Ensuring a comfortable temperature for people living in a private house or apartment in winter is a priority task for every owner. When organizing individual heating or heat supply in an apartment building, all elements are important, starting with what should be the distance from the floor to the heating radiator, and ending with the fluid pressure in the system. Before starting work, you should study the building codes and regulations (SNiP) relating to the organization of heat supply, and also find out at what distance experts recommend hanging the heating device.
In the living room
Distance from the window sill to the heating device
In fact, all modern heating devices and sectional heating batteries surprise with their high efficiency, an indicator of efficiency, providing similar characteristics due to the circulation of air, its natural flow through the heat exchange system. Actually, due to these design properties, it is not enough just to purchase highly efficient heating devices and power them with a coolant; it is necessary to provide conditions for convection - the natural transfer of heat by air. Let us indicate the distance required from the window sill to the heating device, as well as the main installation tips, as conditions for maintaining high efficiency.
Window sill board.
When installing marble window sills in a living space or a privatized house, many focus exclusively on the upper clearance of 100 mm, completely forgetting that by choosing an immensely protruding, wide window sill, you can disrupt not only the thermal cutoff of cold air, but also adjust the overall air circulation along the windows. The window sill board should not cover the heating device, creating a kind of niche for the battery, suggesting an enveloping movement of heat along it. Unfortunately, a specific size cannot be recommended, and the protrusion of the board should minimally interfere with the air circulation around the heating device and move it away from the glass.
Heating device mounting.
Before drawing the first attachment point on the wall, carefully study the existing instructions for the heat exchanger, because Many manufacturers inform about recommended installation gaps, which ensure high heat transfer from the battery itself. In the absence of such advice, they use general ones, according to SNiP 3.05.01-85. "Internal sanitary systems":
From the bottom of the window sill to the heating device, the minimum distance is 100 mm, since reducing it reduces the thermal air flow. From the floor to the bottom of the heating device, the clearance is in the range of 100-150mm, and increasing the distance increases the temperature difference in all rooms, and decreasing it again reduces the intensity of heat transfer. It is very important to provide for the distance from the wall surface to the heating device; it is made 25-30mm, because the rear surface is also actively involved in heat transfer. If factory councils are separated from SNiP, they are guided by the manufacturer who developed the battery.
installation of radiators
Heat transfer of one section
Today there is a wide range of radiators. While most are similar in appearance, thermal performance may differ significantly. They depend on the material from which they are made, on the dimensions, wall thickness, internal cross-section and on how well the design is thought out.
Therefore, it is possible to say exactly how many kW in 1 section of an aluminum (cast-iron bimetallic) radiator only in relation to each model. This data is provided by the manufacturer. After all, there is a significant difference in size: some of them are tall and narrow, others are low and deep. The power of a section of the same height from the same manufacturer, but of different models, may differ by 15-25 W (see the table below STYLE 500 and STYLE PLUS 500). There may be even more noticeable differences between different manufacturers.
Technical characteristics of some bimetallic radiators
Please note that the thermal power of sections of the same height may have a noticeable difference. However, for a preliminary assessment of how many battery sections are needed for space heating, we calculated the average thermal power values for each type of radiator
They can be used for approximate calculations (data are given for batteries with an interaxial distance of 50 cm):
However, for a preliminary assessment of how many battery sections are needed for space heating, average thermal power values were calculated for each type of radiator. They can be used for approximate calculations (data are given for batteries with an interaxial distance of 50 cm):
- Bimetallic - one section produces 185 W (0.185 kW).
- Aluminum - 190 W (0.19 kW).
- Cast iron - 120 W (0.120 kW).
More precisely, how many kW can you have in one section of a bimetallic, aluminum or cast iron radiator when you choose a model and decide on the dimensions. The difference in cast iron batteries can be very big. They are available with thin or thick walls, which causes their thermal output to change significantly. Above are the average values for batteries of the usual shape (accordion) and those close to it. Retro-style radiators have significantly lower thermal output.
These are the technical characteristics of cast iron radiators from the Turkish company Demir Dokum. The difference is more than significant. She could be even bigger
Based on these values and average standards in SNiP, the average number of radiator sections per 1 m2 was calculated:
- the bimetallic section will heat 1.8 m2;
- aluminum - 1.9-2.0 m2;
- cast iron - 1.4-1.5 m2;
How to calculate the number of radiator sections using this data? It's still simpler. If you know the area of the room, divide it by the coefficient. For example, a room of 16 m2, to heat it you will need approximately:
- bimetallic 16 m2 / 1.8 m2 = 8.88 pcs, rounded - 9 pcs.
- aluminum 16 m2 / 2 m2 = 8 pcs.
- cast iron 16 m2 / 1.4 m2 = 11.4 pcs, rounded up - 12 pcs.
These calculations are only approximate. Using them, you can roughly estimate the costs of purchasing heating appliances. You can accurately calculate the number of radiators per room by choosing a model, and then recalculating the number depending on the temperature of the coolant in your system.
Installing a heating radiator
Before starting work, consider some nuances:
Before replacing the battery, the water should be turned off only in the customer’s apartment, and not in the entire house.
Only housing office employees who have the appropriate qualifications for this should shut off the water. Even if you replace the battery yourself, entrust this task to specialists. Otherwise, you risk leaving all residents whose apartments are located along the riser without water supply.
Battery replacement, ideally, should also be carried out by housing office employees or workers specially hired for this. If the customer carried out the removal and installation independently, then all responsibility for the serviceability of the system falls on him.
Installation and replacement of the battery when using the pipe bending method and gas welding, instead of the usual installation system, must also be carried out by workers who have certain qualifications to carry out work at an increased level of safety.
Proper installation of heating radiators, expert recommendations
Rules for successful installation of batteries in the house. Having correctly selected the power of heating radiators, we often do not obtain the desired heat in the house. What determines their productivity?
In order for the heating system to work correctly and effectively, it is necessary to correctly install and assemble the heating devices
It doesn’t matter what heating system you use (independent or centralized), the rules for installing heating devices remain the same
Location of heating radiators
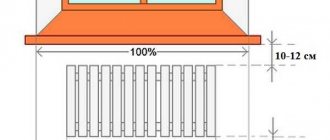
The heating device must be installed in such a way that it operates at 100% efficiency. The ideal installation option is under the window. The greatest heat loss in a home occurs through windows. The placement of heating radiators under the window prevents heat loss and condensation on the glass. For large windows, heaters with a height of 30 cm are used, or they are installed directly next to the window.
The suggested distance from the floor to the heating device is 5-10 cm, from the heating device to the window sill - 3-5 cm. From the wall surface to the back surface of the radiator is 3-5 cm. If you plan to glue some heat-reflecting material behind the heating device, then you can reduce the distance between the wall surface and the battery to very small (3 cm).
The heating device must be placed strictly at right angles, both in a horizontal position and in a vertical position - any deviation leads to the accumulation of air, which leads to corrosion of the heating device.
Pipes in the heating system
Advice for those who have central heating in their home. Naturally, metal pipes are used for heating systems in high-rise buildings.
If the apartment has an iron riser pipe, you cannot switch to polypropylene heating pipes!
In main heating systems, temperature changes in the coolant and its pressure often occur - apartment wiring and heating devices will break down throughout the year.
Also, just do not use unreinforced polypropylene pipes - they are designed for use for water supply and become unusable at a coolant temperature of +90°C.
Fittings for heating radiators
In order for you to be comfortable during the heating season, you should install external water thermostats on each heating device. This way you can save money by shutting off radiators in unused rooms and control the temperature in the house. You can choose programmable external water thermostats - they will turn the heating device off/on, maintaining the desired temperature.
Installation of thermostats on each heating device is possible in a heating system with two pipes. In a single-pipe system (in apartment buildings and high-rise buildings) for thermoregulation, a jumper is installed in front of the battery - a circular pump. A circular pump is a pipe placed perpendicularly between the supply and return. The pipe for the circular pump must be of a smaller diameter than the pipes used in the wiring of the heating system.
A Mayevsky valve is also installed on the battery - a valve for removing air from the system. Such elements make it easier to control the heating device and simplify their repair.
Obstacles to room heating
The effective transfer of heat is also affected by the barriers that we ourselves create. This includes long curtains (70% of heat loss), protruding window sills (10%) and decorative grilles. Thick floor-length curtains interfere with air circulation in the room - you simply heat the window and the flowers on the windowsill. The same effect, but with less results, is achieved by a window sill that completely covers the top of the battery. A dense decorative screen (especially with a top panel) and the location of the battery in a niche reduce the efficiency of the heating device by 20%.
Proper installation of heating radiators is one of the main components of the good functioning of the heating system in general. You should not be led by savings at the expense of comfortable heat supply.
Carrying out installation work
Before carrying out installation work, and when choosing at what distance from the floor and wall the heater will be installed, it is necessary to stick aluminum foil on the wall in the approximate location of the device to increase heat transfer and efficiency (efficiency factor). After which you can mark the fasteners.
You should know that there are several options for connecting radiators to the heating system, some of which you can see from the table diagram.
A medium-sized radiator is hung on 2 brackets
When hanging the radiator, you should check all planes, since the heat transfer of the device depends on maintaining the vertical and horizontal position of the heater.
For medium-sized heaters, install 2 brackets so that they fit between the outer sections; if the radiator is large, then install an additional hook strictly in the middle opening of the radiator. To learn how to hang a radiator, watch this video:
Bypass will allow you to regulate heat
When connecting radiators, there are also a number of features and requirements that must be observed. One of these requirements includes the rule of installing a jumper (bypass) between pipes in a single-pipe distribution system, which will make it possible to independently regulate the required amount of heat in the room. The main advantage of the bypass is that the base for its installation does not need to be legalized, and the installation process can be done independently.
It should be remembered that all the rules for installing radiator systems are the same for both individual heating and central heating. If you are going to install new heating elements, you should obtain permission for this action from the management company or the housing office.
To summarize the article, it should be said that choosing and installing a heating radiator is not an easy task.
All measures, requirements and recommendations for the installation of heating elements of a heating system specified in the article can serve every owner who is planning to install radiators on their own and organize a heating system in their house or apartment.
What to do first: floor or walls
How to remove polyurethane foam from linoleum
How to remove paint from linoleum
Rules for installing aluminum radiators
- Correctly assemble the radiator by screwing in the radiator plugs, plugs and gaskets, install thermostatic valves, shut-off valves, and Mayevsky valve.
- Following the general rules for positioning the radiator relative to the window, mark the mounting locations.
- If necessary, cover the wall surface with heat-reflecting material and attach the brackets to the wall.
- Secure the radiator to the brackets, placing hooks between the sections, and connect to the centralized or room.
Aluminum radiators can be installed in both single-pipe and two-pipe heating systems with vertical and horizontal piping. Today's market can offer two types of aluminum radiators: reinforced radiators with a pressure of up to 16 atm, which are used for heating high-rise buildings, and European aluminum radiators of no more than 6 atm, used for heating in autonomous heating systems.
Necessary theory
There are two types of heating systems that are most widely used these days:
- single-pipe;
- two-pipe.
A special feature of single-pipe systems is the supply of coolant to the house from top to bottom. This scheme is used in most standard apartment buildings. The disadvantage of the system is the inability to control the temperature regime in the home without installing additional equipment. With this heating method, the water in the radiators on the upper floors will be significantly warmer than on those located below.
Heating system installation
With two-pipe heating, the heated coolant is supplied through one pipe, and the water that has given up its heat circulates through the second (return) pipe. This heating system is used in cottages and private houses. The advantage of two-pipe systems is the relative constancy of the temperature of the batteries and the ability to regulate the heating mode.
Radiator installation diagrams
The differences in installation schemes lie in the way they are connected to a private or centralized network.
The most common schemes are the following:
- Lateral connection. Allows you to achieve the greatest heat transfer. The supply pipe is connected to the pipe located at the top, and the return pipe is connected to the bottom. When connected in reverse (water supply from below), the power of the system is reduced.
- The connection is diagonal. Optimal for batteries of considerable length, characterized by minimal heat loss. At the same time, the radiators are evenly heated. The inlet pipe is connected to one side of the upper pipe, and the outlet pipe is connected to the reverse side of the bottom pipe.
- The lower connection (“Leningradka”) is used for hidden pipe laying.
Connection diagram options
Installation of heating devices according to this scheme, characterized by significant heat loss, is used when laying heating pipes in the area of the lower ceiling.
How to determine the required distance
Many construction works carried out inside residential premises are regulated by building codes and regulations (SNiPs). There is also a SNiP for the installation of heating batteries.
From it you can not only find out what distance between the wall and the radiator must be maintained, but also other parameters for its installation:
- the device should be placed directly under the windows so that the centers of the opening and the battery coincide;
- the width of the heating device should not exceed 70% of the width of the window sill niche, if any;
- the distance to the floor should not exceed 12 cm, to the window sill - 5 cm;
- the distance to the wall is within 2-5 cm.
There are several parameters that influence the selection of the optimal gap. Most often it is influenced by the material of the walls of the house and the size of the window sills. In some rooms you can observe an unsightly picture when the batteries protrude significantly beyond its limits.
Connection diagrams
There are several radiator connection diagrams that comply with the requirements and standards of GOST and SNiP. They are represented by the following varieties:
- Lateral connection. Characterized by maximum heat transfer. With this connection, the input is made from the top of the battery, and the output is from the bottom on the same side. This is the most popular connection diagram.
- Diagonal connection. Produced with significant system dimensions. Water enters the radiator through the top and is discharged from the bottom on the opposite side.
- Lower connection or “Leningradka”. It is produced in small one- and two-story houses, as well as when installing pipes hidden under the floor. The efficiency of such a system is 5-15% lower than with a lateral connection.
Diagonal
Lower
Lateral
When pipes are in a rough screed, heat loss increases due to contact with concrete and the ceiling covering of the lower floor.
Heating radiator installation
The main way to adjust the required distance to the walls is high-quality and competent installation of heating devices with your own hands or with the help of specialists. Let's look at this aspect in more detail.
Installation of floor views
This fastening option is optimal for products that have a high mass and are most often made of cast iron. Such batteries are equipped with removable or stationary legs, which are fixed to the floor. Depending on the base material, fastening can be done with wood screws, self-tapping screws and plastic dowels, dowel-nails.
A necessary element for installing a floor heating device is a wall bracket. It is installed at the required height, which is defined as the desired distance from the floor to the upper longitudinal pipe of the radiator, taking into account the gap. Using fasteners and marking their installation locations, the optimal distance to the floor, wall and window sill is achieved.
Hanging a wall radiator
Each heating device is equipped with one or another type of hangers used for installation on walls. The material and strength characteristics of the brackets must correspond to the mass of the heating system, taking into account its filling with coolant. Otherwise, the system may leak.
Before direct installation, it is necessary to determine the installation location and the required distances to the main surfaces.
To do this, follow these steps:
- Let's determine the center of the window and apply markings on the wall to align it with the center of the radiator.
- Let's measure the distance from the bottom edge of the batteries to the top pipe and add 12 cm. Set this measurement aside from the floor where the brackets are installed, checking that the mounting points are horizontal and level.
- In the places where the hangers are installed, we drill holes with a Pobedit drill, install dowels in them and fix the brackets with self-tapping screws.
Design, technical characteristics and features
Structurally, these heating devices are sectioned batteries consisting of two different metals: steel and aluminum.
The steel part of the radiator has direct contact with water or other coolant, and heat transfer is carried out by aluminum plates with excellent heat conductivity.
Due to the successful combination of the properties of these metals, bimetallic radiators have the following advantages:
- High heat transfer coefficient;
- Pressure up to 4 MPa;
- Corrosion resistance;
- Silence;
- Can work in networks with any pipes;
- Thanks to the sectional design, you can dial any estimated number of sections.
The height of radiators is usually 26, 42 or 58 cm. The standard center-to-center distance is 200-800 mm. The width of one section is usually 80 mm.
This choice of geometric dimensions allows you to install bimetallic radiators in any niches, under regular and panoramic windows.
Bimetallic radiators are coated with durable polymer paint, which reliably protects them from external influences and corrosion, in addition, they have a very attractive appearance.
In closed heating systems with a pH of 7 to 9, where the dissolved oxygen content is extremely low, the steel of the internal structures is almost not subject to corrosion, and rusting occurs only when the system is aired.
After some time, a dark, insoluble sediment forms on the inner surface of new radiators, preventing their destruction.
Thermal power (heat transfer) is the main technical characteristic of heating devices that determines their efficiency. For bimetallic radiators, this figure ranges from 100 to 200 W, depending on the height of the area of the aluminum plates.
This property is due to the excellent heat transfer of aluminum.
Aluminum radiators, which have similar heat transfer, but a lower price, resist corrosion much worse, and when the coolant reacts alkaline, they also emit hydrogen, as evidenced by noise and bubbling in the pipes.
They are distinguished from cast iron or steel sectional batteries by their compact size, light weight and attractive design, while the thermal power of bimetal radiators is higher. Their resistance to internal corrosion differs slightly.
In terms of resistance to increased pressure and water hammer, bimetallic radiators have no worthy rival: they can easily withstand pressure of 3-4 MPa. This indicator for cast iron and steel radiators does not exceed 2 MPa, for aluminum radiators – 1.6 MPa.
This feature is especially important for residents of high-rise buildings, where there is significant pressure in the heating system.
The only drawback is their price - it is higher than other heating devices. However, high reliability and efficiency completely compensate for this drawback.
Cost of installing heating radiators
The cost of installing a radiator will directly depend on the material of the product, the number of sections installed for one heating point, as well as the total number of heating points installed in the apartment. The total amount of installation costs will be influenced by both the connection diagram and the cost of components necessary for the work. Of course, you can do such work yourself. However, this will place full responsibility on you for the performance of the system, as well as for all possible negative consequences associated with its failure. So, how much does it cost to install a radiator? On average, all work on arranging one heating point in an apartment can cost $40-50.
Radiator installation:
- Kyiv − 250-350 UAH. per point;
- Moscow − 2,650-3,000 rubles. per point.
- The cost of work on supplying or replacing heating pipes is calculated separately.
How to install heating batteries correctly according to norms and regulations (SNiP)
When installing or reconstructing a heating system, replacement or installation of batteries is often required. Installation of heating radiators can be done on your own, without resorting to the help of specialists, but only by strictly observing the requirements of SNiP. When performing work, both theoretical knowledge and practical experience will be required, because even the slightest mistake can lead to problems during operation of the heating system.
Radiator battery installation
Height calculation
The distance between the radiator and the window sill must be at least 10 cm, regardless of what type of heating device is used. You also need to take into account the height of the battery itself. It is necessary to retreat 8 cm from the rear. The battery itself should rise above the floor by 10 cm, that is, when installing a window sill from the floor according to SNIP, you will need to retreat 70-80 cm.
The projection of the window sill also plays an important role.
: It may extend significantly from the wall or be invisible. If there is no radiator under the window, it is not necessary to meet any requirements, but if heating is present, the projection must be strictly regulated. The task of the window sill is to redirect heat flows. Without it, they will rise upward, and proper heating of the room will not occur, since some of the heat will evaporate and be distributed on the ceiling.
Poor convection can also be caused by a window sill that is too wide. It will not allow warm air to escape, as a result, condensation will begin to accumulate on the window, since the main air flows will go up, and some of them will get stuck under the window, heating the atmosphere
In this case, it is very important to calculate the distance from the window sill to the heating radiator, both in height and how much of a protrusion can be made. You can avoid the problem described above by using a slab that does not extend beyond the wall by more than 8 cm
Tip: when calculating the dimensions, you need to take into account the level of the wall with decoration.
The best option is a solution in which no more than 10% of warm air will be retained in the window niche. To do this, the window sill should not protrude more than 6 cm beyond the radiator, but it should not be shorter than the heating device. If the design solution of the room requires the installation of non-standard wide structures, it is necessary to provide ventilation holes in them. Their size must be sufficient for proper air circulation.
Is clearance necessary?
Some window owners believe that the window sill extends deep under the window frame, but this is not the case. The distance between the window and the window sill is approximately 10 mm. Otherwise, the structure may become deformed. The fact is that under the influence of warm air, the material from which the slab is made expands. The gap is left so that the structure can take the desired shape without being damaged. Visually, this technique is invisible.
How to position the curtain?
The distance of the window sill curtain also plays a role. In order for the curtains to move without clinging, without leaving marks on them, and for warm air to circulate freely, the distance must be at least 5 cm.
Conclusion: it is not always possible to apply the standard distance from the floor, radiator, curtains to the window sill, but you can find a way out by observing certain requirements.
Video: Installation of heating radiators (batteries)
Primary requirements
The distance from the floor to the window sill may vary depending on the type of window. However, GOST provides for the permissible coefficient at which heat is best retained in the room, and the figure is 0.55 W/°C×m². This means that in order to achieve the desired effect, you need to use a plate that will have low thermal conductivity.
The distance of the radiator to the window sill plays an important role: in this case, there is SNiP, the main provisions of which require:
- The window sill should have a slight slope into the room - at least 1˚.
- There must be thermal insulation between the wall and the structure.
- During installation, the height from the floor is taken into account. All window sills must be at the same level.
- The length of the window sill should not be more than 3 meters.
- The length is set relative to the window opening, with a difference of 4 mm.
- The distance required to retreat from the battery to the windowsill should not be less than 8 cm.
- It is recommended to saw off excess parts at room temperature.
Radiator selection
There is a wide range of radiators on the market today, designed for different buyers. The principle “the more expensive the better” does not always work here. You need to make your choice based on the following reasons:
- place of residence;
- heating system wiring;
- on how the heating radiators will need to be installed;
- temperature conditions in the heating system;
- accounting for what material was used in the production of pipes;
- the need for control elements and fittings;
- location of the premises in the building.
Having completed this analysis, you can proceed to choosing a battery.
Today, cast iron radiators can look quite presentable; they can be decorated. Thus, they can easily fit into the overall design of the room.
Cast iron radiators of the modern type are no longer the huge accordions that were in the Soviet apartment, but flat panels with smoothed corners and a presentable appearance. Having good physical heating properties, cast iron retains heat for a long time and gradually releases it into the room. Such radiators have a long service life, 20-50 years. The main disadvantage is their large weight (one section weighs about 8 kg), so it is impossible to install them correctly in rooms where the walls are made of wood or plasterboard. Having a rough surface, they are not very easy to clean.
Aluminum radiators differ little in design from cast iron ones; the only difference is the weight of the sections (1 kg). Also, such devices have good heat transfer properties, a smooth surface, ventilation windows evenly distribute air in the room, and they can be attached to any surface. The main disadvantage is the easy perception of the chemical composition of water and pressure surges in the pipeline.
Bimetallic radiators are a compromise solution between cast iron and aluminum. Externally they are almost no different from aluminum ones, but are not sensitive to the composition of water and pressure surges. They have good heat transfer performance, are easy to install and are inexpensive.
Steel radiators have a panel appearance and a relief surface. They have various connection options and good thermal properties. No major deficiencies were identified.
What sizes are there?
Radiators are available in the following sizes.
Cast iron
According to the specification, standard dimensions:
- Width - 93 or 108 mm.
- Depth from 85 to 140 in increments of 5.
- Height - 588.
Sections made to order can have almost any size.
Knowing the length, the dimensions of the assembled device are determined, since a paronite gasket 1 cm thick is placed between the parts.
If installation is carried out at a point with insufficient space, add the size of the flushing tap.
Important! The distance between the axles is usually 500 mm. Small batteries with a value of 350 are rare
Each section is capable of delivering from 160 W if the average daily air and coolant temperatures differ by 70 degrees. Cast iron can withstand operating pressure up to 9 atm.
Aluminum
Different models have similar internal dimensions. The width is 80 or 88 mm. Depth varies in the range of 10-90 mm. The height is 50 or 35 cm. Models for the bathroom reach three meters in length.
Photo 1. Aluminum radiator model Indigo 500/100 with side connections, section power 196 W, , Russia.
The power of the sections depends not only on the dimensions, but also on the fins of the structure. Low ones develop 150-170 watts, and 500 mm - 185-220. Aluminum can withstand almost twice the pressure than cast iron.
Bimetallic
Standard values are in the ranges:
- Width 80-82 mm.
- Depth 75-100.
- Height 400-420, 550-580.
Power depends on the size, but rarely exceeds 200 watts. This type of section is known for its ability to withstand high pressure, which is due to the steel core. The operating value reaches up to 30 atm, and the test value is 50.