design should be carried out taking into account the instructions and limitations of current standards:
- SP No. 17.13330.2011: “Roofs”;
- SNiP No. 2.08.02-89: “Public buildings and structures”;
- SNiP No. 2.09.04-87 “Administrative and domestic buildings”;
- SNiP No. 31-03-2001: “Industrial buildings”;
- SNiP No. II-3-79: “Construction heating engineering”;
- SNiP No. 3.04.01-87: “Insulating and finishing coatings”;
- SNiP No. 21-01-97: “Fire safety of buildings and structures”;
- SP No. 31-116-2006 “Design and installation of sheet metal roofs”
And finally, one of the main documents according to which the roof should be designed: SNiP No. 2.08.01-89: “Residential buildings”.
Source: krovlyakryshi.ru
Types of roof windows
There are various types of window structures built into the roofs of buildings. The main division of window openings in the roof of buildings is into dormer and attic. By auditory structures we mean structures installed in attics to provide access to air and light. Basically, dormer window openings are arranged vertically and require the construction of a rafter structure.
Dormer window openings are made triangular, arched or trapezoidal, entirely glazed in a vertical plane. Depending on the type of roof, windows are also divided into:
- windows in a pitched roof;
- windows in a gable roof;
- windows in the hip roof;
- arched structures (having a semicircular or beam arch);
- flat french.
Dormer windows differ from dormer windows in that they were originally located sloping, built into the roof surface and provided more light. At the moment, the attic type is spreading more and more widely and, along with the classical design, the following are appearing:
- windows in gable wall;
Advice! It is recommended to choose the type and placement of roof windows taking into account the style of the building and the location of the usual window openings. Otherwise, the appearance of the house will not be aesthetic, and the attic openings will create disharmony. At the same time, one should not deviate from GOSTs.
Varieties of roof slope design
The attic window has a roof, which is designed according to the general rules for arranging roof decking. The frame of the opening can be located in the plane of the slope and be inclined, but more often the window frame is taken out and placed vertically. For the resulting “birdhouse”, a roof of various configurations is made.
- flat covering;
- single-pitched quadrangular roof;
- gable quadrangular;
- semicircular;
- triangular;
- trapezoidal panoramic;
- glass lantern.
Choosing a roof window
The decision on the choice of design, as well as on the number of attic window openings, should ideally be made at the stage of creating the project and building the house. Since the width of window openings directly depends on the design of the rafter system, it is the design specialists who must give recommendations on the size of the openings for dormer window structures. If you have to rebuild an existing roof by constructing an attic in a finished house, then you need to carefully examine the structure of the roof. In old buildings, it may not be possible to build in a window opening of the desired parameters, since the roof rafters will not allow such a structure to be installed; you will have to be content with a dormer window. In relatively new houses, rebuilding the attic into a living space will allow you to install a roof window that meets the standards. [ot-gallery url=”//lestnitsygid.ru/gallery/varianty-mansardnyx-okon”]
Frame structure
Whatever the shape of the window, hip, gable or arched, the main design rule is that the design of its frame should not violate the roof truss system. The “cuckoo” is mounted as follows:
- First, the front beams are installed between the rafters of the roof frame.
- Vertical posts are installed on the rafters that limit the width of the structure.
- A purlin connecting the supports to each other is laid on top of each row of vertical posts.
- Rafter legs are installed on the purlins, which are connected at the ridge purlin.
- The frame is sheathed with siding or clapboard, and the roofing is laid on the sheathing.
Important! It is not easy to install an auditory birdhouse on the roof without damaging the roof rafter frame. To learn more about the process, you can watch the video tutorial or read our instructions.
Design features
Most often, the fastening of dormer window structures is carried out between the rafters. The frames should not allow water to pass through, the amount of which is much greater on the roof, so the structure must be airtight. The easiest way is to buy a ready-made double-glazed window from the manufacturer, which will protect the room from cold and leakage.
Attic window structures are fastened to the roof using a support plate. The frame flashing in the form of a metal frame helps remove moisture. To open a double-glazed window, friction hinges are provided, located above the central axis of the window. The location of the hinges is designed in such a way that when opened, moisture flows onto the roof and not into the room.
Step-by-step instruction
- According to the drawing, the roof rafters are reinforced at the installation sites.
- The structure is built between two rafters, to which two transverse supports of the canopy are attached.
- The window frame is formed.
- The resulting workpiece is attached to the beam with crossbars.
- The frame is reinforced with metal brackets, anchors and bolts.
- When fastening, leveling is carried out.
- The sheathing is being done.
- The gables are covered with boards or plywood.
- The roof covering is laid.
vote
Article rating
How to design
When planning the attic design, designers must adhere to building codes and requirements and GOST. The main ones are SNiP II-26 and SNiP 21-01; by adhering to these standards, it is possible to ensure reliable and long-term operation of roof windows, at the same time, without violating the technical and operational characteristics of the roof and the entire building.
The basic requirements of GOSTs and SNiPs for window structures installed in the roof include:
- requirements for the angle of inclination of the slopes, which should not exceed 35 degrees;
- the location of the superstructures must maintain the required distances from the external walls of the house;
- opening doors cannot have a size less than 0.60x0.80 m;
- permissible size 1.20×0.80 m;
- openings on structures with a hip roof with a 4-corner opening should not be located on facades that are a continuation of the wall of the house.
According to GOST, various types of facing materials can be used: copper and metal sheets, tiles, plastic elements. There are no strict requirements for design characteristics in GOSTs. Dormer windows can have projections or be recessed inward, and have their own canopy and gutter. Large window openings can have a balcony design, which decorates the architectural appearance of the building. Skylight windows, which are characterized by the presence of side walls, also have a place and organically fit into facades with continuous glazing.
Standards and nuances when designing
SNiP 11.26-2010 contains instructions for installation, location, and organization of ventilation.
Installation technology is limited by the following rules:
- the rafters framing the window opening must be double, as they carry an additional load;
- auxiliary purlins should not cut into the body of the rafter legs; their ends are fixed with steel plates;
- the frame is protected with moisture-resistant plywood;
- The pediment of the window is made vertically, the correctness is checked with a level or plumb line.
According to the standards, window houses must have walls whose height starts from 1.2 m. The frames of the vertical side railings rest on the ceiling purlins located under the opening. A distance of 0.8 m is allowed between adjacent dormer boxes; narrower spaces contribute to the accumulation of snow in the gaps.
How to determine the glazing area
The dimensions of the glazed surface in attic rooms, as well as in all residential premises, are determined mainly by the area of the rooms. According to GOST standards existing in construction, the ratio of the living area of the room to the glazing area of the windows should be 1:10, i.e. 1 square meter of windows should correspond to every 10 m2 of room. For children's rooms, as well as living rooms located in the attic, it is recommended to choose a ratio of 1:8. All rooms, excluding toilets and utility rooms (storage rooms, wardrobes) must have at least one window opening.
Where to place
Dormer windows differ from ordinary ones in that, due to their inclined location, they provide more light. Therefore they have become widespread. When designing the location of attic window openings, one should take into account the principle that two windows spaced in different places will provide better illumination than one of the same area. The level of the lower end of the opening recommended by GOSTs is 85 - 125 centimeters from the floor level. The upper edge should not be placed more than 195-225 centimeters from the floor level. Thus, the size of the slope depends on the angle of the roof - the smaller the slope, the longer the opening.
The size of window openings in accordance with GOST should not be more than 10% of the area of the plane located below. If the window openings in the attic are too large, this can lead to unnecessary heat loss. In addition, glass is less durable than roofing and a large area of glazed surface may not be able to withstand natural precipitation and strong gusts of wind. The optimal solution for the location of the openings is strictly in the center between the roof rafters.
General concepts
The term “covering” is often applied to industrial facilities or non-attic structures (also called combined), that is, elements that are also a ceiling.
More generally speaking, the main types of coverings include long-span flat, roofless, and also spatial structures.
The roof must first be designed to accommodate the loads that arise during its operation. Constant - from its own mass, as well as temporary - the weight of the snow cover and wind pressure.
The covering of roofs that is exposed to the external environment is called roofing. It must have waterproof and moisture-resistant properties, and not be afraid of chemically aggressive substances, ultraviolet radiation from the sun and temperature changes.
The main desired advantages of a roof are durability, lightness, aesthetic appearance, and cost-effectiveness during installation and operation.
The design of the roof and the selection of materials for the roof are determined during the design, and depend on the design of the building and the technology of roofing.