Appendix A (reference)
Standard values of external technological installation gaps for internal and inter-glass blinds
To determine the heat transfer resistance class, tables A.1 and A.2 show the standard values of external technological installation gaps for internal and inter-glass blinds, depending on their installation option:
e
1 - lower technological installation gap;
e
2 - upper technological installation gap;
e
3 - lateral technological installation gap.
Table A.1 - Internal blinds - standard values for external technological installation clearances
| Product | Location | Installation | Bottom gap e 1, mm | Top clearance e 2, mm | Side clearance e 3, mm |
| Corrugated blinds | On the window | Accurate | 0 | 0 | 20 |
| Adjustable | 0 | 0 | 2 | ||
| On the edge of the wall | Accurate | 25 | 0 | 60 | |
| Adjustable | 0 | 0 | 17 | ||
| Venetian blinds | On the window | Accurate | 10 | 3 | 10 |
| Adjustable | 5 | 3 | 3 | ||
| On the edge of the wall | Accurate | 50 | 3 | 60 | |
| Adjustable | 5 | 3 | 17 | ||
| Roller blinds without guides and boxes | On the window | Accurate | 50 | 40 | 40 |
| Adjustable | 10 | 20 | 20 | ||
| On the edge of the wall | Accurate | 55 | 40 | 55 | |
| Adjustable | 20 | 20 | 20 | ||
| Roller blinds with guides and box | On the wall or on the edge of the wall | Accurate | 20 | 10 | 15 |
| Adjustable | 10 | 2 | 2 | ||
| Note - Adjustable installation means that the dimensions of the blinds must be determined locally. | |||||
Table A.2 - Interglazed blinds - standard values of external technological installation gaps
| Product | Location | Installation | Bottom gap e 1, mm | Top clearance e 2, mm | Side clearance e 3, mm |
| Corrugated blinds | Built-in | Adjustable | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Venetian blinds | Built-in | Adjustable | 3 | 5 | 2 |
| Roller blinds | Built-in | Adjustable | 10 | 5 | 5 |
Mandatory declaration: responsibility of entrepreneurs
If a company has not declared the CU TR on fabric for blinds, it does not have the right to legally conduct its activities - produce, import, sell products. If an entrepreneur was caught conducting business without permission (or with an expired declaration), he faces administrative liability:
- Removal of blinds;
- Freezing the work of the enterprise;
- Fine of up to 1 million rubles;
- Refusal to carry out customs control.
Who can be an applicant?
In the declaration procedure under the CU TR, the applicant can only be an individual entrepreneur or a legal entity that has officially registered its business in the EAEU. If the products of a foreign manufacturer are subject to declaration, then he can submit documents only through an official representative in the EAEU, who, as a rule, acts as an importer.
Regarding voluntary fire safety certification, the applicant can be any company or individual entrepreneur.
The primary documents that will need to be submitted to the certification center include:
- statement;
- detailed characteristics of products in any form;
- standards used in production (state or internal) or a copy of technical specifications;
- copies of registration certificates of assignment of OGRN and TIN;
- copy of the charter;
- extract from the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs or the Unified State Register of Legal Entities;
- and other documentary evidence of product compliance with quality and safety requirements (QMS certificates, test reports, results of independent examinations).
If you still have unresolved questions about how to obtain a certificate for vertical or other blinds, you can ask our consultants. The information portal on certification "Rosstandart.Info" provides all consultations for free!
5.3 Marking
5.3.1 The marking must contain:
— name or trademark of the manufacturer;
— symbol according to this standard;
— month and year (last two digits) of manufacture.
5.3.2 The method and location of marking are indicated in the technical specifications for a product of a specific type.
5.3.3 General requirements for marking plates - according to GOST 12969 and GOST 12971.
5.3.4 General requirements for labeling of transport containers - according to GOST 14192.
3 Terms and definitions
This standard uses the terms established in GOST 28653, GOST R 51221, as well as the following terms with corresponding definitions.
3.1 shaft:
An element of a roller blind on which the fabric is wound.
3.2 wind load:
Air flow pressure per unit area of roller blinds.
3.3 hacking roller blinds:
A set of actions aimed at violating the integrity of roller blinds and achieving full access to the protected premises.
3.4 roller blinds:
A structure consisting of a canvas, a shaft with elements for its installation and fastening, elements for suspending the canvas to the shaft, guide bars, a drive and a protective box.
3.5 specified load application zone:
The limited area of the test specimen upon which the test load is applied.
3.6 bolt:
A locking element that secures the roller blinds in the closed position.
3.7 end profile:
The last (lower) profile of the roller blinds.
3.8 box:
The part of a roller blind in which the shaft is installed and the fabric wound on it is hidden.
3.9 guide rail:
A fixed load-bearing element of a roller blind fixed in the opening, designed to move the canvas along it.
3.10 full access roller blinds:
The result of a break-in that provides penetration into the protected premises and is characterized by the formation of a hole through which one of the full access templates can pass (according to GOST R 50862) or the canvas can be raised to a height of at least 300 mm.
3.11 canvas:
A part of a roller blind, assembled from movably interconnected profiles, covering an opening in the wall.
3.12 drive unit:
Part of a roller blind designed to raise (lower) the canvas.
3.13 profile:
A part of roller blinds in the form of strips of any configuration, the movable connection of which forms a roller blind fabric.
3.14 bullet resistance of roller blinds:
The ability of roller blinds to resist through penetration by bullets and the absence of secondary destructive elements dangerous to humans.
3.15 crossbar:
An element of a roller blind that connects the curtain to the shaft and blocks the blade when lowered.
3.16 static load:
A load of a certain magnitude acting on a given area of the roller blinds for a certain time.
3.17 load resistance:
The ability of roller blinds to remain operational after exposure to a certain load.
3.18 heat transfer resistance:
The ability of roller blinds to reduce heat exchange between two environments.
3.19 resistance to wind load:
The ability of roller blinds to withstand a certain wind load.
3.20 heat transfer:
Heat exchange between two environments through the roller blinds separating them.
3.21 shock load:
A load created by the mass of a moving body that has a certain amount of kinetic energy.
3.22 resistance of roller blinds to burglary:
The ability of a roller blind to withstand full access when subjected to static, impact and/or tool loads.
3.23 loading device:
A device by which a static or shock load is applied to the test sample.
3.24 fixing profile:
The first (upper) profile of the roller blind fabric, designed to fix it to the shaft.
3.25 roller blind part:
Composite structures and their connections that ensure the functionality of roller blinds and the fulfillment of specified requirements.
3.26 roller blind element:
Parts that ensure the assembly of parts and roller blinds as a whole.
Passing the test
Both declaration and receipt of a certificate for vertical, fabric, and plastic blinds are carried out in the following order:
- The company sends a request to the selected certification center;
- Specialists of this organization provide consultation, help determine the product code and identify the need for quality assessment, and decide on a certification scheme;
- The next stage is the preparation of a package of documents, development/registration of missing technical documentation;
- Next, product samples are selected, they are sent to an independent laboratory for examination, they are tested there, and test reports are issued based on the test results;
- If this is provided for by the selected certification scheme, then an audit is also carried out at the enterprise - the condition of the premises and operating equipment is analyzed, technological procedures are checked (for compliance with standards);
- The result is the issuance of a permit to the applicant and the entry of information about him into a unified register.
8 Control methods
8.1 All tests of roller blinds are carried out under normal climatic conditions in accordance with GOST 15150.
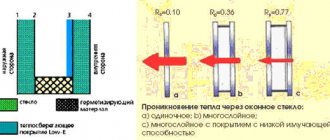
8.2 Heat transfer resistance (5.1.1.1) is checked according to GOST 26602.1.
The tests are carried out in two stages. At the first stage, the heat transfer resistance of a window or door is checked, at the second - the same window or door with installed roller blinds. The test result is the difference between the values of two indicators.
If the window or door has previously been tested for heat transfer resistance and there is a test report with the established value of the indicator, the first stage may not be carried out.
8.3 Tests for resistance to load when exposed to a solid body (see 5.1.1.2) and resistance to burglary (see 5.1.2.1) are carried out in accordance with GOST R 52503.
8.4 Tests for resistance to wind loads (see 5.1.1.3) are carried out in accordance with GOST 26602.5.
8.5 The protection of roller blinds from free penetration into the room (see 5.1.3.1) is checked manually without the use of special tools.
8.6 Tests for bullet resistance (see 5.1.2.2) are carried out in accordance with GOST R 51112.
8.7 Design requirements (see 5.1.3.4-5.1.3.6, 5.1.3.8, 5.1.3.9, 5.1.3.11-5.1.3.13, 5.1.3.15-5.1.3.17), ergonomic requirements in terms of configuration (see 5.1. 6.2), completeness (see 5.3), marking (see 5.4) and packaging (see 5.5) of roller blinds are checked visually and by comparison with design documentation and technological documentation.
8.8 Dimensions and their deviations (see 5.1.3.2, 5.1.3.3), the inertial path of movement of the roller blinds (see 5.1.3.14) are checked with a ruler in accordance with GOST 427, a tape measure in accordance with GOST 7502, a caliper in accordance with GOST 166 or another tool, ensuring the specified accuracy.
8.9 The deflection of the shaft under the influence of the mass of the web (see 5.1.3.7) is controlled by measuring the maximum deflection using a straight edge in accordance with GOST 8026.
8.10 The quality of welds (see 5.1.3.10) is checked visually according to GOST 3242.
8.11 Corrosion resistance of metal elements of roller blinds to neutral salt fog (see 5.1.4) is carried out in accordance with GOST 9.308.
8.12 The reliability of roller blinds (see 5.1.5.1) is checked by practical operation of operating cycles and visual monitoring of violations of the integrity and operability of the product after completion of the tests.
8.13 Ergonomic requirements regarding the muscular force exerted on the manual drive (see 5.1.6.1) are checked with a dynamometer in accordance with GOST 13837.
8.14 Compliance of materials and components with established requirements (see 5.2), including electric drives, for compliance with reliability requirements (see 5.1.5.2, 5.1.5.3) and safety (see section 6) is checked by testing and measurements or by analysis of quality documents (including test reports) received from the supplier.
What happens if certification is not carried out?
The absence of a fire certificate will lead an entrepreneur to serious trouble. For the first violation, he may be given a fine (the amount depends on the specific situation); for repeated violations, the punishment becomes more severe - the fine can reach several hundred rubles, goods will be confiscated, and activities will be frozen for three months. If you are an importer, they may impose a ban on the import of products.
If consumers were injured due to your fault, and non-compliance with fire technical regulations was revealed, you will face criminal liability.
2 Normative references
This standard uses normative references to the following standards:
GOST 2.601 Unified system of design documentation. Operational documents
GOST 2.610 Unified system of design documentation. Rules for the implementation of operational documents
GOST 9.031 Unified system of protection against corrosion and aging. Anodic-oxide coatings of semi-finished products made of aluminum and its alloys. General requirements and control methods
GOST 9.032 Unified system of protection against corrosion and aging. Paint and varnish coatings. Groups, technical requirements and designations
GOST 9.301 Unified system of protection against corrosion and aging. Metallic and non-metallic inorganic coatings. General requirements
GOST 9.308 Unified system of protection against corrosion and aging. Metallic and non-metallic inorganic coatings. Accelerated corrosion test methods
GOST 12.2.007.0 System of occupational safety standards. Electrical products. General safety requirements
GOST 166 (ISO 3599-76) Calipers. Specifications
GOST 427 Metal measuring rulers. Specifications
GOST 3242 Welded joints. Quality Control Methods
GOST 5264 Manual arc welding. Welded connections. Main types, structural elements and dimensions
GOST 7502 Metal measuring tapes. Specifications
GOST 8026 Calibration rulers. Specifications
GOST 12969 Plates for machines and devices. Technical requirements
GOST 12971 Rectangular plates for machines and devices. Dimensions
GOST 13837 General purpose dynamometers. Specifications
GOST 14192 Marking of cargo
GOST 15150 Machines, instruments and other technical products. Versions for different climatic regions. Categories, operating, storage and transportation conditions regarding the impact of environmental climatic factors
GOST 23170 Packaging for mechanical engineering products. General requirements
GOST 26602.1 Window and door blocks. Methods for determining heat transfer resistance
GOST 26602.5 Window and door blocks. Methods for determining wind load resistance
GOST 28653 Small arms. Terms and Definitions
GOST 30778 Sealing gaskets made of elastomeric materials for window and door units. Specifications
GOST R 50862 (EN 1143-1:2012) Safes, safe rooms and storage facilities for valuables. Requirements and test methods for burglary resistance
GOST R 51112 Banking protective equipment. Bullet resistance requirements and test methods
GOST R 51113 Banking protective equipment. Tamper resistance requirements and test methods
GOST R 51221 Banking protective equipment. Terms and Definitions
GOST R 51222 Banking protective equipment. Blinds. General technical conditions
GOST R 52503 Roller blinds. Test methods for burglar resistance and bullet resistance
GOST IEC 60335-1 Household and similar electrical appliances. Safety. Part 1. General requirements
Note - When using this standard, it is advisable to check the validity of the reference standards in the public information system - on the official website of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology on the Internet or using the annual information index "National Standards", which was published as of January 1 of the current year, and on issues of the monthly information index “National Standards” for the current year. If an undated reference standard is replaced, it is recommended that the current version of that standard be used, taking into account any changes made to that version. If a dated reference standard is replaced, it is recommended to use the version of that standard with the year of approval (adoption) indicated above. If, after the approval of this standard, a change is made to the referenced standard to which a dated reference is made that affects the provision referred to, it is recommended that that provision be applied without regard to that change. If the reference standard is canceled without replacement, then the provision in which a reference to it is given is recommended to be applied in the part that does not affect this reference.
Mandatory quality assessment
In the GOST R and TR CU systems, it is not mandatory to obtain a certificate for blinds - this type of product is not included in the relevant lists, in particular, it is not subject to RF PP No. 982 of December 1, 2009.
A mandatory document for blinds is a fire certificate - this document is drawn up in accordance with the requirements of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation “On Fire Safety Requirements” (regulated by Federal Law No. 123 of July 22, 2009). The list of goods for which fire certification is provided is regulated by RF PP No. 241 of 2009. Blinds are included in this list.
Advantages of voluntary certification
For all types of blinds, you can additionally issue a voluntary GOST R certificate. Its presence provides the following advantages:
- Entering new markets;
- Strengthening the image of the enterprise, loyal attitude on the part of consumers, business partners and government departments;
- Increasing the chances of accepting government orders and winning the tender;
- Fast implementation of supervisory examinations;
- Use of the PCT sign in official brochures, on the website, in advertising;
- Effective participation in specialized competitions.