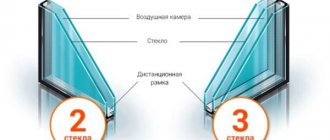
The main component of any modern (wooden, plastic, aluminum) window is undoubtedly a double-glazed window. In terms of area, a double-glazed window occupies from 70% to 90% of the window area; accordingly, the properties of the double-glazed window will be fundamental in the overall properties of the window. Whether a window is warm, energy-saving, or noise-proof directly depends on the double-glazed window.
A window made even from super warm window profiles will not be warm if the selected double-glazed window has low thermal insulation.
A double-glazed window is a structure consisting of two or several glasses, separated along the perimeter by a spacer frame, hermetically sealed with sealant, forming hermetic chambers that are filled with dried air or inert gas.
Symbol of a double-glazed window. Glass unit formula.
The symbol of a double-glazed window includes a strictly defined number of parameters:
- type of double-glazed window (SPO - single-chamber double-glazed window, SPD - double-chamber);
- thickness and type of the first glass (4M1 - sheet glass 4 mm thick, 6C - solar control glass 6 mm thick);
- chamber thickness, type of gas filler . When filling with an air mixture, there is no gas filler code (16 - chamber thickness 16 mm. gas filler is air, 12Ar - chamber thickness 12 mm. type of gas filler - Argon, 16Kr - chamber thickness 16 mm. type of gas filler - Krypton);
- thickness and type of second glass;
- in the case of a two-chamber double-glazed window, steps 3 and 4 are repeated;
- height, width, thickness of the glass unit (1200x900x36 - height 1200 mm, width 900 mm, thickness 36 mm);
- type of double-glazed window (Ud - impact-resistant, E - energy-saving, S - sun-protective, M - frost-resistant, Sh - noise-proof. General building double-glazed window - no parameter);
- designation of the standard (GOST 24866-99 Double-glazed windows for construction purposes).
List of controlled parameters
length (height), width, deviations in length (height), width
Maximum deviations in height (length) and width of double-glazed windows (in millimeters)
| Nominal size in height (length) or width | Single-chamber double-glazed window | Double-glazed window |
| Up to 2000 inclusive | ±2,0 | ±3,0 |
| Over 2000 to 3000 | ±3,0 | ±4,0 |
| Over 3000 | ±4,0 | ±5,0 |
thickness, thickness deviations;
Maximum deviation of the nominal thickness of double-glazed windows: single-chamber - ±1.0 mm, double-chamber - ±1.5 mm.
deviation from flatness
Monitoring deviation from flatness (total deviation from flatness)
For control, use a ruler or building level with a length of at least:
- 1000 mm - if the size of the product (length, width, diagonal) in the direction of which the control is carried out is 1000 mm or more;
- the size of the product (length, width, diagonal) in the direction of which the control is carried out - if this size is less than 1000 mm.
When testing, the middle of the ruler (construction level) must coincide with the center of the controlled surface.
Control is carried out at the following positions of the ruler (building level):
- vertical and horizontal - for all products;
- along each diagonal - additionally for tempered and heat-strengthened glasses and products made from them.
The deviation from the flatness of sheets of glass in a double-glazed window should not exceed 0.001 of the length of the side of the double-glazed window, parallel to which the measurement is made, when using sheet glass in accordance with GOST 111. When using other types of glass, the deviation from flatness should not exceed the values established in regulatory documents for these types of glass ( in the absence of requirements for this indicator in regulatory documents, the value of deviations from flatness can be taken as 0.001 of the length of the side of the glass unit parallel to which the measurement is made).
total depth of the sealing layers of the glass unit
The depth of the internal (primary) sealing layer (F Figure 2) in straight sections must be at least 4 mm. The depth of the outer sealing layer (Figure 1) at the end of the glass unit must be at least 3 mm, the total depth of the sealing layers (D Figure 2) must be at least 9 mm. The thickness of the primary sealing layer is established in the technological documentation depending on the type of sealant used. The sealing layers of the glass unit are shown in Figure 2.
The depth of the outer sealing layer when using silicone sealants should not be less than 6 mm.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
Figure 1 — Sealing layers of double-glazed windows
D is the total depth of the sealing layers; F is the depth of the internal (primary) sealing layer; G—depth of the secondary sealing layer; E is the depth of the outer sealing layer; H - thickness of the primary sealing layer
displacement of spacer frames in double-glazed windows;
In double-glazed windows, the protrusion of the primary (non-hardening) sealant (butyl) into the glass unit chamber is allowed to protrude no more than 2 mm.
In double-glazed windows, the distance frames may be offset relative to each other. In this case, the tolerance is established in the supply contract and should not be more than 3 mm for rectangular double-glazed windows and no more than 5 mm for non-rectangular double-glazed windows.
vices
According to the standards for limiting appearance defects, each glass in a double-glazed unit must meet the requirements specified in the regulatory documents for the types of glass used.
https://docs.cntd.ru/document/1200107378#7D20K3
When using glass with a soft coating (not resistant to external influences), the edge along the entire perimeter of the glass must be cleared of the coating to the depth of the sealing layer, but not less than 9 mm. If the edge around the perimeter of the glass, cleared of coating, is not covered by frames, then the appearance is agreed upon between the manufacturer and the consumer using samples.
It is allowed to have a visible transparent or golden stripe along the spacer frame with a width of no more than 2 mm, unless otherwise specified in the contract for the production of double-glazed windows.
It is allowed to have traces from the wheel for removing the coating in the form of stripes in the sealing area of the glass unit.
It is allowed not to remove the coating along the edge of the glass if this is specified by the manufacturer of the coated glass.
marking
Labeling of double-glazed windows is carried out in accordance with the requirements of GOST 32530.
If laminated, tempered or heat-strengthened glass is used in a double-glazed unit, the markings on the glass unit must be located so that the markings of laminated, tempered or heat-strengthened glass are visible.
The labeling may include additional information upon agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer.
type and quality of edge processing
Double-glazed windows must have smooth edges and intact corners. Chipping of the edge of the glass in a double-glazed unit, unpolished chips, protrusions of the edge of the glass, damage to the corners of the glass are not allowed. By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, the type of edge (unprocessed or processed) is established in the contract. It is recommended to use glass with a treated edge. When using tempered or heat-strengthened glass, the edge is processed until it is strengthened.
continuity of the sealing layers of the glass unit
Each sealing layer (primary and/or secondary) in double-glazed windows (including in places of corner joints) must be continuous, without breaks or violations of integrity. The spacer frame should not be visible at the boundary of the first and second sealing layers. Leaks of sealant in the outer sealing layer (exceeding the tolerance for the glass unit size) are not allowed.
Peeling of the sealing layers from the glass and spacer frame along the entire perimeter of the glass unit is not allowed.
It is allowed to have visible metal (shiny) sections of the spacer frame (between the primary sealing layer and the spacer frame) with a width of no more than 1 mm around the perimeter of the glass unit, provided that the requirements of 4.12 and 5.1.4.1 of this standard are met.
In double-glazed windows, the protrusion of the primary (non-hardening) sealant (butyl) into the glass unit chamber is allowed to protrude no more than 2 mm.
cleanliness of glass in double glazed windows
The internal surfaces of glass in double-glazed windows must be clean; contamination (fingerprints, sealant, inscriptions, dust, lint, oil stains, etc.) is not allowed. Point contamination is allowed, the size of which does not exceed the permissible defects in appearance for the original glass, while the total number of glass defects and contamination must comply with the requirements of regulatory documents for the original glass.
Distance frames in double-glazed windows must be clean. On the lower spacer frame, after installing a double-glazed window into building structures, a small amount of dust particles is allowed that does not cover the spacer frame with a continuous layer.
An example of a symbol for a double-glazed window:
SPO 3M1 – 16Ar – 3M1 1600x850x24 GOST 24866-99
Single-chamber double-glazed window, first glass 3 mm thick. sheet, chamber thickness 16 mm. the chamber is filled with Argon, the second glass is 3 mm thick. sheet, height 1600 mm. width 850 mm. thickness 24 mm. general construction purposes.
SPD 4M1 – 18 – 4M1 – 18Ar – 5I 1350x900x49 ME GOST 24866-99
Double-glazed window, first and second glass 4 mm thick. sheet, the first chamber is filled with an air mixture, chamber thickness 18 mm. the second chamber is filled with Argon; the thickness of the chamber is 18 mm. the third glass is 5 mm thick. energy-saving with soft coating, height 1350 mm. width 900 mm. thickness 49 mm. frost-resistant, energy-saving.
Thermal insulation characteristics of double-glazed windows GOST-24866-99.
The thermal insulation properties of double-glazed windows are characterized by the reduced heat transfer resistance Ropre.
The higher it is, the warmer the double-glazed window.
The table shows the value of the reduced heat transfer resistance Ropr for the most common double-glazed window designs.
| No. | Number of cameras | Glazing options | Given resistance heat transfer Rdef. |
| 1 | 1 | 0,28 | |
| 2 | 1 | 0,29 | |
| 3 | 1 | 0,30 | |
| 4 | 1 | 0,32 | |
| 5 | 1 | 0,30 | |
| 6 | 1 | 0,31 | |
| 7 | 1 | 0,32 | |
| 8 | 1 | 0,34 | |
| 9 | 1 | 0,47 | |
| 10 | 1 | 0,49 | |
| 11 | 1 | 0,51 | |
| 12 | 1 | 0,53 | |
| 13 | 1 | 0,53 | |
| 14 | 1 | 0,55 | |
| 15 | 1 | 0,57 | |
| 16 | 1 | 0,59 | |
| 17 | 1 | 0,51 | |
| 18 | 1 | 0,53 | |
| 19 | 1 | 0,56 | |
| 20 | 1 | 0,59 | |
| 21 | 1 | 0,57 | |
| 22 | 1 | 0,6 | |
| 23 | 1 | 0,63 | |
| 24 | 1 | 0,66 | |
| 25 | 2 | 0,42 | |
| 26 | 2 | 0,45 | |
| 27 | 2 | 0,47 | |
| 28 | 2 | 0,49 | |
| 29 | 2 | 0,52 | |
| 30 | 2 | 0,44 | |
| 31 | 2 | 0,47 | |
| 32 | 2 | 0,49 | |
| 33 | 2 | 0,52 | |
| 34 | 2 | 0,55 | |
| 35 | 2 | 0,53 | |
| 36 | 2 | 0,55 | |
| 37 | 2 | 0,58 | |
| 38 | 2 | 0,61 | |
| 39 | 2 | 0,65 | |
| 40 | 2 | 0,60 | |
| 41 | 2 | 0,62 | |
| 42 | 2 | 0,65 | |
| 43 | 2 | 0,68 | |
| 44 | 2 | 0,72 | |
| 45 | 2 | 0,59 | |
| 46 | 2 | 0,61 | |
| 47 | 2 | 0,64 | |
| 48 | 2 | 0,68 | |
| 49 | 2 | 0,72 | |
| 50 | 2 | 0,64 | |
| 51 | 2 | 0,67 | |
| 52 | 2 | 0,71 | |
| 53 | 2 | 0,75 | |
| 54 | 2 | 0,80 |
GOST 24866-2014. Interstate standard. Double-glazed windows are glued. Specifications
5.1. Characteristics
5.1.1. According to the standards for limiting appearance defects, each glass in a double-glazed unit must meet the requirements specified in the regulatory documents for the types of glass used.
5.1.2. Double-glazed windows must have smooth edges and intact corners. Chipping of the edge of the glass in a double-glazed unit, unpolished chips, protrusions of the edge of the glass, damage to the corners of the glass are not allowed.
By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, the type of edge (unprocessed or processed) is established in the contract. It is recommended to use glass with a treated edge. When using tempered or heat-strengthened glass, the edge is processed until it is strengthened.
5.1.3. The internal surfaces of glass in double-glazed windows must be clean; contamination (fingerprints, sealant, inscriptions, dust, lint, oil stains, etc.) is not allowed. Point contamination is allowed, the size of which does not exceed the permissible defects in appearance for the original glass, while the total number of glass defects and contamination must comply with the requirements of regulatory documents for the original glass.
5.1.4. Requirements for sealing double-glazed windows
5.1.4.1. Each sealing layer (primary and/or secondary) in double-glazed windows (including in places of corner joints) must be continuous, without breaks or violations of integrity. The spacer frame should not be visible at the boundary of the first and second sealing layers. Leaks of sealant in the outer sealing layer (exceeding the tolerance for the glass unit size) are not allowed.
5.1.4.2. In double-glazed windows, the protrusion of the primary (non-hardening) sealant (butyl) into the glass unit chamber is allowed to protrude no more than 2 mm.
5.1.4.3. In double-glazed windows, the distance frames may be offset relative to each other. In this case, the tolerance is established in the supply contract and should not be more than 3 mm for rectangular double-glazed windows and no more than 5 mm for non-rectangular double-glazed windows.
5.1.5. Double-glazed windows must be sealed.
5.1.6. Optical distortion
5.1.6.1. Optical distortions of double-glazed windows (except for double-glazed windows made using patterned, reinforced or curved glass, glass with a light transmittance of less than 30%) in transmitted light when viewing the “brick wall” screen at an angle less than or equal to 30° are not allowed.
It is allowed, by agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, to establish requirements for optical distortion of double-glazed windows (except for double-glazed windows made using patterned, reinforced or curved glass) in reflected light.
5.1.6.2. On double-glazed windows, rainbow stripes (interference phenomenon) are allowed, visible at an angle of less than 60° to the plane of the double-glazed window.
5.1.7. The dew point of double-glazed windows should not be higher than minus 45 °C. For frost-resistant double-glazed windows, the dew point should not exceed minus 55 °C.
5.1.8. Double-glazed windows must be durable (resistant to long-term cyclic climatic influences). The durability of double-glazed windows must be at least 20 conventional years of operation.
5.1.9. The volume of initial filling of a double-glazed window with gas must be at least 90% of the volume of the interglazed space of the double-glazed window.
5.1.10. Requirements for sound insulation of a double-glazed window, taking into account specific operating conditions, are established if there is a consumer requirement.
5.1.11. Requirements for the heat transfer resistance of a double-glazed window, taking into account specific operating conditions, are established if there is a consumer requirement.
5.1.12. Requirements for the optical characteristics of a double-glazed window (directional light transmittance, solar radiation transmittance, etc.), taking into account specific operating conditions, are established if there is a consumer requirement.
5.2. Material requirements
5.2.1. The materials and components used for the manufacture of double-glazed windows must comply with the requirements of this standard and regulatory documents for raw materials and components.
5.2.2. For the manufacture of spacer frames, ready-made profiles from aluminum, stainless steel alloys, fiberglass or metal-plastic profiles are used. It is recommended to make spacer frames using the bending method, assembled on linear connectors (to ensure better sealing of the glass unit), and also to use frames with a thermal break. The number of joints is not regulated.
In the case of manufacturing a spacer frame using the assembly method from straight elements and corners, all joints between frame elements must be carefully filled with non-hardening sealant (butyl).
It is allowed to make spacer frames from other materials, provided that the requirements for double-glazed windows established in this standard are met and the possibility of transporting, storing and operating double-glazed windows with these frames in the conditions and designs provided for by this standard is verified.
In spacer frames that have perforated (dehydration) holes on the side of the interglass space, the size of these holes should be less than the diameter of the desiccant granules.
Tolerances for geometric dimensions and deviations from the shape of spacer frames must ensure that the requirements for the size, shape and tightness of double-glazed windows are met.
Examples of spacer frame designs are shown in Figure 3.
a) Distance frame; made by bending and closed on one connector (or several connectors)
b) Spacer frame made of straight parts; assembled on four connecting corners
Note. Option a) recommended, option b) acceptable.
Figure 3. Examples of spacer frame designs (without sealants)
5.2.3. In the manufacture of double-glazed windows, synthetic granular zeolite without binders (molecular sieve) is used as a desiccant, which is used to fill the cavities of the spacer frames. The size of the desiccant granules must be larger than the dehydration holes in the spacer frame. When filling a glass unit with inert gases, the pore sizes in the desiccant should be less than 0.3 microns.
The effectiveness of the desiccant, determined by the temperature rise method, must be at least 35 °C. In controversial issues, tests are carried out to determine the moisture capacity of the desiccant using methods approved in the prescribed manner.
The procedure for filling the spacer frames with a desiccant and its control is established in the technological documentation, depending on the size of the double-glazed windows and the sealants used. In this case, the filling of the desiccant must be at least 50% of the volume of the spacer frames.
When thermoplastic frames and spacer strips with a desiccant embedded in the mass are used in double-glazed windows, the effectiveness of the desiccant is not controlled.
5.2.4. For the primary sealing layer, polyisobutylene sealants (butyls) are used (except for double-glazed windows for structural glazing). For the secondary sealing layer, polysulfide (thiokol), polyurethane or silicone sealants are used. In double-glazed windows for structural glazing, structural silicone sealants are used as an outer sealing layer, which perform additional load-bearing functions.
The sealants used must comply with the requirements of GOST 32998.4 according to the indicators specified in GOST 32998.6 for each sealing layer, and have adhesive ability to the glass and spacer frame and strength that ensures the required characteristics of double-glazed windows in the operating temperature range. The sealants used must be compatible with each other and with sealants used when installing double-glazed windows in building structures. Mutual penetration of sealants and chemical reactions between them are not allowed.
For the manufacture of double-glazed windows, sealants must be used that meet the hygienic requirements established in sanitary standards and rules approved in the prescribed manner.
5.2.5. For the manufacture of double-glazed windows, glass with a thickness of at least 3 mm is used.
5.2.6. When using glass with a soft coating (not resistant to external influences), the edge along the entire perimeter of the glass must be cleared of the coating by 8 - 10 mm (the width of the sealing layer). If the edge around the perimeter of the glass, cleared of coating, is not covered by frames, then the appearance is agreed upon between the manufacturer and the consumer using samples.
It is allowed not to remove the coating along the edge of the glass if this is specified by the manufacturer of the coated glass.
5.2.7. In cases where unstrengthened glass (including laminated glass) is used in double-glazed windows for external glazing, its solar radiation absorption coefficient should be no more than 50%. It is allowed to use the coefficient of light absorption by glass instead of the absorption coefficient of solar radiation when designing double-glazed windows. For non-strengthened glass (including laminated glass), it should be no more than 25%. If one criterion is met and the other is not, then the solar radiation absorption coefficient is applied.
Glass with a higher light (or solar radiation) absorption rate must be toughened.
5.2.8. The materials used for the manufacture of double-glazed windows must be tested for compatibility and frost resistance during the durability testing of double-glazed windows.
5.3. Labeling, packaging
5.3.1. Labeling of double-glazed windows is carried out in accordance with the requirements of GOST 32530.
If laminated, tempered or heat-strengthened glass is used in a double-glazed unit, the markings on the glass unit must be located so that the markings of laminated, tempered or heat-strengthened glass are visible.
The labeling may include additional information upon agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer.
5.3.2. Marking of transport containers is in accordance with GOST 32530.
5.3.3. Packaging of double-glazed windows is carried out in accordance with the requirements of GOST 32530.
5.3.4. When packing, glass units must be separated by cork or elastic polymer spacers at the corners of the glass unit. The thickness of the gaskets is selected based on the size of the glass unit and possible changes in temperature and ambient air pressure during transportation and storage of the glass units.
5.4. Safety requirements
5.4.1. Safety requirements for the production of double-glazed windows are established in accordance with hygienic requirements, electrical safety rules, fire safety rules in accordance with the technological equipment used and production technology.
5.4.2. Fire safety in the production of double-glazed windows must be ensured by fire prevention systems, fire protection, organizational and technical measures in accordance with GOST 12.1.004. The use of open fire is not allowed in rooms where double-glazed windows are manufactured and stored.
5.4.3. Persons involved in the production of double-glazed windows must be provided with special clothing in accordance with regulatory documents. In the premises where double-glazed windows are produced, there should be water and a first aid kit with medications to provide first aid for cuts and bruises.
5.4.4. All persons employed in the production of double-glazed windows, upon hiring and periodically, must undergo a medical examination, safety instructions and training in accordance with GOST 12.0.004.
5.4.5. During loading and unloading operations, safety rules in accordance with GOST 12.3.009 must be observed. It is prohibited to move glass and double-glazed windows over people.
5.4.6. During the production of double-glazed windows, all operations associated with the possibility of harmful substances entering the human body should be carried out in accordance with the instructions for ensuring work safety, approved in the prescribed manner. At the same time, the requirements of sanitary rules for organizing technological processes and hygienic requirements for production equipment must be observed.
5.5. Environmental requirements
5.5.1. When manufacturing double-glazed windows, compliance with environmental standards and requirements must be ensured.
5.5.2. Double-glazed windows during operation and storage should not have a harmful effect on the human body; safety is confirmed by the hygienic requirements established in sanitary standards and rules approved in the prescribed manner, and on the sealants used.
5.5.3. During the manufacture of double-glazed windows, inorganic dust with a silicon dioxide content of over 70%, MPC, may be released into the air of the working area. h. = 1 mg/m3, hazard class 3.
5.5.4. The maximum permissible concentration for butyl in the air of the working area must comply with the requirements of sanitary standards and rules approved in accordance with the established procedure.
5.5.5. Determination of the content of maximum permissible concentrations of hazardous substances in the air of the working area is carried out according to methods, sanitary standards and rules approved in the prescribed manner.
5.5.6. When disposing of double-glazed windows, they must be disassembled into components. Each type of component product must be disposed of separately.
5.5.7. Disassembly is carried out according to technological documentation, which establishes the requirements for the rules of work, including safety requirements.
5.5.8. Disposal of glass waste that is not subject to industrial processing is carried out at specialized landfills.
5.5.9. Disposal is carried out through specialized enterprises in accordance with the law.
Parameters of gas-filled double-glazed windows.
Results of experimental studies of double-glazed windows
(lab. G.G. Farenyuk, NIISK, Kyiv)
| No. | Number of cameras | Glazing options | Gas composition, % | Heat transfer resistance, R def. m2 K/W | |||
| Air | Krypton | Argon | Xenon | ||||
| 1 | 1 | 100 | 0,32 | ||||
| 2 | 1 | 100 | 0,38 | ||||
| 3 | 1 | 100 | 0,53 | ||||
| 4 | 1 | 100 | 0,67 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 100 | 0,7 | ||||
| 6 | 1 | 100 | 0,59 | ||||
| 7 | 1 | 100 | 0,78 | ||||
| 8 | 1 | 100 | 0,83 | ||||
| 9 | 1 | 75 | 25 | 0,73 | |||
| 10 | 1 | 50 | 50 | 0,7 | |||
| 11 | 1 | 50 | 50 | 0,79 | |||
| 12 | 1 | 25 | 75 | 0,67 | |||
| 13 | 2 | 100 | 0,45 | ||||
| 14 | 2 | 100 | 0,51 | ||||
| 15 | 2 | 100 | 0,47 | ||||
| 16 | 2 | 100 | 0,59 | ||||
| 17 | 2 | 100 | 0,91 | ||||
| 18 | 2 | 100 | 1,16 | ||||
| 19 | 2 | 75 | 25 | 0,88 | |||
| 20 | 2 | 50 | 50 | 0,82 | |||
| 21 | 2 | 50 | 50 | 0,89 | |||
| 22 | 2 | 25 | 75 | 0,81 | |||
| 23 | 2 | 100 | 0,73 | ||||
| 24 | 2 | 100 | 1,48 | ||||
| 25 | 2 | 100 | 1,54 | ||||
| 26 | 2 | 100 | 0,64 | ||||
| 27 | 2 | 100 | 1 | ||||
| 28 | 2 | 100 | 1,34 | ||||
| 29 | 2 | 75 | 25 | 0,94 | |||
| 30 | 2 | 100 | 0,93 | ||||
| 31 | 2 | 50 | 50 | 0,9 | |||
| 32 | 2 | 50 | 50 | 0,92 | |||
| 33 | 2 | 25 | 75 | 0,81 | |||
| 34 | 2 | 100 | 1,58 | ||||
| 35 | 2 | 100 | 1,93 | ||||
| 36 | 2 | 75 | 25 | 1,48 | |||
| 37 | 2 | 50 | 50 | 1,36 | |||
| 38 | 2 | 50 | 50 | 1,48 | |||
| 39 | 2 | 25 | 75 | 1,3 | |||
Example: 4M1-(Kr75/Ar25)16-4I – On the street side, uncoated glass 4 mm thick, a gas layer 16 mm thick, filled with a mixture of 75% krypton and 25% argon, glass with a soft low-emission coating 4 mm thick.